File - DIV-A

Civil Engineering is Everywhere
Branches of Civil Engineering.
– Surveying
– Transportation Engg
– Geotechnical or Soil Mechanics
– Environmental Engg
– Structural Engg
– Quantity Surveying
– Construction Management and Project
Management
– Irrigation
– Fluid Mechanics
– Town Planning
– Remote Sensing
Housing –
BRANCHES OF CIVIL
1) Surveying
2) Construction Management
3) Quantity Surveying
4) Structural Engg
5) Geotechnical and Foundation Engg
6) Earthquake Engg
7) Town Planning
8) Remote Sensing
Water 1) Irrigation Engg
2) Fluid Mechanics
3) Environmental Engg
Transportation – 1) Roadways
2 ) Railways
3) Airways
4) Waterways
Surveying
Def Surveying:* Relative Point
* Prepare Maps
* Linear and Angular Measurements
* Leveling
Classification of Surveying- * Plane Surveying
* Geodetic Surveying
Types of Surveying - * Based on Purpose
* Based on Instruments
Principals of Surveying –
Work from Whole to part
To Locate a pt by atleast 2 independent measurements.
TYPES –
Based on Purpose –
1) Topographic Surveying – Natural and Artificial Features like hills, Lakes, Roads, Villages, Railway tracks……. Etc.
2) Cadcestral Surveying –
Boundaries of Fields, Houses, Plots…
3) City Survey – boundaries of plots, watersupply, sanitary…..
4) Route Surveying - ……………
5) Mine Surveying –
Underground material…..
6) Hydrographic Surveying
– Nature of Bed Surface.
Based on Instruments –
1) Chain Survey
2) Compass Survey
3) Chain and Compass Survey
4) Theodolite Survey
5) Tachometric Surveying
6) Plane Table Surveying
7) Electronic Distance Meter Surveying.
•
Applications Of
Surveying
1) Plans and Maps
2) Measure Area of Plot or Land
3) Horizontal and vertical
Measurements
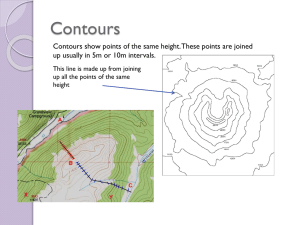
4) CONTOUR Maps
5) Selection of Suitable site
6) Quantity of Earth Work
7) Capacity of Reservoir…….. And many more…….
Structural Engg.
Structural engineers design steel, concrete, timber framed structures such as:
– Tall buildings, towers
–
Bridges
– Chimneys, Tanks
–
Retaining walls, foundations
– Stadiums …….. Etc…
–
Calculates LOAD on Structure
1)
2)
3)
4)
TYPES OF LOADS
Dead Load
Live Load
Wind Load
Earthquake Load.
Classification of STRUCTURES
1) RCC
2) Steel Structure
(HW…) Application of Structural
Engineering??????
Environmental Engineering.
-
-
-
It’s also “PUBLIC HEALTH
ENGINEERING”
It’s the branch which deals with
Water Supply Engg
Sanitary System Engg
Environmental Pollution
Applications of Environmental Engg
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
Testing Quality of Water for diff. purposes.
Design – Water Treatment Plant
Design – Sewage Treatment Plant
Study Population and design proposed projects.
Control and Reduce POLLUTION
Dispose Waste….etc..
Transportation
Transportation
Engineers design and analyze
– Roadways
–
Railways
– Airports
–
Waterways
– Parking Lots
–
Traffic Control Signal
Systems.
ROADWAYS
Classification of Roadways –
According to IRC
–
Expressway
– National Highway (NH)
–
State Highway (SH)
– Major District Road (MDR)
–
Village Road (VR)
According to Material used for Construction
–
Bituminous Road or Tar Road
– Concrete Road
–
Water Bound Macadem Road (WBM)
– Earth Work.
Classification according to IRC
Expressway – (HW) ???????
National Highway –
– Run through LENGTH and WIDTH of
Country
–
Connects Capitals
– 2 Lane
–
Width – 7 to 15 m
– Fast and Heavy Loaded traffic.
State Highway –
– Connects Major Cities to NH
–
2 lane or some times 1
– Width – 7 to 10 m
–
Used for fast Traffic
Major District Road –
Connecting District places to taluka, main cities, major market places in cities
- Width 5 to 8 m
- Use of Moderate Traffic
Village Roads -
- Connects Village to taluka, village to nearest railway station, village to village…
- EARTH ROAD or KUTCHA ROAD
- Light and Slow moving Vehicles
- (Bullock Cart Road)
Home Work --------
Write min 3 Examples of each type of Roadways according to
IRC…
Classification based on Material
Classification based on Material
Bituminous Road or TAR Road
– Tar is a Binding Material
–
Easily Repaired and Maintained
– Due to Bitumen Layer Wearing surface is small
–
Life is Short
Concrete Road
- Wearing surface is Cement Concrete
- Rigid Pavement
- Life is High as strength is high.
- Difficult to repair and Maintain
- HIGH COST.
