Climate Change Impact & Risk Management
advertisement
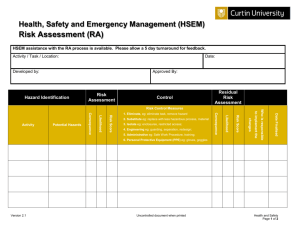
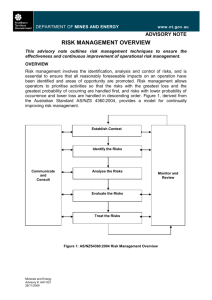
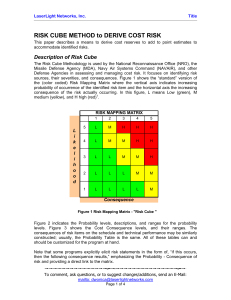
Assessing climate change risk Introduction Welcome & Acknowledgement Background [Insert Council logo] • Workshops action plan • General Manager’s support Housekeeping • Facilities, OH&S, Turn off mobiles Introduction Purpose • Developing a Climate Change Action Plan Program • Keeping to time • Respectful discussion Introductions Right: An action planning workshop at The Hills Shire Council Progress Gain internal support Identify Planning Team Steering Committee Meeting 1 -Develop a planning program Workshop 1 -Introduction Workshop 2 -Risk assessment Steering Committee Meeting 2 -Research adaptation options Workshop 3 -Adaptation actions Steering Committee 3 -Mitigation Steering Committee Meeting 5 -Review Steering Committee Meeting 4 -Action plan Workshop 4 -Mitigation actions Expected outcomes Participants will: • Understand concepts of risk assessment • Brainstorm/ undertake group work to: – Identify potential risks to Council service areas – Analyse risk statements to determine preliminary levels of risk – Evaluate risks to determine priorities What is risk? Level of Risk = Likelihood of an occurrence x Consequence of that occurrence What is the likelihood it will occur? What are the potential consequences of the occurrence? © State of New South Wales through the Department of Planning Risk assessment • AS/NZS ISO 31000:2009 Risk Management – Principles and Guidelines • Climate Change Impacts and Risk Management – A Guide for Business and Government Australian Greenhouse Office, 2006 Photo courtesy of Scott Lenton, Clarence Valley Council Risk assessment Communicate & consult Monitor & review Establish the context - Objectives - Stakeholders - Success criteria - Climate scenarios Identify the risks - What can happen - How can it happen Analyse the risks - Review controls - Likelihood -Consequence - Level of risk Risk Assessment Evaluate the risks - Evaluate risks - Prioritise risks - Screen risks Treat the risks - Identify options - Select the best - Develop plans - Implement (AGO, 2006) Establishing the context • Climate change scenarios • Scope – activities; geographic boundaries; time horizon • Stakeholders – involvement & communication • Framework for evaluating risks • Organisation’s concerns Photo courtesy of Scott Lenton, Clarence Valley Council Identification of risks • Understanding the links between climate change and risk Climate Impact: (e.g. Increased frequency of hot days) Hazard associated with the impact: (e.g. accelerated deterioration of buildings) Consequence of hazard to Council objectives: (e.g. increased maintenance costs to Council) Risk statement: “Increased frequency of hot days, leading to accelerated deterioration of buildings resulting in increased maintenance costs to Council” Examples Climate impact Increased frequency of hot days Hazard associated with impact Increased energy demand and increased brownouts Increased indoor patronage at Council community centres Increased beach/pool patronage Increase in heat related illness for outdoor staff Decrease in Council service delivery Increased service requirements Increased water related injury Increase in time lost for stop work orders Further consequences to Council objectives may cascade from the above Consequences of hazard to Council objectives Risk Statements • Example of an adequate risk statement: Increased frequency of hot days, leading to accelerated deterioration of Council assets resulting in increased maintenance costs to Council • Example of a risk statement which may not be detailed enough: Increased hot days leading to increased maintenance of buildings It is not clear how the maintenance of buildings will affect council activities Identifying risks Activity • Divide into groups of 3 -5 people (different roles) • You will be assigned a key element • Think of all risks for the key element: o o o o o o Service delivery Related services and service providers Personnel General public Systems and equipment Administration and support Identifying risks ….Activity continued…. • • • • Record all ideas Aim for cause effect statements Link risk statements to service objectives Ensure risk statement will be understood by staff who have not attended this workshop Identifying risks • Link risk statements to service objectives: – Public safety – Local economy and growth – Community and lifestyle – Environment and sustainability – Public administration Activity to be followed by break while facilitator enters into spreadsheet Analysis of risk statements Level of Risk = Likelihood of an occurrence x Consequence of that occurrence • Analysis should take into account controls including any current management regimes & responses in place to control each