UNIT 6: Environmental Issues - theory
advertisement

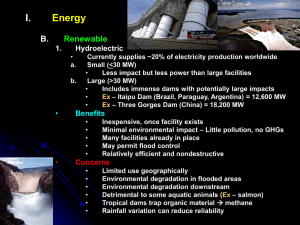
UNIT 6: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES SUBJECT: CONTEMPORARY SCIENCE Group: 1º Bachillerato Teacher: Irene Martínez Clares Academic year: 2011-2012 1 SUBJECT: CONTEMPORARY SCIENCE Name:________________________________________________________Date:______ UNIT 6: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES - THEORY INDEX A) MAIN ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES 1.- Climate Change / Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect 2.- 'Hole' in the Ozone Layer 3.- Acid Rain 4.- Air Pollution 5.- Water Pollution 6.- Introduced Species 7.- Biological Control 8.- Biological Magnification 9.- Soil Salinity 10.- Population Explosion B) ENERGY CRISIS & ENERGY ALTERNATIVES 1.- Non-renewable energy sources 2.- Renewable. energy sources A) MAIN ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES 1.- Climate Change / Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect The earth's atmosphere allows a lot of sunlight to reach the earth's surface, but reflects much of that light back into space. Some gases trap more sunlight, so that less light reflects back into space. These gases are called Greenhouse Gases, because the effect is like being in a plant glasshouse, or in a car with the windows wound up. The result is a gradual increase in earth's temperature or Global Warming. The major greenhouse gases are water, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and chlorofluorocarbons (CFC's). The main man-made causes are thought to be carbon dioxide and methane from factory, power station and car emissions, the waste products of respiration, logging, the mining of fossil fuels and the breakdown of plant matter in swamps. The long-term effects may include melting of glaciers and a rise in sea level, and a global change in climate and type of vegetation. Video: GLOBAL WATCH: Global Warming and the Environment | PBS http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3KtKr3gAtGI&feature=player_embedded 2 2.- 'Hole' in the Ozone Layer Ozone is a gas in the earth's upper atmosphere whose chemical formula is O 3. Ozone acts to block out much of the sun's ultraviolet radiation which causes skin cancer and contributes to the fluctuations of global climatic conditions that affect the environment. Above Antarctica is a thinner layer of ozone caused by the destruction of ozone gas by emissions of chlorofluorocarbons and hydrochlorofluorocarbons that are propellants in pressure-pak spray cans and refrigerants in refrigerators and air-conditioning units. In 1987, a treaty called the Montreal Protocol was introduced to reduce usage of ozonedestroying gases. Australia has banned CFC's, but many nations such as China still use them. 3.- Acid Rain When gases such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides react with water in the atmosphere to form sulphuric acid and nitric acid, they form an acidic 'rain' which can destroy vegetation. Some of these gases are from natural sources such as lightning, decomposing plants and volcanoes. However, much of these gases are the result of emissions from cars, power stations, smelters and factories. 4.- Air Pollution Air pollution is the release into the atmosphere of excessive amounts of harmful gases (e.g. methane, carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides) as well as particles (e.g. dust, tyre rubber, lead from car exhausts). To reduce emissions, the Australian government has legislated that all new cars use unleaded petrol and have catalytic converters fitted to the exhausts. 5.- Water Pollution 1. Sewage is all household waste water. Many detergents contain phosphates which act as plant fertilisers. When these phosphates and the sewerage reach rivers, they help water plants to grow in abundance, reducing the dissolved oxygen in the river water. The result is death of aquatic animals due to suffocation by the algal blooms. This harmful effect is called eutrophication. 2. Biodegradable detergents are more environmentally friendly because they are readily broken down to harmless substances by decomposing bacteria. 3. Suspended solids in water such as silt reduce the amount of light that reaches the depths of the water in lakes and rivers. This reduces the ability of aquatic plants to photosynthesise and the result is less plant and animal life. Turbidity is the measure of 'cloudiness' or the depth to which light can reach in water. 6.- Introduced Species They are species of plants or animals that have migrated or been brought to Australia. Many fit into the natural ecosystems and are kept in control by natural predators and parasites. However, some become pests as they are well-adapted to our environment, readily obtain nutrients, and lack natural predators or parasites. Examples include rabbits, foxes, carp, and prickly pear cactus plant. 3 7.- Biological Control It is an environmentally-friendly method to control these pests by the introduction of species-specific, living organisms to control their numbers. Successful examples include the myxoma virus and the calici virus for rabbits, and the cactoblastis moth feeding on the prickly pear. Unsuccessful examples include the introduction of the cane toad to reduce the numbers of natural cane beetles. 8.- Biological Magnification It is the accumulation in body tissues of certain chemicals such as DDT pesticide and mercury. The higher along the food chain, the greater is the accumulation, sometimes to toxic levels, causing birth defects and death. 