Unit 4 Study Guide KEY
advertisement

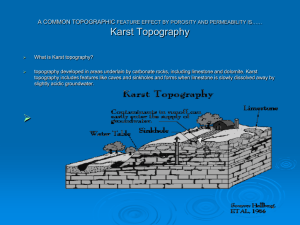
EARTH SCIENCE Unit 4 Study Guide Use this Study Guide to direct your study. Also study your Unit 4 Stapled Packet which should include your notes, FRAMES, practice sheets, foldable and diagrams. Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition When limestone rock responds with carbonic acid (weak), what kind of weathering is it? Chemical What are some common signs of erosion and deposition? Ripple marks and mud cracks What substance plays the most important part in chemical weathering? Water What are the two types of weathering? Chemical & Mechanical/Physical What are the four agents of erosion? Water, wind, ice, and gravity Which horizon of the Soil Profile has the most biological activity? Top or A Horizon What is the organic matter in soil made from? Decayed plants and animals Define Mechanical Weathering: Breakdown of rocks & minerals into smaller particles without change in composition. Which mountains are older? Rocky Mountains or the Appalachian Mountains? Appalachian Label the horizons of a Soil Profile diagram: Groundwater & Karst Topography Define Karst Topography: Weak carbonic acid from carbon dioxide mixes with freshwater, dissolving limestone which creates spaces in the rock. This leads to caverns/caves, sinkholes, natural bridges What is the equation for creating Karst Topography? Limestone + Slightly acidic groundwater = Karst Topography What features are typically associated with karst topography? Limestone caves, sinkholes, disappearing rivers How are sinkholes and caves formed? Karst topography caused by weak acid dissolving limestone rock What are the steps (in order) of the Water Cycle aka Hydrologic Cycle? Label the features of Karst Topography: Label the features of a Groundwater System: What happens if there are three water wells in an area and three more wells are added? The water table will sink. Define impermeable: NOT allowing liquid to pass through Define permeable: Allowing liquid to pass through Define porosity: Has holes or pores so liquid can pass through it Surface Water What happens to a rock that has been at the bottom of a riverbed a long time? The edges round off from abrasion against the bottom and against other rocks Define watershed: Land area that drains a particular set of streams and rivers Label the watersheds in Virginia and know what cities are in each: What rivers are part of the Chesapeake Watershed? Label the order of river development: Label the layers of soil deposited in a lake bed: What are the sources for fresh water? Define tributaries: Smaller streams and rivers that feed into a larger river. Why can activity in Maryland and Pennsylvania affect water quality in the Chesapeake Bay? Mapping Latitude runs E/W and divides the earth in N & S, and can be no higher than 90 degrees. Zero degrees latitude is called Equator. Longitude runs N/S and divides the earth in W & E, and can be no higher than 180 degrees. Zero degrees longitude is called the Prime Meridian, and the International Date Line is 180 degrees longitude. N/S goes first, and E/W goes second when writing the coordinates for a point on earth. Natural Resources What are the environmental benefits of using renewable resources? Less drilling or mining, fewer greenhouse gases in atmosphere, few pollutants in the air What resource mined in Virginia is used for building? Limestone for cement What are the coordinates for Richmond, Virginia? 38 degrees N, 75 degrees W What is the main disadvantage of using nuclear power for energy? Long half-life of its waste products What is one largely untapped renewable energy source in Virginia? Tidal