Precautionary Principle
Precautionary Principle
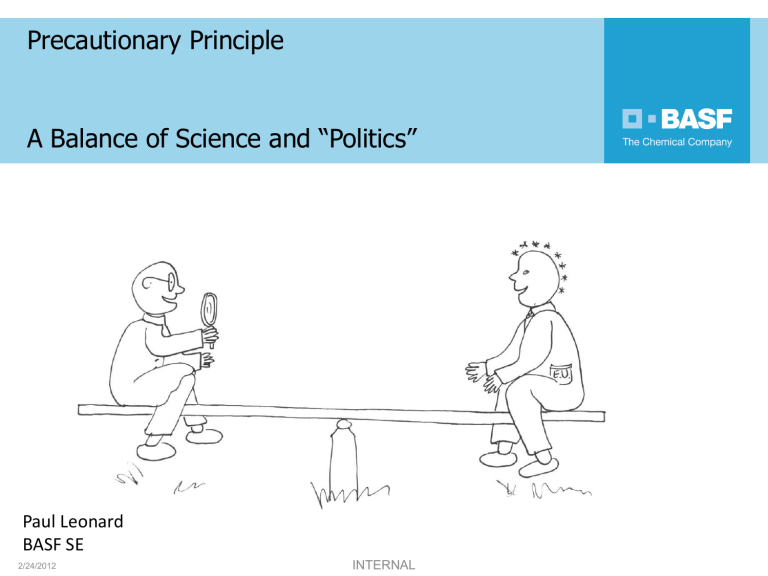
A Balance of Science and “Politics”
Paul Leonard
BASF SE
2/24/2012
INTERNAL
Precautionary Principle
Origins
Use
Hazard based legislation, the ultimate form of Precaution
Case law?
Innovation
Trade
Risk-Risk trade-offs & substitution
Conclusions
Origins and Evolution
Principle 15 of the 1992 Rio
Declaration:
"Where there are threats of serious or irreversible damage, lack of scientific certainty shall not be used as a reason for postponing cost-effective measures to prevent environmental degradation."
The PP was designed to address situations where political action is required, but science is not clear or readily available.
The EU Policy Treadmill
It ´s a complex & lengthy process
NGOs
Public
Media
Revision
Regulation
&
Opinion
Elections
•27 Member
States
•NGOs
•Lobbyists
•Think tanks
•Chambers of commerce
•Journalists
Members of
European
Parliament
Opinions
Commission
Drafts
Legislation
Parliament amends legislation
Political
Compromise Council
Reaction
Precaution is faster, more decisive, less complex to administer & can be justified by Scientific Uncertainty
What Is Scientific Uncertainty?
Lack of scientific certainty should not prevent regulatory action
A statistical probability of 95% is also equivalent to 5% scientific uncertainty
Science is built on uncertainty, but this can be missused
What About Scientific Risk Assessment?
Traditional basis for regulation of uncertainty,
Hazard X Exposure potential = Risk
Management of risk and uncertainty by application safety factors
EFSA and Risk Assessment are increasingly criticised by
NGOs and politicians as,
“ An unreliable practice of guessing without adequate knowledge”
The Precautinary Principle is Promoted as a Responsible Solution
Guidance on Interpretation of the
Precautionary Principle
2/24/2012
INTERNAL
COM(2000) 1
COMMUNICATION FROM THE COMMISSION on the precautionary principle
“The implementation of an approach based on the precautionary principle should start with a scientific evaluation , as complete as possible, and where possible, identifying at each stage the degree
of scientific uncertainty.
Where action is deemed necessary, measures based on the precautionary principle should be, inter alia:
•proportional to the chosen level of protection …..”
2001, European Environment Agency’s
“ Late lessons from early warnings: the precautionary principle 1896–2000”
Important shifts:
Stress alternatives in cases of uncertainty
Scrutinise claimed benefits
Importance of lay knowledge (including public domain science)
Reverse the burden of proof
Precaution – as an environmental policy management tool
Lisbon Treaty
December 2007
Paragraph 2 of article 191 of the Lisbon Treaty,
"Union policy on the environment shall aim at a high level of protection taking into account the diversity of situations in the various regions of the Union. It shall be based on the precautionary principle and on the principles that preventive action should be taken , that environmental damage should as a priority be rectified at source and that the polluter should pay."
Legislative Guidance on PP?
There are:
Guidelines for risk assessments, risk management & impact assessments
Several pieces of relevant legislation, and semi-legislative texts, relating to the precautionary principle
Case law
Academic and public debate & eminent opinions
Would a surgeon practice new invasive procedures without reference to tried and tested medical guidelines?
No single comprehensice legislation laying down rules for its use
How is the Precautionary
Principle Being Used?