risk. Determining consequence • Consequence = “How bad is it likely to be” • Risks can affect Council in many different ways depending on objectives (Success Criteria) • Success Criteria suggested by the AGO (2006): – Public safety – Local economy and growth – Community and lifestyle – Environment and sustainability **Replace with Council risk framework if – Public administration applicable** Determining consequence Public Safety Rating Catastrophic Large number of injury or loss of life Major Isolated instances of serious injury or loss of life Moderate Small number of injury Minor Serious near misses or minor injuries Success Criteria Community and Environment and lifestyle sustainability The region would be Major widespread loss seen as very of environmental unattractive, moribund amenity and and unable to support progressive its community irrecoverable environmental damage Regional stagnation such Severe and Severe loss of that businesses are unable widespread decline in environmental amenity to thrive and employment services and quality of and a danger of does not keep pace with life within the continuing population growth community environmental damage Local economy and growth Regional decline leading to widespread business failure, loss of employment and hardship Public administration Public administration would fall into decay and cease to be effective Public administration would struggle to remain effective and would be seen to be in danger of failing completely Significant general General appreciable Isolated but significant Public administration reduction in economic decline in services instances of would be under performance relative to environmental damage pressure on several current forecasts that might be reversed fronts with intensive efforts Individually significant but Isolated but noticeable Minor instances of Isolated instances of isolated areas of reduction examples of decline in environmental damage public administration in economic performance services that could be reversed being under severe relative to current forecasts pressure Insignificant Appearance of a Minor shortfall relative to threat but no actual current forecasts harm There would be minor No environmental areas in which the damage region was unable to maintain its current services **Replace with Council risk framework if applicable** There would be minor instances of public administration being under more than usual stress but it could be managed Other success criteria A level that would constitute a complete failure A level that would constitute a major problem close to complete failure A significant issue which may be reversed with major efforts No significant harm, but should be considered to prevent further escalation A level that would attract no additional attention or resources Determining likelihood Likelihood rating Recurrent Risks Single Events Almost Certain May occur several times a year >50% chance of occurring Likely May occur around once a year 50% chance of occurring Possible May occur once every 10 years <50% chance of occurring Unlikely May arise once in 10 - 25years >0% chance of occurring Rare Unlikely in the next 25 years Close to 0% change of occurring **Replace with Council risk framework if applicable** Analysing risks Level of Risk = Likelihood of an occurrence x Consequence of that occurrence Likelihood Consequence Insignificant Minor Moderate Major Catastrophic Almost Certain Medium Medium High Extreme Extreme Likely Low Medium High High Extreme Possible Low Medium Medium High High Unlikely Low Low Medium Medium Medium Rare Low Low Low Low Medium **Replace with Council risk framework if applicable** • Any questions? Analysing risks Activities: • Analysing each risk statement – using the Risk Assessment Tool • Prioritising risk statements – can be completed after the workshop by the Steering Committee Risk Assessment Tool Controls • Council’s current controls are considered when determining the likelihood and consequence of each risk statement • Only measures that are already in place can be considered as controls • Examples: routine monitoring and repair systems, existing levees, incentive programs Achievements from the workshop During the workshop we have: • Developed a list of detailed risk statements relevant to Council service areas • Analysed risk statements to determine preliminary levels of risk • Evaluated risks to develop a list of priority risk statements to be addressed in the climate change action plan Conclusion • Thank you • Evaluation forms References • AGO, 2006, Climate Change Impacts and Risk Management – A Guide for Business and Government. http://www.climatechange.gov.au/community/~/media/pu blications/local-govt/risk-management.ashx • Australian and New Zealand Standard AS/NZS 4360: 2004 Risk Management. • AS/NZS ISO 31000: 2009 Risk Management – Principles and guidelines.