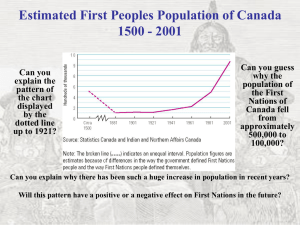
Direct & Indirect Taxation (A.Y. 2010-11)
advertisement

Direct & Indirect Taxation (A.Y. 2010-11)
•
•
•
•
•
Course
Semester
Marks
Faculty
: PGDM (2009-11)
: II
: 60+40
: Prof. Akshay Damani
FCA, MBA (UK), Mcom, SET.
DEATH
&
TAXES
ARE UNAVOIDABLE
Classification of Taxes
• Direct and Indirect taxes
• Direct taxes – directly levied on source of
income and wealth
• E.g. Income tax and Wealth tax
• Indirect taxes – indirectly levied on
activity/transaction which generates income
or wealth
• E.g. sales tax, service tax, etc.
KINDS OF TAXES
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Income-tax
Sales tax
Wealth tax
Service tax
Custom duties
Securities transaction tax
Excise duties…… and many more
INCOME TAX ACT,
1961
(will be replaced by Direct tax codes from 1.4.2011)
Income tax
INCOME
TAX
WHO
WHEN
INCOME
U/s 2 (24): Meaning and Characteristics
A
PERIODICAL MONETARY
RETURN COMING IN WITH
REGULARITY
OR SOME SORT OF
REGULARITY
FROM A
DEFINITE SOURCE
Characteristics of Income
• Legal or Illegal incomes are taxable
• Moral or Immoral incomes are taxable.
• Cash or kind
• Real and not imaginary. E.g. sales supported by invoice
documents
• Examples: profits, gains, donations, perquisites, allowances,
compensation, export cash assistance, lottery prize, kaun banega
crorepati ?, etc…….
Tax
The outflow
from income
paid to the Government.
Who is liable to pay TAX?
PERSON – U/s 2 ( 31 )
INDIVIDUAL
HUF
COMPANY
FIRM
BOI / AOP
LOCAL AUTHORITY
ANY OTHER ARTIFICIAL JURIDICAL PERSON
What is the status of the following person
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Ms. Katrina
Mr. Salman – a minor
Ms. Ruby – a person of unsound mind
Ram, his wife Sita and two sons
M/s Chip and Dale – 2 CAs in partnership
Tata limited
Mumbai Municipal corporation
Roha Gram Panchayat
Joint venture between X ltd and Y ltd
Joint venture between Mr. A and Mr. B
Mumbai University
Tirupathi Devasthanam
Assessee U/s 2 ( 7 )
a) every person in respect of whom any
proceedings are taken under the act
b) every person who is deemed to be an
assesses under the act
e.g. a trustee of a trust
c) every person who is deemed to be as assessee
in default.
e.g. an employer who does not deduct TDS from
employees salaries
When to pay tax ?
PREVIOUS YEAR - U/S 3
ASSESSMENT YEAR U/S 2 ( 9 )
Previous year u/s 3
Year in which the income is received
Always ends on 31st march
E.g. P.Y. 2009-2010 begins on 1.4.2009 and ends
on 31.3.2010
P.Y. 2008-09 begins on 1.4.2008 and ends on
31.3.2009
ASSESSMENT YEAR u/s 2(9)
Year in which final tax is payable relating
to the previous year.
Always for 12 months.
Example:
PY 2008-09 AY 2009-10
PY 2009-10 AY 2010-11 (this is relevant or exam)
Assessment U/s 2(8)
• Assessment 2 (8): Process of
determining and
computing the amount
of income and tax dues
of a person.
Charge of Income tax u/s 4:
•
•
•
•
•
•
Income tax shall be charged,
At the rates laid down by the finance act,
For that assessment year,
In respect of the total income,
Of the previous year,
Of every person.
Residential status u/s 6
• Tax liability is based on the residential
status of a person.
• Citizenship is NOT the main criteria for
tax purposes and is different from
residential status
• Residential status may change from year
to year depending upon the stay in India.
Kinds of Residential status:
All Assesses
Resident
Non-resident
Individual & HUF
R & OR
R but not OR
Conditions for determining residential status for an individual sec 6(1)
BASIC
ADDITIONAL
Stay in India
Stay in India for
for
at least 60*
At least
days in current
182 days OR PY.
AND
&
in Current PY
Stay in India
09-10
for at least
365 days in 4
PY preceding
(A)
current PY.
