Characteristics of People with Multiple Sclerosis Associated with Mistreatment
M. Gironda, A. Nguyen, L. Mosqueda, D. Sorkin, A. Wiglesworth, S. Beach, E. Morrison
University of California, Irvine, School of Medicine – Department of Family Medicine
st
141 Annual American Public Health Association Meeting and Exposition
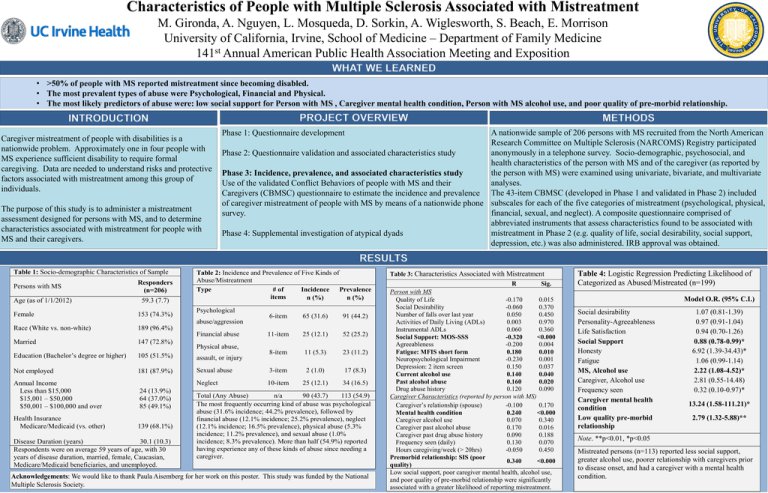
• >50% of people with MS reported mistreatment since becoming disabled.
• The most prevalent types of abuse were Psychological, Financial and Physical.
• The most likely predictors of abuse were: low social support for Person with MS , Caregiver mental health condition, Person with MS alcohol use, and poor quality of pre-morbid relationship.
Caregiver mistreatment of people with disabilities is a
nationwide problem. Approximately one in four people with
MS experience sufficient disability to require formal
caregiving. Data are needed to understand risks and protective
factors associated with mistreatment among this group of
individuals.
The purpose of this study is to administer a mistreatment
assessment designed for persons with MS, and to determine
characteristics associated with mistreatment for people with
MS and their caregivers.
Table 1: Socio-demographic Characteristics of Sample
Persons with MS
Age (as of 1/1/2012)
Female
Responders
(n=206)
59.3 (7.7)
153 (74.3%)
A nationwide sample of 206 persons with MS recruited from the North American
Research Committee on Multiple Sclerosis (NARCOMS) Registry participated
anonymously in a telephone survey. Socio-demographic, psychosocial, and
Phase 2: Questionnaire validation and associated characteristics study
health characteristics of the person with MS and of the caregiver (as reported by
the person with MS) were examined using univariate, bivariate, and multivariate
Phase 3: Incidence, prevalence, and associated characteristics study
analyses.
Use of the validated Conflict Behaviors of people with MS and their
Caregivers (CBMSC) questionnaire to estimate the incidence and prevalence The 43-item CBMSC (developed in Phase 1 and validated in Phase 2) included
of caregiver mistreatment of people with MS by means of a nationwide phone subscales for each of the five categories of mistreatment (psychological, physical,
financial, sexual, and neglect). A composite questionnaire comprised of
survey.
abbreviated instruments that assess characteristics found to be associated with
mistreatment in Phase 2 (e.g. quality of life, social desirability, social support,
Phase 4: Supplemental investigation of atypical dyads
depression, etc.) was also administered. IRB approval was obtained.
