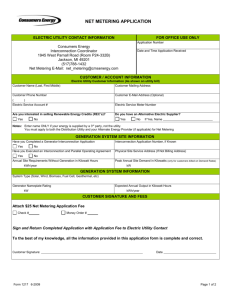
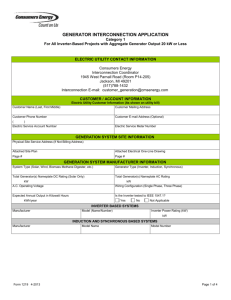
Utility Interconnection Package
advertisement
Closed Transition ATS’s John J. Stark Marketing Services Coordinator, Russelectric Inc. Why Operate in Parallel with the Utility? • Closed Transition Transfer of non-utility generator, re-transfer and generator test • Cogeneration • Peak Shaving • Curtailable Rate Structure • Distributed Generation Types of Operational Modes • Open Transition • Closed Transition First let’s talk about open transition mode An open transition mode of operation is a method of transferring a load between two sources with an interruption of power during transfer. Open transition ATS N N LL M1 M2 Motor #1 drives the normal source contacts Open. This is all done with verysource reliable The load is disconnected mechanical for an interlocking and adjustable does not require period to allow an elaborate regenerative electrical power to decay interlocking design. Motor #2 then drives the emergency source contacts closed Closed Transition Mode A closed transition mode of operation is a method of either: 1) Transferring a facility’s load between the utility and generator or 2) operating a generator in continuous parallel with the utility service, without an interruption of service. Utility Concerns • Reliability and quality of utility power to other customers • Safety and protection of utility service personnel • Protection of utility equipment Type of Parallel Operation • Passive Momentary utility parallel operation – 100ms or less Closed transition ATS Operator #1 drives the normal source contacts open N S1 S2 Closed Transition Operation L The load source is connected to both sources momentarily Operator #2 drives the emergency source contacts closed Closed Transition Transfer Switches Advantages •No interruption of power for load test and return to utility as well as peak shave operation •Fast transfer operation Closed Transition Transfer Switches Disadvantages •No phase lock synchronizing •No Protective relays •No mechanical interlock, thus no safe manual operation •Lacks true load test function •Higher fault current requirements Sophisticated Controls and Safety Features Full 3-Phase over and under voltage and frequency sensing on both normal and emergency sources. Protection against running over 100 msecs: Signals to operators Fail to Transfer Function Provides trip signals to the generator or utility breakers.