A Historical Perspective of Human Interaction With Karst
advertisement

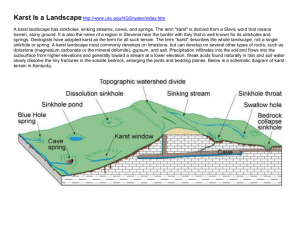
Monica Mustain From groundwater encyclopedia: “Refers to lands primarily underlain by limestone and dolomite where surface water is integrally connected to the ground water system from preferential flow routes.” Roughly 15-20% of Earth has karst land surfaces Water from karst terrain supports upwards of 25% of the current world population (Ford and Williams, 2007) A map of karst terrain in the United States ( from USGS) Caveman Ancient China Mayan Civilization Jerusalem Caves are a feature of karst terrain Caves were used for water, dwelling, and shelter Some of the cave drawings date back 40,000 years ago (Seiveking, 1997) Chinese were some of the first to study and record about karst hydrogeology Early recordings started before the Qin and Han Dynasties, 221 BC- 220 AD Karst was targeted for studies because of its water properties Water would be redirected to irrigate crops and for use in water mills “ There is much water and many caves in the south mountain, the water flows into the cave in the spring and out of the cave in the summer and stops in the winter.” Mountain Scripture (between 475 BC-8 AD) from LaMoreaux, 1999 SE China karst topography Guilin (top) and Yunnan (right) Mayan population expanded over Belize, Guatemala, southern Mexico and western Honduras Some evidence for Mayans mining clays and minerals from karst caves (Stone, 1997) Heavily relied on water from karst caves as their primary source of water A major engineering project was undertaken: the Siloam Tunnel Tunnel would carry water over 530 meters through Jerusalem Thought to have been built on already existing fractures Tunnel is fed by the Gihon Spring Siloam Tunnel was estimated to have been built on existing fractures and these fractures were widened by quarrying Figure from Sneh et. al. 2010 Agricultural Industries Mining and extracting industries Direct pumping of groundwater Karst is highly vulnerable to contamination because • Transport water several orders of magnitude greater than nonkarst systems • There is minimal absorption or other natural cleaning processes • To large to provide effective filtration of pathogens • In areas of localized recharge, surface water is directly linked to groundwater Deforestation and clearing of land Pollutants from pesticides and fertilizers Irrigation and drainage A study in Turkey showed that a limestone quarry was acting as a direct sinkhole for contaminants to flow into groundwater (Ekmekci 1991) Some mining operations want to work below the saturated zone; this can cause failures of springs, changes in the direction of water flow, and increased potential for direct contamination from oil or sediments When large volumes of water are pumped from karst aquifers, a greater number of sinkholes will appear in the pumped area A study in china looked at different variables for the formation of sinkholes Results showed that pumping does not cause sinkholes but is a factor in their formation