(B)
* exceptions:
a) A citizen of India/crew of Indian Ship leaving India for
Employment or self-employment OR b) A citizen of
India or a persons of Indian origin comes to a visit in India
REPLACE 60 by 182 days
Stay in India
for 730 days
in 7 PY
preceding &
the current
PY 09-10
Resident in India
for 2# out of 10
PY preceding
current PY
(D)
(C)
If {a or b}+ {c & d} satisfied: ROR
If only a or b satisfied: RNOR
If a or b NOT satisfied: Non-resident
Counting of days
•
•
•
•
a) the stay need be in the same place
b) the stay need not be continuous
c) the days of entry and exit are both counted
d) a stay in a boat in territorial waters of India is treated as
stay in India
• e) For February, where applicable 29 days are considered.
E.g. Mr. George Bush comes for the first time to India on 26.1.201009
and leaves India on 15.3.2010. Determine his residential status for AY
2010-11
Solution:
Mr. George Bush
Foreign Citizen
PY 2009-10
AY 2010-11
Days in India in P.Y. 2009-10
Jan : 6 days
Feb: 28 days
Mar: 15 days
Total: 49 days
He does not satisfy any of the conditions.
Therefore he is Non resident.
Conditions for determining residential status
BASIC
ADDITIONAL
Stay in India
Stay in India for
for
at least 60 days
At least
in current PY.
182 days OR
AND
&
in Current PY
Stay in India
05-06
for at least
365 days in 4
PY preceding
(A)
current PY.
(B)
Stay in India
for 730 days
in 7 PY
preceding &
the current
PY 05-06
Resident in India
for 9 out of 10 PY
preceding current
PY
(D)
(C)
If {a or b}+ {c & d} satisfied: ROR
If only a or b satisfied: RNOR
If a or b NOT satisfied: Non-resident
Class exercises
• (1) Mr. Sanjay, an Indian citizen went to USA for the
first time for the purpose of employment on 10th
May, 2009. He came back to India on 19th November,
2009. Determine his residential status for
Assessment year 2010-11.
•
• Ans: Non resident
• No. of days in India – 173(30+10+12+31+31+28+31)
• Employment so replace 60 by 182
Class exercise 2:
• Ishant sharma, an Indian cricketer submits the
following information of stay outside India for the
year ending 31.3.2010
Days
12.4.09 to 27.4.09
2.5.09 to 8.7.09
26.8.09 to 9.9.09
10.9.09 to 1.10.09
3.1.10 to 25.3.10
place
Sharjah for Asia cup 2009
Summer tour to england
triangular series in Sri lanka
singapore on tour
summer cricket tour to south africa
He made his debut in international cricket on 10th march, 2007. Then in
a match against the West Indies, he suffered a major injury needing two years
of hospitalization in USA. He recovered and returned back to India on 28.3.2009.
Thereafter, he was employed by China Cricket board as Manager of the team.
Determine his residential status For A.Y. 2010-11.
Solution
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Total no. of days in PY 09-10
Less: stay out of India:
12.4 to 27.4
16
2.5 to 8.7
68
26.8 to 9.9
15
10.9 to 1.10
22
3.1 to 25.3
Therefore, stay in India = 365-203 =
365
82
203
162
• He has not stayed in India for 182 days from employment
condition, therefore he is Non-resident.
Class exercise
• Mr. Bond an Indian citizen leaves India for
honeymoon with his wife for the first time on
18.2.2010. Determine his residential status?
• Mr. Khiladi an Indian citizen leaves India for
employment purposes for the first time on
18.2.2010. Determine his residential status?
Residential Status for a Company
• Depends on the management and control of
affaires, i.e. where is the majority decision
making taking place. Irrespective of the type
of company.
• For HUF – the residential status of Karta is
considered as residential status of HUF.
• Assignment sums:
• Please see hand out.
Scope of total income: Section 5
Nature of Income
ROR
RNOR
NR
Income received in India
Taxable Taxable
Taxable
Income accruing in India
Taxable Taxable
Taxable
Taxable Taxable
Not-Taxable
Foreign Income:
a)
From business /
profession controlled or
set up IN India
b) From business/profession
controlled or set up
OUTSIDE in India
Taxable Not Taxable Not-Taxable
E.g.:
Items of Income
Nature
ROR
RNOR
NR
Salary received in India
Received in
India
T
T
T
Salary earned in India but
received in Sri Lanka
Accruing in
India
T
T
T
Income from business in
Nepal controlled form
Delhi
Foreign Income
controlled
from India
T
T
NT
Income from business in
Sri Lanka received
there.