Phase 1: Questionnaire development
Table 2: Incidence and Prevalence of Five Kinds of
Abuse/Mistreatment
Type
# of
Incidence
Prevalence
items
n (%)
n (%)
Psychological
abuse/aggression
Race (White vs. non-white)
65 (31.6)
91 (44.2)
11-item
25 (12.1)
52 (25.2)
8-item
11 (5.3)
23 (11.2)
189 (96.4%)
Financial abuse
Married
6-item
147 (72.8%)
Physical abuse,
Education (Bachelor’s degree or higher)
105 (51.5%)
assault, or injury
Not employed
181 (87.9%)
Sexual abuse
3-item
2 (1.0)
17 (8.3)
Neglect
10-item
25 (12.1)
34 (16.5)
Annual Income
Less than $15,000
$15,001 – $50,000
$50,001 – $100,000 and over
Health Insurance
Medicare/Medicaid (vs. other)
24 (13.9%)
64 (37.0%)
85 (49.1%)
139 (68.1%)
Disease Duration (years)
30.1 (10.3)
Respondents were on average 59 years of age, with 30
years of disease duration, married, female, Caucasian,
Medicare/Medicaid beneficiaries, and unemployed.
Total (Any Abuse)
n/a
90 (43.7)
113 (54.9)
The most frequently occurring kind of abuse was psychological
abuse (31.6% incidence; 44.2% prevalence), followed by
financial abuse (12.1% incidence; 25.2% prevalence), neglect
(12.1% incidence; 16.5% prevalence), physical abuse (5.3%
incidence; 11.2% prevalence), and sexual abuse (1.0%
incidence; 8.3% prevalence). More than half (54.9%) reported
having experience any of these kinds of abuse since needing a
caregiver.
Acknowledgements: We would like to thank Paula Aisemberg for her work on this poster. This study was funded by the National
Multiple Sclerosis Society.
Table 3: Characteristics Associated with Mistreatment
R
Sig.
Person with MS
Quality of Life
-0.170
0.015
Social Desirability
-0.060
0.370
Number of falls over last year
0.050
0.450
Activities of Daily Living (ADLs)
0.003
0.970
Instrumental ADLs
0.060
0.360
Social Support: MOS-SSS
-0.320
<0.000
Agreeableness
-0.200
0.004
Fatigue: MFIS short form
0.180
0.010
Neuropsychological Impairment
-0.230
0.001
Depression: 2 item screen
0.150
0.037
Current alcohol use
0.140
0.040
Past alcohol abuse
0.160
0.020
Drug abuse history
0.120
0.090
Caregiver Characteristics (reported by person with MS)
Caregiver’s relationship (spouse)
-0.100
0.170
Mental health condition
0.240
<0.000
Caregiver alcohol use
0.070
0.340
Caregiver past alcohol abuse
0.170
0.016
Caregiver past drug abuse history
0.090
0.188
Frequency seen (daily)
0.130
0.070
Hours caregiving/week (> 20hrs)
-0.050
0.450
Premorbid relationship: SIS (poor
0.340
<0.000
quality)
Low social support, poor caregiver mental health, alcohol use,
and poor quality of pre-morbid relationship were significantly
associated with a greater likelihood of reporting mistreatment.
Table 4: Logistic Regression Predicting Likelihood of
Categorized as Abused/Mistreated (n=199)
Model O.R. (95% C.I.)
Social desirability
Personality-Agreeableness
Life Satisfaction
Social Support
Honesty
Fatigue
MS, Alcohol use
Caregiver, Alcohol use
Frequency seen
Caregiver mental health
condition
Low quality pre-morbid
relationship
1.07 (0.81-1.39)
0.97 (0.91-1.04)
0.94 (0.70-1.26)
0.88 (0.78-0.99)*
6.92 (1.39-34.43)*
1.06 (0.99-1.14)
2.22 (1.08-4.52)*
2.81 (0.55-14.48)
0.32 (0.10-0.97)*
13.24 (1.58-111.21)*
2.79 (1.32-5.88)**
Note. **p<0.01, *p<0.05
Mistreated persons (n=113) reported less social support,
greater alcohol use, poorer relationship with caregivers prior
to disease onset, and had a caregiver with a mental health
condition.