Water Bound Macadam Road -
– Base Course of Bitumen or Concrete
–
Constructed with 2 to 3 layers of aggregates and soil material
– Normally provided on VILLAGE ROAD
Earth Road –
–
Earth material is main Constituent of the road
– Kutcha road (Loacally available material)
– Formed by trace passers or bullock carts….
HOME WORK…….
Any 6 Applications of
TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING???
RAILWAYS
It is also called as
‘ PERMAENT WAY’
Cross Section of Permanent Way.
Gauge: -The Clear Distance between the inner faces of Rails
Indian Railways are divided in 3 types based on Gauge
Broad Gauge 1.676m
Meter Gauge -
Narrow Gauge -
1.000m
0.762m
I.R. divided in Different 8 Zones
1) Northern
2) Central
5) Western
6) North Eastern
3) Southern
4) Eastern
7) South Central
8) South Eastern
HOME WORK…..
1) Short Note on Construction of Permanent way?
2) Comparison between ROADWAYS and
RAILWAYS…… (4 mrks)
Geotechnical OR
Soil Mechanics
-
-
Geotechnical engineering is essential for a safe and secure structure.
Deals with SOIL Study
Behavior of Soil under applied LOAD
TESTS –
Trials Pits
Plate Load Test
Application of Geotechnical Engg.
5)
6)
7)
8)
1)
2)
3)
4)
Properties of Soil
Classification of Soil
Bearing Capacity of Soil
Design of Earth Dam ------EG??????
Study of different SOIL STRATA
Capability of SUB- GRADE of road.
Design of FOUNDATION in any type of soil
Analyze the WATER SEEPAGE for Dams
Quantity Surveying
Deals with measuring various Quantities and
Probable cost of Construction.
CLASSICATION:-
Quantity
Surveying
ESTIMATE VALUATION
Estimation
–
To find/ Calculate the
‘approximate cost’ of Construction.
Valuation – Determining the
‘PRESENT VALUE’ of existing property.
(HOME WORK…….)
1)
2)
Difference between Estimation and Valuation
(Min 5 Pts.)
Applications of Q.S ???? (6 pts.)
Fluid Mechanics or Hydraulics
Water management involves the use of hydraulic principles to design:
– Water Retaining Structures like DAMS,
Canals, Weirs, Water Tanks……
– Hydraulic machines like CP, RP, Turbines etc.
– Gates of Dam, Valves to regulate water flow
– Spillway
– Ship/ Boat
– Measure Velocity, viscosity, pressure, discharge of flow……..
Def. FLUID ????
•
•
Types of Fluid –
Ideal Fluid – No Viscosity, Surface Tension, and
Incompressible (Imaginary Fluid)
Real Fluid – Having VISCOSITY
Classification –
Kinematic F
Dynamic F
FM Kinetic F
Static F
HOME WORK……..
APPLICATIONS of Fluid
Mechanics?????
Construction Management
The job of a construction manager is to:
–
Provide quality control and insure project is completed on time .
–
Within budget.
4 M’s
–
–
–
–
Men
Money
Material
Machine
Constuction of Structure
Divided in 2 parts
SUBSTRUCTURE
SUPERSTRUCTURE
Applications..........
1) Use of Modern Techniques, Machinery for SAFE and SPEEDY work.
2) Use od Modern Material in Special Construction
Work like DAMS and TUNNELS
3) Plan the project and decided the sequence
4) Control Labours
5) Economical
6) Good Quality of Work
Irrigation Engineering
-
-
1) Process of Supplying Water for
Agriculture
Domestics
Industries
2) Construction of DAMs Reservoirs, Weirs….
3) Management of Water:- train the farmers for
OPTIMUM use of Water.
4) Natural Source of Water
(HW) - Application of Irrigation Engg. ??????
EARTHQUAKE Engg.
Earthquake is a destructive and deadly natural phenomenon.
Deals with Seismic Zones and their effects on the structure.
“SHIFTING Of EARTH” – Design of Foundation
Study of Load On Building – DYNAMIC
Earthquake PROTECTION-
1)
2)
3)
4)
Compact Rectangular Plan
All Building Parts Tied Together
Parapet or any PROJECTION should not be more than 750 mm
Safe distance bet 2 structures
5) Provide Strong FOUNDATION resting on HARD STRATA.
• ROLE OF CIVIL ENGINEER
IN DIFFERENT
CONSTRUCTION WORKS…..
Role of C.E. in Const. of BUILDING
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
1) Planning and preparing a drawing and its approval
Preparation of Design
Estimating and Costing
Study of Foundation
Testing, Supervision and execution
Maintenance
Role of C.E. in Const. of DAM’s
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
10)
Site Selection
Conduct various Surveys and Collection of Various
Data
Study of Foundation
Study of Catchment Area
Reservoir Capacity
Selection of DAM
Structural and Hydraulic Design
Estimate
Testing Supervision Execution and maintenances
Socio Economic ROLE (Political and Social)
4)
5)
6)
7)
1)
2)
3)
Role of C.E. in Const. of EXPRESS WAYs
Planning and Surveying
Alignment of Road
Contour Plan
Design of Road and Pavement
Estimate of Road
Construction and testing of Express Way
Maintenance
Importance of Interdisciplinary Approach in Engg.