Hazardous-waste
advertisement
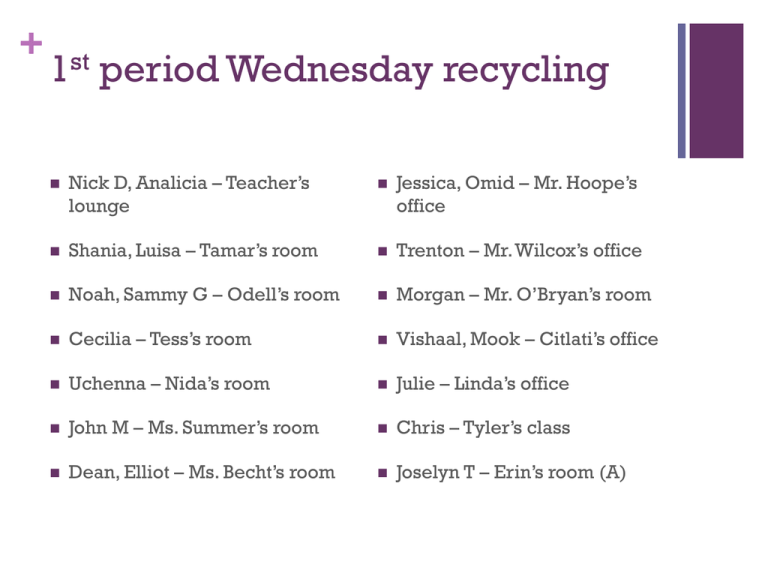
+ 1st period Wednesday recycling Nick D, Analicia – Teacher’s lounge Jessica, Omid – Mr. Hoope’s office Shania, Luisa – Tamar’s room Trenton – Mr. Wilcox’s office Noah, Sammy G – Odell’s room Morgan – Mr. O’Bryan’s room Cecilia – Tess’s room Vishaal, Mook – Citlati’s office Uchenna – Nida’s room Julie – Linda’s office John M – Ms. Summer’s room Chris – Tyler’s class Dean, Elliot – Ms. Becht’s room Joselyn T – Erin’s room (A) + 2nd period Wednesday Recycling Jessica, Omid – Mr. Hoope’s office Trenton – Mr. Wilcox’s office Morgan – Mr. O’Bryan’s room Vishaal, Mook – Citlati’s office Julie – Linda’s office Chris – Tyler’s class Joselyn T – Erin’s room (B) + Hazardous Waste and Sanitary Landfills 9/2/11 + What is an open dump landfill? Open dump landfills are uncovered piles of solid waste. They are more common in undeveloped countries. + What are Sanitary Landfills? Solid wastes are spread into thin layers, compacted and covered daily with fresh clay or plastic foam to prevent leachate. + What are the Pros and Cons of Sanitary Landfill? pros Low operating Costs Can Handle Large amounts of waste. Filled Land can be used for other purposes. There limited landfill space in many areas. cons Noise, traffic, dust Greenhouse gases Output approach that encourages waste reduction Leachate – groundwater contamination + What is incineration? Burning trash + What are the pros and cons of Incineration? pros Reduces volume trash Produces energy Concentrates hazardous substances for burial Sale cost of E reduces cons Expensive Produces hazardous waste Emits air pollutants Encourages production waste + What is hazardous waste? Any substance that is: Flammable Reactive Toxic Corrosive + How can we detoxify hazardous waste? Physical methods Chemical methods Nanomagnets Biological – bioremediation and phytoremediation Plasma Arch torch + What are the physical methods for detoxifying hazardous waste? Charcoal Distilling resins to filter solids liquid wastes to separate out harmful chemicals + What are chemical methods to detoxify hazardous waste? Chemical reactions (i.e. neutralization) to convert hazardous chemicals to less harmful chemicals. + What are nanomagnets? Magnetic particles coated with compounds to remove various pollutants from water. + What is bioremediation? Use of biological agents, such as bacteria or enzymes to destroy toxins or convert them to less hazardous waste. + What is Phytoremediation? The use of naturally or genetically engineered plants to absorb, filter or remove contaminates from soil and water. + What does a plasma arch torch do? Breaks down hazardous waste at very high temperatures. + How can we store hazardous waste? Deep well disposal Surface Above impoundments ground storage facilities + What is deep well disposal? Hazardous wastes are pumped through a pipe full of dry, porous rock, where they soak into the rocks. + What are the pros and cons of deep well disposal of Haz. Waste? pros Safe at certain sites Wastes can often be retrieved Low cost cons Leaks from corrosion of well casing Emits air pollutants Encourages production waste + What are surface impoundments? Lined ponds, pits or lagoons in which liquid hazardous wastes are stored. + What are the pros and cons of surface impoundments? pros Low Costs Waste can often be retrieved Can store wastes indefinitely with secure double liners cons Groundwater contamination from leakage liners and overflow Air pollution from volatile organic compounds Encourages production waste + FRQ check Annual precipitation at a landfill in the town of fremont is 100 mm per year, and 50 percent of this water runs off the landfill without infiltrating the surface. The landfill has a surface of 5,000 m2 . Underneath the landfill, the town installed a leachate collection system that is 80 percent effective. Any leachate not collected by the system enters the surrounding soil and ground water. This leachate contains cadmium and other toxic materials. Calculate the volume of water in cubic meters (m3) that infiltrates the landfill per year. + 100 0.1 mm/year = 0.1 m/year m/year x 5,000 m2 x 50% = 250 m3 So the volume of leachate in a m3 that is treated per year is 250 m3 x 80% = 200 m 3 + Presentation Requirements 1) Everyone in the groups speaks 2) Name, Chemical structure of pollutant(s) and characteristics 3) Why is it “Hazardous”? 4)Summary 5) of Case Study Recommended management plan 6) Visual (ppt or poster)