Media
“ Speaking at the event, ALDE deputy
Chris Davies called on the EU to invoke the precautionary principle in relation to certain pesticides, which could result in their withdrawal from the market were they found to constitute a health risk .
”
EU and National policy makers were put under pressure to ban neonicotinoid insecticides – without substantiated evidence
Hazard Based Legislation,
the Ultimate form of Precaution
Hazard criteria
Plant Protection & Biocides
Ground Water Protection
0.1ppb Cut Off
A political decision in 1980 to use
0.1 ppb as a surrogate for zero tolerance - Not a health-based standard
= one drop in an Olympic-sized swimming pool!
= 1 stem in 111,000 hay bales, or
= 1 baked bean in 21 million cans
The Ultimamte Precaution “ Better don ´ t do it at all ”
Hazard criteria
Plant Protection & Biocides
1107/2009 &
New Biocide Regul.
CMR category 1a & 1b
Endocrine disruptors
POP*/PBT/vPvB
Cut-off
No Registration
Market Removal
Exposure no longer relevant - Removal from the European market
Regulation 1107/2009
Endocrine Disruption
Annex II, 3.6.5 prevents regulation of active ingredients which are, “ considered to have endocrine disrupting properties ”
What is an endocrine disruptor?
Which level of ED should trigger in a ban?
Triazole fungicides are associated with endocrine “activity”, by virtue of their aromatase mode of action (*) – Also used as medication for fungal infections
Endocrine activity is NOT the same as Endocrine Disruption
* http://ec.europa.eu/environment/endocrine/documents/bkh_report.pdf#page=1 http://ec.europa.eu/environment/docum/pdf/bkh_main.pdf and http://www2.mst.dk/common/Udgivramme/Frame.asp?http://www2.mst.dk/Udgiv/publications/2007/978-87-7052-538-1/html/default.htm
Endocrine Disruption
Potential impact for a wide range of chemicals:
phthalates, parabenes, alkylphenols, BPA, synthetic hormones, various pesticides including triazoles,
EU Commission must define criteria for endocrine disruption by end of 2013, for the Biocide Regulation
Industry argues that potency and exposure should be taken into account by the EU Commission, when defining criteria for the ED definition
ED criteria are not just relevant for plant protection and biocides
Economic importance of Azoles in European Agriculture: Wheat Case Study
With azoles, estimated wheat production to increase by 13% in 2020, but the class is potentially under threat from EU Regulations
Removal of azoles would:
reduce EU wheat production by 7% in 2013 and by 12%
Loss of 2,4 billion euros in 2013 and 4,6 billion in
2020
Cultivated area would need to increase by 7,5 % and13,9 % respectively, to maintain EU ´s wheat self sufficiency
Without increased cultivation, EU would become a net importer
Uncertainty concerning global food security would further increase
Prices would continue to rise
The assessment of the economic importance of
Azoles in European agriculture: wheat case study,
Nomisma, Sept. 2012
19
New Biocide Regulation
June 2009
Hazard-based cut-off criteria, copied & pasted from the Plant Protection Regulation
1107/2009
EU Commission Proposed Article 5.1(c)
No chance of derogation for product types 4 and 14 to 19
This would have resulted in removal of anticoagulant rodenticides, with no viable alternative and no chance of derogation
EU Commission was Persuaded to Remove Article 5.1(c)
Hazard criteria under REACH,
Plant Protection & Biocide Regulations
1107/2009 &
New Biocide Regul.
CMR category 1a & 1b
Endocrine disruptors
POP*/PBT/vPvB
REACH
CMR category 1a & 1b
Endocrine disruptors
POP/PBT/vPvB
Cut-off
No Registration
Market Removal
Substances of very high concern
(SVHC)
Authorisation
• Risk Assessment
• Socioeconomic assessment
No limitation
Mitigation
Use restriction
Substitution
Similar Hazard Criteria for REACH, Diffferent Regulatory & Market Consequences
Case Law?
Paraquat
Sweden challenged Comm’s view that non-GLP studies were irrelevant, raised “scientific uncertainty ”
& invoked use of the PP.
The Court of First Instance (CFI) ruled against the
Commission.
Source, 2009, http://www.papers.ssrn.com/so13/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1325770 , and
Hudig, The European Risk Forum Study, The Precautionary Principle Application and Way Forward
EU Case Law*
Artegon (marketing of certain pharmaceuticals),
The CFI and the Eu Court of Justice confirmed that:
economic and financial considerations do not take precedence over risk to public health, even if uncertain, &
perception of risk may lead to differences in scientific opinion, even arising from the same scientific evidence!
*Alemanno, 2009, http://www.papers.ssrn.com/so13/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1325770 , and
Hudig, The European Risk Forum Study, The Precautionary Principle Application and Way Forward
EU Case Law*
Pfizer / Alpharma (virginiamycin and bacitracin)
CFI imposed that “ a public institution can be required to act even before any adverse effects have become apparent ”
Implying that EU institutions may be obliged to apply the
PP.
