Russia and the Republics
advertisement

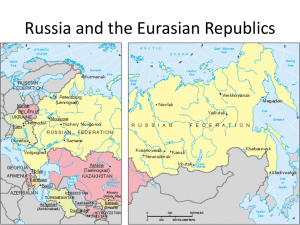
Russia and the Republics Landforms and Resources And Climate Overview Russia and the Republics occupy an amount of land equal to about 3 times the size of the United States. Russia and the Republics span two continents (Asia and Europe) Russia and the Republics span 11 time zones Russia and the Republics cover over 8.5 million square miles Russia and the Republics cover nearly one-sixth of the Earth’s surface Why do you think the population clustered on the West side of the region?? Let’s answer this by the end of the presentation Northern Landforms Northern European Plain Lowland area from western border of Russia to the Ural Mountains Home to chernozem, or black earth, which is very fertile. Because of this, many of the region’s agricultural areas are located here. Home to nearly 75% of the region’s population 3 of region’s largest cities are located there Northern Landforms West Siberian Plain Western boundary at Ural Mountains Eastern boundary at Yenisey River Because the plain tilts northward, its rivers flow toward the Arctic Ocean The left bank of the river includes a huge Vasyugan Bog covering the area of 53 thousand sq. km. Altogether there are 573 rivers with a length more than 20 km. and 35 lakes with an area larger than 5 sq. km. in the Region. 1/5 of the Region’s territory is a spot of river valleys. Northern Landforms Central Siberian Plateau Made up of high plateaus with average heights of 1,000 to 2,000 feet Russian Far East Made up of a system of volcanic ranges, with many active volcanoes Southern Landforms Caucasus and other mountains Caucasus - stretch across land between the Black and Caspian Seas Tian Shan - along the southern border of Russia and the Republics Turan Plain Lies between the Caspian Sea and Central Asia Kara Kum Desert These two deserts (the Kara Kum in Turkmenistan and the Kyzyl Kum in Uzbekistan) cover about 230,000 square miles. Kyzyl Kum Desert Rivers and Lakes Rivers Volga, Ob, Yenisey, Lena Rivers are largest in the region Lakes Caspian Sea - actually a saltwater lake. It stretches for nearly 750 miles from North to South Aral Sea - has lost about 80% of its water in the past 40 years Lake Baikal - the deepest lake in the world. At its deepest point, it is more than a mile from the surface to the bottom. It holds 20% of the world’s fresh water Aral Sea Lake Baikal Natural Resources Huge reserves of coal, iron ore, oil, and natural gas, as well as timber Mismanagement of resources , harsh climates, rugged terrain, and vast distances make it difficult for Russia and the Republics to remove resources from the ground and transport them to market. Human-Environment Interaction The Trans-Siberian Railroad covers more than 5,700 miles and 7 time zones. Its completion aided in the migration of many European Russians to Siberia, helping develop natural resources. Environmental issues – mining operations have caused significant damage the many hydroelectric plants discharge thermal pollution, damaging surrounding plant and animal habitats Agricultural practices devestated rivers and lakes with chemical runoff from pesticides. Chernobyl- nuclear plant explosion in 1986 1971, geologists discovered a massive underground deposit of natural gas on this site. Whilst excavating the hole to tap the gas, the drilling rig collapsed leaving a massive hole. To prevent poisonous gasses from escaping, the hole was allowed to burn. It continues to burn to this day and has done so without ceasing. The Trans-Siberian Railroad covers more than 5,700 miles and 7 time zones. Its completion aided in the migration of many European Russians to Siberia, helping develop natural resources. Major climate regions: 1. Humid continental- variety in temperature and precipitation, Northern hemisphere, 4 seasons 2. Subarctic- huge temperature variations, usually freezing or below 5-8 months a year. Short cool summers, harsh winters. 3. Semiarid- low precipitation, interior of continents 4. Desert-less than 10 inches rain per year extreme temperature changes ContinentalityA region’s distance from the moderating influence of the sea. (rain, moisture, temperature, etc) Russia’s extreme climate effected by this. Vegetation 1. Tundra- flat, treeless land with permafrost 2. Deciduous Forest- lands with leafy trees 3. Steppe- temperate grasslands or prairie 4. Desert- plants that conserve water, (cactus or shrubs)