Foreign Income
NOT
controlled
from India
T
NT
NT
Foreign Income:
T- Taxable
NT - Not Taxable
Mr. Tom, a British citizen had the following income during the
year ended on 31st March,2010
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
1. Income from house property in India
15000
2. Income from property in Rome
10000
3. Interest from bank account in India
1200
4. Income from business in Bangladesh, being controlled from
India
16000
5. Interest on Bank account in USA
11000
6. Salary earned and received in Tokyo
12000
7. Income earned and received in London
13000
8. Dividend from British company received in India
17000
• Compute his total income for AY 2010-11 in 3 different cases:
• A) ROR, b) RNOR and C) NR.
NON- TAXABLE INCOMES: (EXEMPTIONS) Section 10
• Section 10 (1) -
Agricultural Incomes from land
situated in India
• Section 10 (2) -
Sums received by a member of the
HUF from a Family income
• Section 10 (2A) -
Share of partner in profits out of the
partnership firm
• Section 10 (16) -
Scholarships granted to meet the
cost of education – like tuition fees.
• Section 10 (32) -
Minors income upto Rs.1500 per
child.
Heads of Income
•Income from Salaries
•Income from House property
•Income from profits and Gains
of business or profession
•Income from capital gains
•Income from other sources
Computation of Total Income
PY 09-10
AY 10-11
Particulars
Rs.
Income from Salaries
XX
Income from House property
XX
Income from P & G of Business or profession
XX
Income from capital gains (short term)
XX
Income from Other sources
XX
Rs.
X
Add: Clubbed incomes
X
GROSS total Income
XX
Less: deductions u/s 80
- X
Net taxable income
YY
Add: Long term capital gains
GG
Net taxable income
MM
Computation of Final tax payable :
Net taxable income
YY
Rates of tax (10 % 20% 30%) or as relevant
----------
Net tax payable
1
Add: Surcharge (tax on tax)
2
Tax payable
[1+2]
3
Add: {education cess 3%}
[1 x 3 %]
4
FINAL tax payable
Less: Tax already paid (T.D.S. / Advance tax)
Assessed tax payable/refund
5
[5-6]
6
7
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Income tax slab for ay 10-11
Income Tax Slabs for ay 10-11 for Resident Senior Citizens
(FY 2009-10)
S. No. Income Range
Tax percentage
1 Up to Rs 2,40,000
No tax / exempt
2 2,40,001 to 3,00,000
10%
3 3,00,001 to 5,00,000
20%
4 Above 5,00,000
30%
•
•
•
•
•
Income Tax Slabs for ay 10-11 for Resident Women (below 65 years) (FY 2009-10)
1 Up to Rs 1,90,000 No tax / exempt
2 1,90,001 to 3,00,000
10%
3 3,00,001 to 5,00,00
20%
4 Above 5,00,000
30%
•
•
•
•
•
Income Tax Slabs for ay 10-11 Others & Men (FY 2009-10)
1 Up to Rs 1,60,000
No tax / exempt
2 1,60,001 to 3,00,000
10%
3 3,00,001 to 5,00,000
20%
4 Above 5,00,000
30%
• Levy of surcharge has been withdrawn for personal
income tax payers
• “Education Cess on Income-tax” and “Secondary and
Higher Education Cess on income-tax” shall continue
to be levied at the rate of two per cent and one per
cent respectively of income-tax.
For the next class….
• Assignment 1 to be submitted – Residential
status and Scope of total income
• Presentation:
• A) Group formation
• B) List of topics next slide
•
Session no. Group no.
2 G1
3 G2
4 G3
5 G4
6 G5
7 G6
8 G7
9 G8
10 G9
11 G10
Topic
MVAT
What is Vat, Procedure, set off, state VAT, CENVAT, rates, 2 sums
Mvat - turnover tax, tax invoices, registration procedure, payment, 2 sums
MVAT, Incidence of tax, dealers liable to tax, Filing of returns and forms, challans.
Cenvat act , definitions, duties eligible, when and how much to take credit, cenvat credit
rules , exempted goods, documents and forms, procedure, 2 sums
Central excise act, definitions, duties specified under the schedule, valuation , 2 sums
Registration process, forms, challans, procedure, remission of duty, interest and penalty
Section 10 and 11 of the income tax act and 2 sums
Section 44 to Sec 44 AE
List of wards, departments in Mumbai, challans, forms, itr forms, tds forms, challans,
Pan card and TAN card procedure, sec 234 a , b, c , 3 sums
Corporate style Presentation guidelines:
a) Max 25 minutes, warning bell at 24 min, wind up in last minute
b) 6 members in a group
c) 12 slides, 1 -topics n members, 12th - references
d) only 9 bullet points
e) each bullet point - max 15 words
f) pre approval of ppt compulsory, 2 days prior to presentation
g) akshaydamani@gmail.com, 9969772252
h) no sounds but use customer animations and pictures
To do….
Income tax is the price
one pays for
Civilization……..