Water Security initiative
advertisement

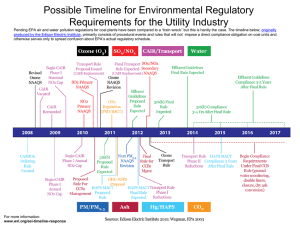
Water Security Initiative Building Laboratory Capabilities for Responding to Possible Water Contamination Elizabeth Hedrick U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Water Security Division Water Laboratory Alliance Security Summit Nashville, Tennessee March 22-23, 2012 1 Presentation Overview • Background on EPA’s Water Security Initiative • Sampling and Analysis for Water Security – Responding to Possible Water Contamination – Process for Building Laboratory Response Capabilities – Example Utility Capabilities for Water Security • Upcoming WSi-CWS S&A Products for Water Utilities 2 WSi-CWS System Architecture WSi-CWS Demonstration Pilots • Greater Cincinnati Water Works (June 2006-June 2009) • San Francisco Public Utilities Commission (July 2008 – September 2012) • New York City Department of Environmental Protection (July 2008 – September 2012) • Philadelphia Water Department (Dec 2008 – Dec 2012) • Dallas Water Utilities (Dec 2008 – Dec 2012) Responding to Possible Contamination • In the absence of information to guide the analytical investigation, laboratory analyses are performed for a wide range of contaminants of concern to water security. • Through advance planning, water utilities can identify contaminants of concern to water security, methods for analyses, and laboratory response partners. 5 Challenges Facing Utilities • What are contaminants of concern to water security? • How do I find appropriate methods? • How do I determine if acquiring a new in-house method capability for water security is sustainable in the long run? • Are there special considerations I should be aware of if I want to use my regulatory compliance lab partners? • Who are possible lab partners for contaminants such as chemical warfare agents, radionuclides, and select pathogens, and how do I engage them during planning? • When is Federal assistance available to my utility for laboratory analyses? 6 New WSi-CWS Guidance for Water Utilities Water Security Initiative: Guidance for Building Laboratory Capabilities to Respond to Drinking Water Contamination • Answers common questions utilities have regarding building laboratory capabilities for responding to a wide range of contaminants of concern to water security. • Is the first of a series of guidance documents for water utilities desiring to build field and laboratory capabilities for Contamination Warning Systems, or desiring to enhance water security practices for sampling and analysis. 7 Process for Building Laboratory Response Capabilities 8 Example Utility Response Capabilities Contaminant Class Contaminants Method Laboratory Bacillus anthracis Burkholderia spp. Francisella tularensis Yersinia pestis Variola (orthopoxvirus) LRN BT Agent Screening Protocol State LRN Lab Cryptosporidium parvum EPA 1622 Utility Biotoxins Brevitoxin a- Conotoxin Microcystin LR Tetrodotoxin SOP#53 Biotoxins and Pharma by LC-MS/MS Utility Carbamate Pesticides Aldicarb, Carbofuran, Oxamyl EPA 531.1 Commercial lab. Rodenticides Crimidine Strychnine SOP#53 Biotoxins and Pharma by LC-MS/MS Utility Heavy Metals, Mercury, Arsenic Pb, Cd, Hg, As, plus metals screen EPA 200.8 Utility Organophosphate Pesticides, PCBs Dichlorvos, Mevinphos, fenamiphos screen, PCBs (as Aroclors) EPA 525.2 Utility CWA Degradates Screen: Ethyl methylphosphonic acid , Ethyl hydrogen dimethyl-amidophosphate ASTM D7597-09 Commercial lab. Pathogens Notes Collect 100 L . Notify local health department to activate LRN lab if needed. In-house developed and validated method. In-house developed and validated method. ERLN lab for confirmation of parent CWA if positive on screen. Example Utility Response Capabilities, cont’d Contaminant Class Contaminants Method Laboratory Herbicides Paraquat EPA 549.2 Commercial lab. Cyanide Total cyanide EPA 335.4 Commercial lab Gasoline and Petroleum Products BTEX/volatiles indicative of gasoline EPA 524.2 Utility Pharmaceuticals Colchicine Digoxin Plus illicit drug screen SOP#53 Biotoxins and Pharma by LCMS/MS Utility Radionuclides Gross Alpha/Beta Screen: Uranium -238 Strontium -90 EPA OO-02/900.0 State Health Lab Radionuclides Gamma Emitters Cesium-137 EPA 901.1 State Health Lab Notes Utility performs free CN analysis in field. In-house developed and validated method. Utility performs beta/gamma screen in the field. • In response to possible contamination, all labs are notified and readied. • Samples are collected for all methods outlined above. • If the investigation can not be closed, all samples are analyzed. 10 Upcoming WSi-CWS S&A Products for Water Utilities Guidance • Building Laboratory Capabilities to Respond to Water Contamination • Baseline Monitoring of Field and Laboratory Methods • Development of Effective Procedures for Incident Response Sampling and Analysis Training • Hazard Awareness and Safe Work Practices for Responding to Possible Water Contamination • Hazard Assessment Tools for Water Utilities Journal Articles • S&A for Select Pathogen Analysis – A Water Utility Case Study • Partnering With HazMat – WSi Pilot Utility Perspectives and Lessons Learned 11 Contact Information Elizabeth Hedrick U.S. EPA 513-569-7296 Hedrick.elizabeth@epa.gov 12 Questions 13