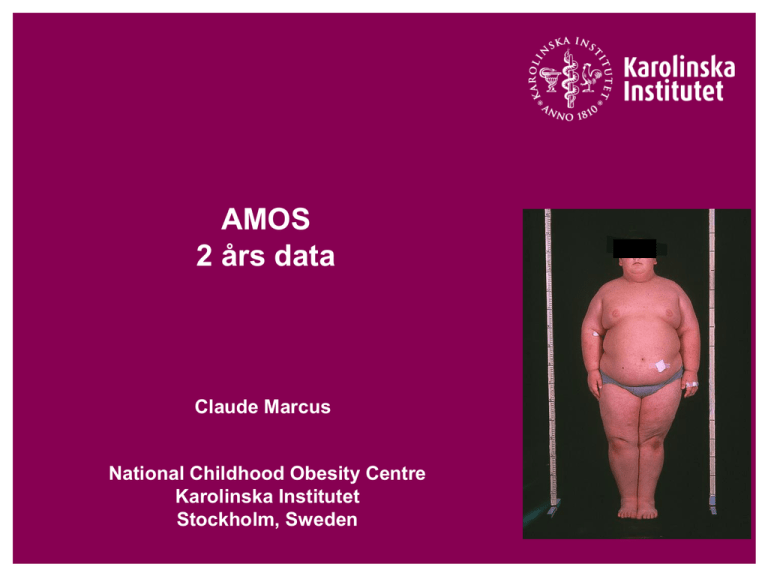
AMOS
2 års data
Claude Marcus
National Childhood Obesity Centre
Karolinska Institutet
Stockholm, Sweden
Varför överväga läkemedel och kirurgi:
Shorter life:
Morbid obesity at the age of 20-30
results in a 13 y reduced life expectancy
= 22% reduction of expected remaining
life time
(Fontaine, KR JAMA 2003)
Claude Marcus, 2011
Why adolescent obesity surgery:
Poor outcome of behavioral obesity
treatment in adolescents
Why adolescent obesity surgery:
We have no treatment
with acceptable
efficacy to offer
severely obese
adolescents today
AMOS study :
( Adolescent Morbidity Obesity Surgery study)
• started 2006 in Sweden, all subjects through
surgery April 2009
• Prospective non-randomized study
• Controls: conventionally treated obese
adolescents and GB operated obese adults
• Multicenter study, Stockholm, Göteborg,
Malmö
• Follow up visit at 1, 2, 5 and 10 years post
surgery
• Inclusion criteria: BMI > 40 or 35 with comorbidities Age: 13-18 yr
• Exclusion criteria severe depression, mental
retardation, obesity syndromes, drug abuse,
severe eating disorder
Stockholm
Göteborg
Malmö
AMOS study flow-chart
Enrollment
Allocation
Intervention
Assessed for
eligibility
Allocated to
intervention
gastric bypass
(n=97)
(n=82)
(n=81)
Excluded (n =15)
•Not meeting inclusion crit. (n=0)
•Decline to participate (n=15)
•Other reasons (n=0)
Excluded (n =1)
•Other reasons (n=1) ,
Change his mind on the day
of surgery (01-35)
1 year
(n=81)
Follow-Up
2 year
(n=81)
5 year
Age at surgery
•n=81 mean 16.9 SD 1.20 range 13.8 – 19.0 yr
25
20
15
10
5
0
13år
14år
15år
16år
17år
18år
19år
Gastric bypass study for adolescents in Sweden,
the AMOS study
Why not adjustable gastric banding?
Previous study:
8 subjects, 15-17y
One year follow-up:
5 severe complications
2 had >10kg weight loss
The study was terminated!
Paul E O’Brien et al JAMA 2010
84% of gastric banding subjects lost > 50% of excess
body weight
Claude Marcus
Paul E O’Brien et al JAMA 2010
84% of gastric banding subjects lost > 50% of excess
body weight
Different populations with different comorbidity
patterns and psychosocial background
Claude Marcus
Psychosocial background in th AMOS study
(preliminary data)
prevalence
Ongoing or previous contact with child psychiatric team
50%
Defined psychiatric disorder (ADHD, depression, anxiety) 40%
Use of psychoactive drugs (present or previous)
20%
Very poor school performance (truancy, leaving school
without diplomas etc)
60%
Claude Marcus
Weight change from inclusion to one year after surgery
*
kg
Negative side effects
Reoperation due to internal hernia
Unwanted pregnancies
Decreased self-esteem
Suicidal attempts
Eating disorder
Drug abuse
Gall bladder surgery
Low vitamine levels despite substitution
Claude Marcus 2011
5
2
5
2
2
2
7
55
Two year results of Swedish GB study in 81
obese adolescents – the AMOS study
48
46
44
Cell Mean
42
40
Adol contr
Adol surg
Adults surg
38
36
34
32
30
28
BMI0
BMIår
BMI2år
1
2
3
AMOS: Weight change (kg) during the second year
after surgery
AMOS: Weight change (kg) during the second year
after surgery
Weight gainers vs loosers year two:
•Mean insulin levels higher among
gainers
•No other differences in
cardiometabolic risk markers
Fig #. BMI by sex.
50
40
30
20
0
Men, Surgery
Men, Control
Women, Surgery
Women, Control
1
Follow-up time, years
2
Fig 3 Mean (95% CI) for major biochemical data ( a) insulin, glucos HbA1C, b) Triglycerides, LDL, HDL, c) high
sensitive CRP, leukocytes and d) blood pressure in 81 adolescents operated with GBP at baseline, 1 and 2 years
follow up
a)
40
insulin
35
***
c)
6
glucos
HbA1C
8
*
5
Lpk
***
Hs CRP
***
7
***
30
4
25
9
6
5
3
20
4
15
2
10
3
0
2
1
5
1
0
b)
3
triglycerides
LDL
HDL
***
d)
systolic bp
***
diastolic bp
120
2,5
100
2
1,5
***
***
***
80
***
60
1
40
,5
20
bl 1yr 2yr
0
bl 1yr 2yr
bl 1yr 2yr
bl 1yr 2yr
bl 1yr 2yr
SF-36 QoL in 81 sdolescents after gastric bypass
.
100
PF
RP
BP
GH
VT
SF
RE
MH
Mean SF-36 Score
80
60
40
20
Estimated postsurgery values are expected means from the linear mixed-effects models; a score of 0 represents worst possible health and 100 represents best possible health. PF = physical
functioning; RP = role limitations due to physical health problems; BP = bodily pain; GH = generl health perceptions; VT = vitality; SF = social functioning; RE = role limitations due to
emotional problems; MH = general menthal health; SF-36 = Short Form-36 Health Survey;
Plastikkirurgi ofta
nödvändig för en rimlig
livskvalitet för en 16
åring som operererats
med gastric bypass
Men varför fungerar det?
Liten magsäck
Maten direkt till jejunum
Kraftig GLP-1 stegring
Bättre val av födoämnen
..och varför inte:
Enbart hindrande
Ingen mättnadskänsla
Ökar småätandet
Vad händer nu?
För tidigt att avgöra om gastric bypass ska användas för
ungdomar generellt!
All obesitaskirurgi före 18 års ålder i Sverige ska göras i
longitudinella studier
Ungdomar före 18 års ålder ska följas upp i minst två år på
specialistenhet med erfarenhet av fetmakirurgi bland ungdomar
Etisk ansökan
SLUT!