Chapter 10: Human Development Across the Life Span

Chapter 10: Human
Development Across the
Life Span
Development
• Physical, behavioral, cognitive, and personality changes or lack of changes that occur throughout the lifespan.
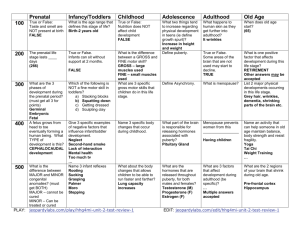
Chronological Periods
• Prenatal
• Infancy
• Preschool/Early Childhood
• School Age/Middle Childhood
• Adolescence
• Early Adulthood
• Middle Adulthood
• Late Adulthood
• Conception – Birth
• 0 to 2
• 2 to 5/6
• 6 to 12
• 12 to 20
• 20 to 40
• 40 to 65
• 65 and older
Prenatal Period
Conception - Birth
Conception
• Zygote
– One-celled organism formed by the union of the sperm and the egg.
– Usually occurs in fallopian tubes.
Female Reproductive Organs
Fertilization
1 5 14 28
• Egg is viable for
24 hours
• Sperm is viable for
3 to 5 days
• “Unsafe period” is from day 9 to 15 if ovulation occurs on day 14 day 7 to 17 could be unsafe
• 3 phases
Progress Before Birth:
Prenatal Development
– Germinal stage = Conception to 2 weeks
• Conception
• Implantation
• Formation of placenta
Fertilization
1 5 14 28 1
• Many miscarriages happen at the end of the Germinal phase
• Many sexually active women of childbearing age have had a miscarriage and did not know it.
• 3 phases
Progress Before Birth:
Prenatal Development
– Embryonic stage = 2 weeks – 2 months
• Formation of vital organs and systems
• Most birth defects occur during this stage
• Sexual differentiation
• 3 phases
Progress Before Birth:
Prenatal Development
– Fetal stage = 2 months – birth
• Bodily growth continues, movement capability begins, brain cells multiply
• Age of viability – 22 to 26 weeks
• Movement can be felt
• Average weight and height
Figure 10.1 Overview of fetal development
Environmental Factors and Prenatal Development
• Maternal nutrition
– Malnutrition linked to increased risk of birth complications, neurological problems, and psychopathology
• Maternal drug use
– Tobacco, alcohol, prescription, and recreational drugs
– Fetal alcohol syndrome
Environmental Factors and Prenatal Development
• Maternal illness
– Rubella, syphilis, mumps, genital herpes,
AIDS, severe influenza
– Prenatal health care
– Prevention through guidance
Childhood
0-12 years
The Childhood Years: Motor Development
• Basic Principles
– Cephalocaudal trend – head to foot
– Proximodistal trend – center-outward
• Maturation – gradual unfolding of genetic blueprint
• Developmental norms – median age
– Cultural variations
Attachment Theories
• Behaviorism
– Food is a reinforcer
• Harlow’s Monkeys
– Contact Comfort
• Bowlby
– Biological Basis
• Current
– Bi-directional
Early Emotional Development: Attachment
• Separation anxiety
– Ainsworth (1979)
– The strange situation and patterns of attachment
• Secure
• Anxious-ambivalent
• Anxious-Avoidant
Becoming Unique: Personality Development
• Stage theories , three components
– progress through stages in order
– progress through stages related to age
– major discontinuities in development
• Erik Erikson (1963)
– Eight stages spanning the lifespan
– Psychosocial crises determining balance between opposing polarities in personality
Figure 10.6 Erikson’s stage theory
Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory
• Trust vs. Mistrust
• Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
• Initiative vs. Guilt
• Industry vs. Inferiority
• Identity vs. Confusion
• Intimacy vs. Isolation
• Generativity vs. Stagnation
• Integrity vs. Despair
The Growth of Thought:
Cognitive Development
• Jean Piaget (1920s-1980s)
– Children think different at different ages
– Basic Concepts
• Schemes
• Adaptation
– Assimilation/
– Accommodation
Figure 10.7 Piaget’s stage theory
Cognitive Development
Jean Piaget
4 stages and major milestones
• Sensorimotor
– Object permanence
• Preoperational
– Centration, Egocentrism
• Concrete Operational
– Decentration, Reversibility, Conservation
• Formal Operational
– Abstraction
Figure 10.8 Piaget’s conservation task
Evaluating Piaget’s Theory
• Criticisms
– Piaget underestimated children’s abilities
– Problems with stage theories
– Universality
• Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory
The Development of Moral Reasoning
• Kohlberg (1976)
– Reasoning as opposed to behavior
• Moral dilemmas
–Measured nature and progression of moral reasoning
– 3 levels, each with 2 sublevels
• Preconventional
• Conventional
• Postconventional
Figure 10.10 Kohlberg’s stage theory
Adolescence: Physiological Changes
• Puberty
– Secondary sex characteristics
– Primary sex characteristics
• Menarche
• Spermarche
– Maturation: early vs. late
Figure 10.12 Physical development at puberty
Adolescence: Neural Changes
• Increasing myelinization
• Changes in prefrontal cortex
The Search for Identity
• Erik Erikson (1968)
– Key challenge - forming a sense of identity
• James Marcia (1988)
– Four identity statuses
• Identity diffusion
• Identity foreclosure
• Identity moratorium
• Identity achievement
The Expanse of Adulthood
• Early Adulthood
• Middle Adulthood
• Late Adulthood