CFI also signalled that precautionary measures can not be based on hypothetical risks, but must be based on scientific studies available at the time, even if inconclusive
*Alemanno, 2009, http://www.papers.ssrn.com/so13/papers.cfm?abstract_id=1325770 , and
Hudig, The European Risk Forum Study, The Precautionary Principle Application and Way Forward
Interpretatin of the Precautionary Principle is increasingly being defined by public concern, through EU Law Courts
Bisphenol A (BPA)
EU Ban of use in Baby Bottles
Adopted under comitology procedure, no impact assessment was conducted,
Data on alternatives was limited or non-existent
Results on “risk-risk trade-off” were not taken into account
No evidence that alternative materials are safer than BPA.
EU Comm
´s 2000 Guidance Was Not Followed
BPA – EU Commission
Overruling EFSA's opinion and presenting the EU Directive to ban BPA use in baby bottles, Commissioner Dalli stated the ban,
"represents a landmark in our efforts to protect better the health of EU citizens, in particular when it comes to our children, following the precautionary principle“
Public concern appeared to have greater influence on DG SANCO than EFSA ´s expert and independent scientific opinion
Innovation
Innovation is one of the 3 key priorities of the European Commission Europe 2020
Strategy . It also plays a key role in the Horizon 2020 framework programme for
Research and Innovation and is recognised as a key enabling technology.
Source: COM(2011) 808; COM(2012) 341.
“Risk” Perception
EU Member State GMO Interest/Concern
Country Vote
Germany
France
UK
Italy
Spain
Poland
Romania
29
29
29
29
27
27
14
Netherlands
13
Portugal
12
Belgium
12
Czech
Hungary
Greece
Sweden
Austria
Bulgaria
Slovakia
Finland
Denmark
Ireland
Lithuania
Latvia
Slovenia
Luxemburg
Cyprus
Estonia
Malta
12
12
12
10
10
10
7
7
7
7
7
4
4
4
4
4
3
Positive to GM
Negative to GM
Wavering
Profound Differences in Risk Perception, within the EU
Source:
EuropaBio
Professor Anne Glover
Eu. Comm.Chief Scientific Advisor
“There is no substantiated case of any adverse impact on human health, animal health or environmental health, so that’s pretty robust evidence, and I would be confident in saying that there is no more risk in eating GMO food than eating conventionally farmed food ,” http://m.euractiv.com/details.php?aid=514072
stating that, as a result the precautionary principle no longer applies!
What is a sufficient level of evidence to overturn precaution?
Public Perception of Chemicals
Public are:
More concerned about involuntary Risks than voluntary ones
Fear technological hazards more than natural ones, & are
More frightened of unfamiliar risks than familiar risks*
*Fishhoff et. Al. “ How safe is safe enough ”
**Ragnor E. Lofstedt, “ Risk v Hazard – How to Regulate in the 21 st Century”
Chemicals tend to be involuntary, technplogical and unfamiliar
Re-Registration, under Directive
91/414/EEC
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
Prepared by the European Crop Protection Association
The Tool Box has been reduced by more than 70%
“Re-Registration”
Directive
91/414/EEC
New AS
Existing AS
Regulation
1107/2009
Hazard Criteria
&
Comparative
Assessment
Cost of Bringing a New Product to Market
$m
300
Total $256 m.
250
25
Total $184 m.
24
200
Total $152 m.
32
150
100
13
13
18
18
18
10
30
Development
67
11
16
18
25
20
9
Development
79
54
36
11
32
Development
146
50
Research
72
44 Research
94
41 42
32
0
1995 2000 2005-8
Results of 2010 Study undertaken for ECPA and CropLife America
Research
85
Cost of compliance has increased
Registration
Environmental
Chemistry
Toxicology
Field Trials
Chemistry
Tox/Env Chemistry
Biology
Chemistry
© Phillips McDougall
Rate of Product Introductions and R&D by Crop
Number of new Active Ingredients
Herbicides
Insecticides
Fungicides
Cereals
Soybean
Maize
Rice
F&V
Other
Total
F&V
Rice
Cotton
Others
Total
F&V
Cereals
Rice
Others
Total
Others
Total
Average annual rate of introduction
1980/1989
11
5
9
4
29
13
14
9
0
15
11
2
11
2
10
51
36
7
1 23
12.3
Results of 2010 Study undertaken for ECPA and CropLife America
1990/1999
16
2
12
37
7
9
16
5
0
12
10
10
19
57
1
5
30
3
127
12.7
Time period
2000/2009
12
1
9
14
32
5
101
10.1
5
26
17
8
7
0
0
2
38
15
3
3
In R&D
3
13
6
8
3
1
6
3
1
1
1
10
1
4
3
0
18
1
42
8.4
© Phillips McDougall
Innovation can not always keep pace with precaution
Why should industry invest if it is not possible to demonstrate safe use?
