Unit 5: Russia and the Republics Physical Geography Landforms
advertisement

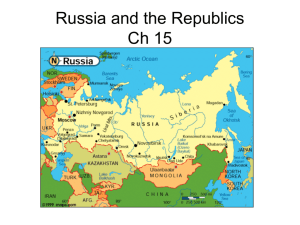
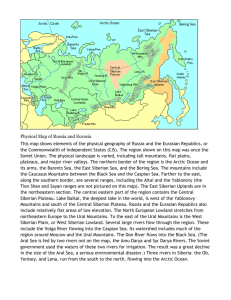
Unit 5: Russia and the Republics Physical Geography Landforms and Resources Northern Landforms • This region can be broken down into 4 areas: – Northern European Plain – West Siberian Plain – Central Siberian Plateau – Russian Far East Northern Landforms • Northern European Plain – Lowland area – 1,000 miles from western border to Ural Mountains – Chernozem-“black earth”, very fertile soil – Lots of agriculture in this area – 290 million people inhabit this land – Big Cities: Moscow, St. Petersburg, Kiev (Ukraine) Northern Landforms • West Siberian Plain – Ural Mountains and Yenisey River – Because this area is tilted northward, rivers flow toward Arctic Ocean • Eurasia?? Northern Landforms • Central Siberian Plateau and Russian Far East – Central Siberian: • Plateaus: 1,000-2,000 feet are common • Yenisey and Lena Rivers – Russian Far East • Volcanic ranges • Kamchatka Peninsula (120 volcanoes, 20 actives) • Sakhalin and Kuril islands Southern Landforms • Caucasus and Other Mountains – Black and Caspian seas – Border between Russia and Transcaucasia • Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia – Tian Shan is part of a huge mountainous region farther east – Central Asia-Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan • Ranges in this area are so high, stops moist air from reaching the areas beyond the mountains Southern Landforms • Turan Plain – lowland – Caspian Sea to mountains and uplands of Central Asia – Syr Darya and Amu Darya are the 2 major rivers of the area – Kara Kum and Kyzyl Kum plains Rivers and Lakes • Drainage Basins and Rivers – Drainage Basins-area drained by a major river and tributaries • Arctic Ocean, Caspian Sea, Pacific Ocean, Baltic Sea, Black Sea, Aral Sea basins – Arctic basin is the larges • Rivers: Ob, Yenisey, Lena drain 3 million sq. mi. Rivers and Lakes • Lakes – Caspian and Aral Seas • Both are saltwater lakes • Caspian is largest inland sea in the world • Aral has lost about 80% of its water volume since the 1960s due to irrigation – Lake Baikal • • • • Deepest lake in the world Mile depth, 400 miles long 20% of Earth’s freshwater Thousands of plants and animals live in the lake – Only species of freshwater seal lives here Regional Resources • Issues with managing the many resources of this region – Corruption – Environmental issues • Coal, iron ore, other metals • Oil and natural gas • Timber • Hydroelectric power Regional Resources • Harsh climates, difficult terrain, and large distances make management unstable • Many resources are located in Siberia • Mining, oil, natural gas production has caused severe damage to the environment • Dams and thermal pollution have damaged plant and animal habitats Climate and Vegetation Varying Climates • Major Climate Regions – Humid continental and subarctic dominate the area – High latitude and impact of mountains – Because the land is so large, sea/ocean influence doesn’t impact the majority of the region • Continentality Varying Climates • Distance from sea can impact precipitation and temperature • Siberia: highs of 50 degrees, lows of -90 degrees – Weather impacts life Varying Climates • Warmer climates do exist: southeastern areas – Semiarid and desert • Transcaucasia: moist air from Mediterranean Sea created a subtropical climate zone. – Before ethnic cleansing issues, resorts here were a popular tourist destination Vegetation Regions • Tundra – Mosses – Lichens – Low shrubs • Forest – Taiga-largest forest on earth, contains mostly coniferous trees – Animals: fox, vermin, bear, elk, wolves Vegetation Regions • Steppe – Grassland – Southern Ukraine through northern Kazakhstan – Fertile soil: grain • Desert – Plains of west and central areas of Central Asia – Kara Kum and Kyzyl Kum Human-Environment Interaction Shrinking Aral Sea • Gets most of its water from Amu Darya and Syr Darya • Irrigation projects took water out of these rivers and towards agriculture – Sea is beginning to evaporate • Effects of Agriculture – Pesticides and fertilizers on cotton farms were picked up by runoff and brought into streams/rivers – Killing much plant and animal life in the area – Diseases for people: cancer, respiratory issues, dysentery, typhoid, hepatitis “Wild East” • Traveling through Siberia was dangerous and slow during the 19th century • Trans-Siberian RR-linked Moscow to Pacific port of Vladivostok “Wild East” • Trans-Siberian RR – 5,700 mi long – 7 time zones – 1891-1903 – 70,000 workers – 77 million cubic feet of land, 100,000 acres of forest cleared