9.- Soil Salinity Soil Salinity has increased greatly since the widespread logging of trees by farmers. Deep tree roots normally draw water from the underground water table. However, when logging of trees occurs, the water table rises close to the surface bringing with it salt from rocks. This creates soil that is so salty that vegetation cannot grow effectively. The result is loss of vegetation and erosion. 10.- Population Explosion It is the rapid increase in population in developing countries causing famine, and also in developed countries causing more demand for energy and with that, increased pollution and destruction of the environment. Video: 7 Billion, National Geographic Magazine http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sc4HxPxNrZ0&feature=player_embedded 4 B) ENERGY CRISIS & ENERGY ALTERNATIVES With population growth comes increased usage of energy. The energy crisis is the inability of the earth's resources to keep pace with the population's needs. The solution to the energy crisis is twofold - build more power stations to supply more energy, or reduce the usage of energy by building more energy-efficient devices. There are 2 types of energy sources - non-renewable and renewable. 1.- NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES e.g. fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) and nuclear energy (uranium, plutonium) Takes a long time to form (e.g. millions of years) Cannot be reused Advantages Cheap Readily available Efficient Multipurpose (e.g. oil for cars, heating) Disadvantages Polluting or radioactive Running out Fossil fuels began forming millions of years ago. At the time when it is believed that dinosaurs roamed the earth, forests of trees fell into swamps and were covered by silt and mud. They gradually changed into the coal, oil and natural gas that we use today. The advantages of using fossil fuels are that they are readily available at the present time and are cheap. They can also be used for many purposes e.g. coal can be burnt in power stations to make electricity and also in homes for heating. These fossil fuels took millions of years to form, yet humans are using them rapidly in cars, power stations and factories. They will probably run out within the next 100 years. So the disadvantages of fossil fuels are that they will run out and also that they are polluting. Video: 300 Years of FOSSIL FUELS in 300 Seconds http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cJ-J91SwP8w&feature=player_embedded 5 2.- RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES e.g. biomass, solar, wind, wave, tidal, hydroelectric, geothermal Takes a shorter time to form (e.g. decade or two) Can be reused or is very abundant Advantages Won't run out Environmentally friendly Disadvantages Inefficient Geographically selected Biomass is plant matter that is used as an energy source. For example, timber can be burnt for both cooking and heating in many homes around the world. Methane gas that is flammable can be made from rotting vegetation in methane digesters. Also alcohol made from sugar cane can be used as an environmentally-friendly alternative to petrol. Solar Energy can be used in many ways. Buildings can be designed to take advantage of the sun's warmth in the winter so that we don't use electric heaters. Solar hot water heaters can reduce our electricity bills. Photovoltaic or solar cells can generate electricity. Solar energy is particularly useful here in Australia because of our abundance of sunlight. Hydroelectric Power Stations are initially expensive to build but are cheap to run. They can be located in mountainous areas where water is stored in dams and then released to turn turbines that generate electricity. Wind Energy from windmills can be used to generate electricity by turning turbines in the same way as in hydroelectric power stations. These are particularly useful in areas close to the coast where the winds are strong and continuous. Wave and Tidal Power can be used to generate electricity from the rise and fall of the waves and the tides. These forms of power can only be utilised at the moment in places such as Broome where the tide rises and falls through a considerable height very rapidly. Geothermal energy is energy harnessed in areas of the earth that are near volcanoes or hot springs such as in Rotorua in New Zealand. The heat can be used for domestic use. It can also be used to generate electricity by heating steam to turn turbines. The advantages of using renewable energy sources are that they won't run out and they are relatively friendly to the environment. Unfortunately, they are not as efficient in producing electricity as coal-powered power stations. Also another disadvantage of solar, wind, wave, tidal and geothermal energy sources is that they can only be used in certain areas around the world. Video: Sustainability explained through animation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B5NiTN0chj0&feature=player_embedded 6 SUBJECT: CONTEMPORARY SCIENCE UNIT 6: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES – ACTIVITIES INDEX ACTIVITY 1. CLOZE: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES ACTIVITY 2. CLOZE: ENERGY CRISIS AND ENERGY ALTERNATIVES ACTIVITY 3. CANAL DEVELOPMENT DEBATE ACTIVITY 4. DEBATE : ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF ENERGY RESOURCES ACTIVITY 5. QUIZ: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES 7 ACTIVITY 1. CLOZE: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES Name:________________________________________________________Date:______ Topics: 1. Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming 2. „Hole‟ in the Ozone Layer 3. Acid Rain 4. Air Pollution 5. Water Pollution (includes Eutrophication) 6. Introduced Species (includes biological control) 7. Biological Magnification 8. Soil Salinity 9. Population Explosion 10. Energy Crisis and Energy Alternatives Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming – The earth‟s atmosphere allows a lot of sunlight to reach the earth‟s surface, but reflects much of that light back into s____. Some gases trap more sunlight, so that less light r_______ back into space. These gases are called Greenhouse Gases, because the effect is like being in a plant glasshouse, or in a car with the windows wound up. The result is a gradual i_______ in earth‟s temperature or Global Warming. The major greenhouse gases are water, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and chlorofluorocarbons (CFC‟s). Possibly, the main man-made causes are thought to be carbon d______ and methane from factory, power station and car emissions, the w____ products of respiration, logging, the mining of fossil f____ and the breakdown of plant matter in swamps. The long-term effects may include m______ of ice-caps and a rise in sea l____, and a global change in climate and type of vegetation. “Hole” in the Ozone Layer – Ozone is a gas in the earth‟s upper atmosphere whose chemical formula is O3. Ozone acts to block out much of the sun‟s ultraviolet r_________ which causes skin c_____ and contributes to the fluctuations of global climatic conditions that affect the e__________. Above Antarctica is a thinner layer of ozone caused by the destruction of ozone gas by e________ of chlorofluorocarbons and hydrochlorofluorocarbons that are propellents in pressure-pak spray c___ and refrigerants in refrigerators and air-conditioning units. In 1987, a treaty called the Montreal Protocol was introduced to reduce usage of ozone-destroying gases. Australia has b_____ CFC‟s, but many nations such as China still use them. Acid Rain – When gases such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides r____ with water in the atmosphere to form sulphuric acid and nitric a___, they form an acidic „rain‟ which can destroy vegetation. Some of these gases are from natural sources such as lightning, decomposing plants and volcanoes. However, much of these gases are the result of emissions from cars, power stations, smelters and f________. Air Pollution – Air pollution is the release into the atmosphere of excessive amounts of harmful g____ (e.g. methane, carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides) as well as particles (e.g. dust, tyre rubber, lead from car exhausts). To reduce emissions, the 8 Australian government has legislated that all new cars use unleaded p_____ and have catalytic converters fitted to the e_______. Water Pollution – 1. Sewage is all household waste water. Many detergents contain phosphates which act as plant fertilisers. When these p_________ and the sewerage reach rivers, they help water plants to g___ in abundance, reducing the dissolved o_____ in the river water. The result is death of aquatic animals due to suffocation by the algal blooms. This harmful effect is called eutrophication. 2. Biodegradable detergents are more environmentally friendly because they are readily broken d___ to harmless substances by decomposing bacteria. 3. Suspended Solids in water such as silt reduce the amount of l____ that reaches the depths of the water in lakes and rivers. This reduces the ability of aquatic plants to p______________ and the result is less plant and animal l___. Turbidity is the measure of „cloudiness‟ or the depth to which light can reach in water. Introduced Species are species of plants or animals that have migrated or been brought to A________. Many fit into the natural ecosystems and are kept in c______ by natural predators and parasites. However, some become pests as they are well-adapted to our e__________, readily obtain nutrients, and lack natural predators or parasites. Examples include rabbits, foxes, carp, and prickly pear cactus plant. Biological Control is an environmentally-f_______ method to control these pests by the introduction of species-specific, living organisms to control their numbers. Successful examples include the myxoma virus and the calici virus for rabbits, and the cactoblastis moth feeding on the prickly pear. Unsuccessful examples include the introduction of the cane t___ to reduce the numbers of natural cane beetles. Biological Magnification is the accumulation in body tissues of certain chemicals such as DDT pesticide and mercury. The higher along the food c____, the greater is the accumulation, sometimes to toxic levels, causing birth defects and d____. Soil Salinity has increased greatly since the widespread logging of t____ by farmers. Deep tree roots normally draw water from the underground water table. However, when logging of trees occurs, the water table rises close to the surface bringing with it salt from rocks. This creates soil that is so s____ that vegetation cannot grow effectively. The result is loss of vegetation and e______. Population Explosion is the rapid increase in p_________ in developing countries causing famine, and also in developed countries causing more demand for energy and with that, increased pollution and d__________ of the environment. 