Permeable Pavements - Ed Mattheissen
advertisement

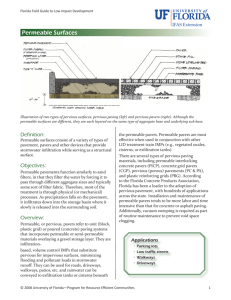
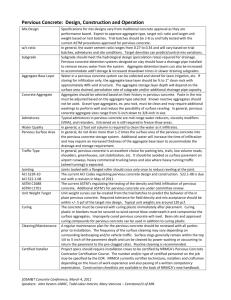
Permeable Pavements Shingle Creek Watershed Management Commission May 31, 2011 Outline Purpose of presentation Types of pavements and applications Benefits Design considerations Maintenance considerations Example projects Questions Types of Permeable Pavements Porous Asphalt Pervious Concrete Pervious Pavers Permeable pavement has pores or openings that allow water to pass through the surface and stone base material and infiltrate into the underlying soils. Porous Asphalt Pervious Pavers Pervious Concrete Pervious Pavement Hydrology Porous HMA (or Dense HMA with Piping) John Barten, second from right, riding on pervious pavement in Medina around 1905. Water Storage in Pervious Concrete System Porous Asphalt Section Pervious Concrete Paver Project Applications Streets Parking lots Sidewalks and paths Driveways Patios Playgrounds Potential Benefits Reduces the rate and quantity of stormwater runoff Reduces stress on the sewer system Recharges groundwater Filters out silt, pollutants, and debris Maintains natural drainage paths Reduces standing water nuisance Potential Benefits Reduces stormwater infrastructure needs (pipes, ponds, catch basins) Offers good alternative to conventional stormwater mitigation Better erosion control Reduces ice buildup and need for salting during the winter Provides better traction Design Considerations Soils Depth to groundwater Traffic loading Slopes Blowing dust and debris Design Considerations Unique site features Agency stormwater regulations Frost penetration Permeable Pavement Limitations Use of permeable pavement is not recommended in the following cases: Industrial “brownfield sites or sites with contaminated soils Where site layouts direct clogging sediment on the pavement surface Sites with excessively steep grades Maintenance Considerations Protect pavement from silt and sediment during and after construction Vacuum sweep at least twice a year Do not seal coat Do not sand Use caution when snowplowing Post signs advising maintenance crews Maintenance Considerations Perform periodic inspections; look for clogging, raveling, cracking, and wear Other??? Ongoing Maintenance Vacuum Sweeping Sweepings Maintenance Warning Signs Paired Intersection Study, Robbinsdale, MN Porous asphalt test section - Abbott/41st , 2009 Porous Subgrade Preparation Porous Asphalt Placement Cost Test section = 150 feet long, 27 feet wide Traditional pavement, contract unit prices = $14,125 =$32/SY Porous pavement – Site 1 = $42,670 – Site 2 = $32,200 “Upcost” = $35-50/SY Residential Street Paving Project, Shoreview, MN Lake Owasso Asphalt replaced with pervious concrete, 2009 Water Infiltration Demo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j_z0xRPbExY Shoreview Water Infiltration Demo Pervious Concrete Cost Comparison Common Excavation – 11,000CY($6.00/CY) Fabric – 11,000SY($1.00/SY) 1-1/2” Crushed Rock – 5000CY($52.00/CY) 7” Pervious Concrete – 8470SY($46.50/SY) Total Cost for Pervious Concrete System Per SY Cost for Pervious Concrete System *Average depth beneath concrete = 1.75-feet = $ 66,000* = $ 11,000 = $260,000* = $394,000 = $731,000 = $ 86.30** Estimated Bituminous Road Cost Estimated Underground Infiltration Cost Total Est Cost – Bit Road & Infiltration Per SY Est Cost – Bit Road & Infiltration = $257,000 = $417,500 = $674,000 = $ 79.60** **8.5% Increased Cost for Pervious Concrete Wolner Field Parking Lot, Mound, MN Before After Asphalt replaced with pervious concrete and draintile, 2007 Pavement Cost Comparison Mound Transit Center, Mound, MN Installed pervious pavers, 2007 Subgrade preparation Little Six Casino, Prior Lake, MN Porous asphalt pavement in parking lot, 2009 Brainerd Area Porous asphalt parking lot, 2006 • You've carefully thought out all the angles. • You've done it a thousand times. • It comes naturally to you. • You know what you're doing, its what you've been trained to do your whole life. • Nothing could possibly go wrong, right ?