Trade
TransAtlantic Perspective
• 1960 and 1990, US health, safety, and environmental regulations were more stringent, risk averse, comprehensive, and innovative than those adopted in
Europe.
• Since around 1990, Europe has increasingly taken a leading regulatory position.
• EU policymakers have grown more willing to regulate risks on precautionary grounds, while American policymakers have called for higher levels of scientific certainty before imposing additional regulatory controls on business.
Professor, Haas School of Business & the Department of Political Science at the University of California, Berkeley.
Why has Europe become more risk averse while American policy makers are calling for greater levels of scientific evidence?
EU USA Trade Implications
June 4, 2008, following an 11 year precautionary ban on marketing of poultry washed in chlorinated water, the EU Commission proposed to permit marketing with labelling for consumer choice.
The EU Council described the proposed compromise solution as “onerous”.
The EU Parliament objected
The US Poultry & Egg Export Council attacked the EU position as “pure and simple protectionism”.
EU ´ s Interpretation of the precautionary principle was contested by
Washington
Use of the precautionary principle can result in trade disputes
Risk-Risk Trade-Offs
& Substitution
Regulation 1107/2009
Non-Chemical V Traditional Pest Control
10 X references to Non-chemical pest control:
Definition 8:
" Non-chemical methods means alternative methods to chemical pesticides for plant protection and pest management, based on agronomic techniques such as those referred to in point 1 of
Annex III* to Directive 2009/…/EC +, or physical, mechanical or biological pest control methods ”
*ANNEX III. General principles of integrated pest management
General Principle for IPM, non-chemical MUST be preferred
Introduced “natural enemies”
The harlequin ladybird
Harmonia axyridis
Source: National Biodiversity Network
Introduced to North America in 1988, Already invaded much of northwest Europe,
Now the most widespread ladybird species on the continent.
Arrived in Britain in summer 2004 widespread
– now
Risk-risk trade-offs were not taken into account
Non-Chemical Solution Resulted in Serious and Irreversible Environmental Damage
Weed control - Flames
Risk-risk trade-offs not taken into account
Fire hazard?
Air pollution?
Carbon footprint?
Selectivity to non-target species?
Impact on biodiversity?
Impact of Ploughing on Earthworms?
Aspects of Applied Biology 47 (1996), Rotations and cropping systems. The influence of crop management systems and rotation on earthworm populations 1990-
1994. J A Hutcheon and D R Iles
It can take up to 6 years for earthworms to recover from deep furrow ploughing
Organic V Conventional Agriculture?
May 2001
Been shoots produced according to organic guidelines infected more than
4000 people, of which 53 died. About 500 became seriously ill, and were treated in hospital.
What would have happened if 53 people died as a result of chemical contamination?
Quality of Science and Precaution?
The European Food Safety Authority concluded that Séralini et al ´s paper which raised international concerns about the potential toxicity of genetically modified (GM) maize NK603 and of a herbicide containing glyphosate, “is of insufficient scientific quality to be considered as valid for risk assessment.”
EFSA initial review on GM maize and herbicide study Press Release 4 October
2012
How good does scientific evidence need to be to trigger precaution?
Risk-Risk Analysis?
“bisphenol A, phthalate, PVC and polycarbonate free” http://www.makeuwell.com.au/glass-baby-bottle-240ml-bpa-free.html
2/24/2012
What about other risks which may be associated with use of glass baby bottles?
INTERNAL
What about other risks associated with
Glass Baby Bottles?
“Avoid heating glass baby bottles. These bottles absorb microwave energy rapidly, which may result in the bottle cracking or exploding.” http://www.ext.nodak.edu/food/factsheet/warming.pdf
2/24/2012
Where is the evidence that it really is safer to use glass baby bottles?
INTERNAL
Failure to account of risk-risk trade-offs can result in replacing known and mitigated risks with unknown and unmitigated risks
Precaution is not risk free
Conclusions
The Precautionary Principle is valuable, when intrepretted according to EU
Commission ´s 2000 Guidance Document, but this guidance is not always followed
Policy makers are under increasing pressure to be “ precautionary ”, fuelled by media
´s focus on potential hazards
Hazard-based legislation can be viewed as an extreme interpretation of the
“precautionary” approach
Scientific risk assessment and EFSA are increasingly challenged as a basis for regulation by the precautionary principle
Precautionary legislation can result in known and mitigated risks being replaced by unknown and unmitigated risks
Use of the precautionary principle can result in trade disputes
Out of context use of the precautionary principle, can remove valuable technologies, increase cost and prevent innovation