9 ACTIVITY 2. CLOZE: ENERGY CRISIS AND ENERGY ALTERNATIVES Name:________________________________________________________Date:______ Fill in the blanks using words from the word list. Word List: sunlight, electricity, strong, stations, fuels, polluting, out, oil, electricity, cooking, environment, world, methane, electric, solar, plant, energy, heating, gas, generate, cheap, dams, waves, New, out, stations, tides, crisis, cheap, burnt, cane, water, bills, power, years, earth, energy, mud, electricity, heating With population growth comes increased usage of energy. The energy c________ is the inability of the earth’s resources to keep pace with the population’s needs. The solution to the energy crisis is twofold – build more p________ stations to supply more e________, or reduce the usage of energy by building more energy-efficient devices. There are 2 types of energy sources – non-renewable and renewable. NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES e.g. fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) and nuclear energy (uranium, plutonium) Takes a long time to form (e.g. millions of years) Cannot be reused Advantages Cheap Readily available Efficient Multipurpose (e.g. oil for cars, heating) Disadvantages Running out Polluting or radioactive e.g. biomass, solar, wind, wave, tidal, hydroelectric, geothermal Takes a shorter time to form (e.g. decade or two) Can be reused or is very abundant Advantages Won’t run out Environmentally friendly Disadvantages Geographically selected Inefficient 10 NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Fossil fuels began forming millions of y________ ago. At the time when it is believed that dinosaurs roamed the e________, forests of trees fell into swamps and were covered by silt and m________. They gradually changed into the coal, o________ and natural g________ that we use today. The advantages of using fossil fuels are that they are readily available at the present time and are c________. They can also be used for many purposes e.g. coal can be b________ in power stations to make e_________ and also in homes for h_________. These fossil f________ took millions of years to form, yet humans are using them rapidly in cars, power s_________ and factories. They will probably run o________ within the next 100 years. So the disadvantages of fossil fuels is that they will run out, and also that they are p________. RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Biomass is plant matter that is used as an e_________ source. For example, timber can be burnt for both cooking and h_________ in many homes around the world. Methane gas that is flammable can be made from rotting p________ vegetation in m________ digesters. Also alcohol made from sugar c________ can be used as an environmentally-friendly alternative to petrol. Solar Energy can be used in many ways. Buildings can be designed to take advantage of the sun's warmth in the winter so that we don't use e________ heaters. Solar hot w________ heaters can reduce our electricity b________. Photovoltaic or s________ cells can generate electricity. Solar energy is particularly useful here in Australia because of our abundance of s________. Hydroelectric Power Stations are initially expensive to build but are c________ to run. They can be located in mountainous areas where water is stored in d________ and then released to turn turbines that generate e____________. 11 Wind Energy from windmills can be used to g________ electricity by turning turbines in the same way as in hydroelectric power stations. These are particularly useful in areas close to the coast where the winds are s________ and continuous. Wave and Tidal Power can be used to generate e________ from the rise and fall of the w________ and the t________. These forms of power can only be utilised at the moment in places such as Darwin where the tide rises and falls through a considerable height very rapidly. Geothermal energy is energy harnessed in areas of the earth that are near volcanoes or hot springs such as in Rotorua in N________ Zealand. The heat can be used for c________ and heating in homes. It can also be used to generate electricity by heating steam to turn turbines. The advantages of using renewable energy sources is that they won't run o________ and they are friendly to the e____________. Unfortunately, they are not as efficient in producing electricity as coal-powered power s________. Also another disadvantage of solar, wind, wave, tidal and geothermal energy sources is that they can only be used in certain areas around the w________. Because Australia has a lot of sunlight and many places where we could use wind, wave and tidal power, more research must be done in these areas for our future e________ use. 12 ACTIVITY 3. ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Name:________________________________________________________Date:______ Task: Cut out all the boxes. Match one box from the left column with one box from the right column. Glue the matching boxes onto a large sheet of paper. PROBLEM SOLUTION - Too much lead in air from car - Make laws to control factory gas emissions exhausts -Organise car-pooling between workers - Logging forests to make pine bark - House is too hot in summer and too - Better regulation of chemicals made and used by factories cold in winter - Slowly rotting grass clippings make - More regular car maintenance too much methane gas - Detergents in rivers kill fish - Build dams that are friendly to the environment - Electricity bill is too high - Have fewer children - Flooding - Use unleaded petrol - Old car that ‘blows smoke’ - Spread grass clippings out to speed up decay - Too many poisonous factory gases - Turn off lights when not in use - Overpopulation - Put insulation in roof and walls - Too many car exhaust fumes - Make laws to control the movement of oil tankers - Cats kill wildlife - Use detergents that are phosphate-free - Too many waterways toxic chemicals - Non-decaying packaging in - Have air-circulating areas in the roof to release hot air - Solar or wind-powered power - - CFC gases from spray cans destroy Walk or ride a bike more often the ozone layer 13 - Noise pollution - Use safer gases in spray cans stations - Oil spills in the ocean - Plant more trees - Detergents in rivers kill fish -Kill cats in national parks -Too much sunlight enters windows to heat the house in summer -Wash the car on the grass not the road so soapy water does not enter stormwater drains -House is too hot in summer and too cold in winter - Plastic bait bags that strangle marine animals -Too much litter -Make bottles from recycled plastic -Electricity bill is too high -Build wide verandahs to shade the windows the bin -Put all plastic bags in the bin and not in the ocean -Use natural predators to kill insects pests not pesticides -Have shorter showers -Too many insect pests -Pollution from coal-burning power stations -Destruction of animal habitats by mining -Damage to beaches by 4WDs -Overfishing -Waste of too much fresh water in houses -Endangered or extinct animals -Too much air pollution from tyre rubber vaporising into air -Too many cars on the road with just one person -Land clearing for more and more housing estates -Too many polluting softdrink bottles -Too much salt in the soil -Install a solar hot water system -Put litter in -Restrict mining leases and encourage land reafforestation -Save the habitats of animals so they -can breed successfully -Ban fishing in fish breeding grounds -Ban 4WDs from certain beaches -Use cardboard and not plastic packaging -Make laws to have parks in new housing estates -Plant more trees to reduce soil salinity -Walk or ride a bike more often -Fine people who operate noisy machinery outdoors 14 ACTIVITY 3. CANAL DEVELOPMENT DEBATE Name:________________________________________________________Date:______ Background Information Sunny Bay is a popular fishing spot fringed by mangroves. A development proposal for a new canal housing estate and marina has been put to the local shire council for debate by interested parties. The Topic of the Debate Should the canal housing and marina development go ahead? The 3 Parties in Favour of the Development. - - Real Estate Agent – His concerns include more housing in the fast-growing area to cater for all types of people, to bring income to the shire through tourism and recreation and to rid the area of mosquitoes that breed in the mangroves. Builder – Future employment for many tradespeople and a considerable profit for his company are his interests in this matter. Shop Owner – Her concerns are the increased profits for her business and long-term employment for the small shire. The 3 Parties Against the Development - - Local Resident – Her concerns are for the increased demand on the infra-structure (i.e. bus transport, schools, medical facilities, electricity and water supply, sewerage etc) and for the increase in noise and pollution with building and the greater number of residents. Conservationist – Her concerns are that fish breeding habitats containing mangroves and eel grass will be destroyed, that the detergent-containing run-off from canal front houses may pollute the waterways and that the lead-based anti-fouling paint used on boats will further accumulate causing long-term problems. Representative from the Local Fishing Club – His concern is that fish breeding areas will be destroyed and that there is insufficient regulation to prevent over-fishing in the area. 15 ACTIVITY 4. DEBATE : ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF ENERGY RESOURCES Name:________________________________________________________Date:______ Background Information Due to increased residential and industrial demand for energy, the state government is considering a proposal for a new coal-powered power station to be built. The proposal is the building of a power station at Brownfield, an arid country town which is close to coal mines and has both a well-maintained highway for truck transport and a nearby deepwater port for coal export. The Topic of the Debate Should the development of the power station go ahead? The 3 Parties in Favour of the Coal-Powered Power Station - - Local Member of Parliament in the Brownfield Electorate – She is pleased that there is an opportunity to bring employment and prosperity to a small country town. Chief Executive Officer of the NRG Coal Mining Company – His company provides coal for electricity production that is used by a large range of local and international manufacturing businesses. State Director of Energex – Demand for electricity has been increasing in recent years because of the increase in global warming and the need for cooling devices such as air conditioners. He believes that a new power station will supply the needs of the growing population and associated industry. The 3 Parties Against the Coal-Powered Power - - Station Local Mayor of Brownfield – Her concerns are for the increased demand on the infra-structure (i.e. bus transport, schools, medical facilities, electricity and water supply, sewerage etc) and for the increase in noise and pollution with mining and building and the greater number of residents. Greenpeace Conservationist and Local Doctor – His concerns are that the emission gases are unhealthy and will put stress on the state health system. Representative from the World Alternative Energy Commission (WAEC) – Her concerns are that insufficient money is being spent on renewable energy research and development and that the millions of dollars for a new power station would be better spent in scientific research for solar energy and the like. 16 More information: POWER SOURCE Coal Natural Gas Oil Nuclear Solar HydroElectricity Wind Tidal Geothermal ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES Cost effective Appropriate for large scale use High employment Readily available and transportable in some countries Non-renewable Limited resource Waste emissions of CO2, SO2, NOx Large scale chronic health risk Land degraded by mining Solid waste disposal of ash Appropriate for large scale use Non-renewable Valuable as raw material in Limited resource industry, residential and Waste emissions of CO2, SO2, NOx commercial heating Appropriate for large scale use Non-renewable Readily available in some Limited resource countries Waste emissions of CO2, SO2, NOx Large scale chronic health risk Expensive Used in production of plastics, pharmaceuticals, transportation, and commercial and residential heating Mostly available from politically volatile countries Cost effective in large scale Non-renewable use Accident risk Almost unlimited resources Radioactive waste disposal can be a using reprocessing methods problem No greenhouse emissions High initial building costs Renewable Not cost effective at present Occupies Pollution-free large expanses of land Limited Good for small scale heating hours developing technology Need to store energy Renewable Limited sites available Pollution-free Large scale accident risk Reliable, continuous resource Large scale environmental damage High initial building costs Renewable Limited areas suitable Pollution-free Winds must be greater than 21km/h Low cost Good for small scale Backup provisions necessary ‘wind farms’ Visibly disturbing on a large scale Interference to TV and microwave transmission Renewable Pollution-free Not cost effective at present Only available on certain coastlines Renewable in the long term Local use only Bad smelling gases Cost effective Reliable constant Contains corrosive harmful gases resource such as H2S, NH3 and radon 17 ACTIVITY 5. QUIZ: ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES Name:________________________________________________________Date:______ 1. The main gases responsible for the Greenhouse Effect are: A water and ozone B oxygen and nitrous oxide C carbon dioxide and methane 2. According to the United Nations, the main cause of climate change / global warming is the result of: A water pollution B factory and car emissions C sewage 3. It is believed that the thinning of the ozone layer is the result of chlorofluorocarbons. These gases have been used in: A electric heaters and clothes driers B spray cans and refrigerators C cigarette lighters and air-conditioners 4. The main gases that produce acid rain are: A sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides B ozone and oxygen gas C chlorofluorocarbons 5. The release of excessive amounts of harmful substances such as car and factory fumes and tyre rubber into the atmosphere is called: A noise pollution B mutagenic pollution C air pollution 6. To reduce pollution from cars, the Australian government has legislated that all new cars must use: A unleaded petrol B diesel fuel C leaded petrol 18 7. When phosphate-containing wastes from detergents and fertilisers reach our waterways, water plants grow excessively extracting oxygen from the water causing fish to suffocate. This process is called: A phosphatisation B sewage recycling C eutrophication 8. Substances that are easily broken down into harmless substances by decomposers are termed: A environmentally unfriendly B biodegradable C non-biodegradable 9. An example of a species that was introduced to Australia with harmful results is the: A cactoblastis moth B cane toad C potato 10. Instead of using pesticides to eradicate pests, another method using the pest's natural predators or parasites to control its numbers is frequently used. This environmentally friendly method is termed: A biological control B predator release C insecticide management 11. Examples of toxins that biologically magnify or accumulate in organisms are: A heavy metals and carbon dioxide B mercury and DDT C fat and CFC's 12. Examples of fossil fuels are: A uranium and carbonised dinosaur remains B renewable fuels C coal, oil and natural gas 13. Renewable energy alternatives are those that: A are abundant or can be regrown or recycled in a short time period B are environmentally friendly such as coal C never cause pollution nor environmental damage at all 19 14. Examples of biomass energy alternatives are: A uranium and plutonium B coal, oil and natural gas C timber, methane and alcohol 15. Present disadvantages of using renewable energy alternatives are that they are: A expensive to run and environmentally unfriendly B relatively inefficient and geographically selective C inefficient and polluting 20