Organizational Change

Organizational Change
Chapter 18
Organizational Change
• All companies must change in order to remain competitive
• Change is difficult
– Organizational Inertia
• There are benefits to stability
18-3
Forces of Change
External
Demographic Characteristics
Technological Advancements
Shareholder, Customer, and Market Changes
Social and Political Pressures
Internal
Human Resource Problem/Prospects
Managerial Behavior/Decisions
The Need for Change
Types of Organizational Change
18-4
Adaptive
Change
Reintroducing a familiar practice
Low
Innovative
Change
Introducing a practice new to the organization
Degree of complexity, cost, and uncertainty
Potential for resistance to change
Radically
Innovative
Change
Introducing a practice new to the industry
High
Lewin’s Change Model
• Unfreezing
– Creates the motivation to change
• Benchmarking Data
• Financial data, emerging trends
Changing
– Provides new information, new behavioral models, or new ways of looking at things
Refreezing
– Helps employees integrate the changed behavior or attitude into their normal way of doing things
18-5
Assumptions of Lewin’s Model
• Change involves learning something new & unlearning the old way of doing things
• Change will not occur without motivation
• People are the hub of all organizational change
• Resistance to change is found even when change is desirable
A Systems Model of Change
Inputs
Internal
Strengths
Weaknesses
External
Opportunities
Threats
Strategy Goals
Target Elements of Change
Organizing
Arrangements
People
Social
Factors
Outputs
Internal
Organizational level
Department/ group level
Individual level
Methods
18-7
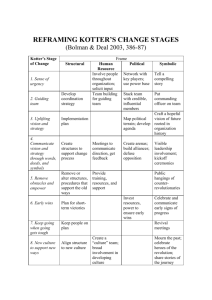
Kotter’s Eight Steps for Leading Organizational
Change
Table 18-1
Step
1) Establish a sense of urgency
Description
Unfreeze the organization by creating a compelling reason for why change is needed
2) Create the guiding coalition Create a cross-functional, cross-level group of people with enough power to lead the change
3) Develop a vision and strategy
4) Communicate the changevision
Create a vision and strategic plan to guide the change process
Create and implement a communication strategy that consistently communicates the new vision and strategic plan
18-8
Kotter’s Eight Steps for Leading Organizational
Change
Table 18-1
Step
5) Empower broad-based action
Description
Eliminate barriers to change, use target elements of change to transform the organization
6) Generate short-term wins Plan for and create short-term “wins” or improvements
7) Consolidate gains and produce more change
The guiding coalition uses credibility from short-terms wins to create change. Additional people are brought into the change process as change cascades throughout the organization
8) Anchor new approaches in the culture
Reinforce the changes by highlighting connections between new behaviors and processes and organizational success
18-9
Organizational Development
Resistance to Change
• Emotional/behavioral response to threats to an established work routine
– Passive or active
– One of three possible outcomes of influence attempts (Compliance & commitment)
Recipient Characteristics & Resistance
• Resilience to change
– Self-esteem, optimism, internal locus of control
• Fear of the unknown
• Fear of failure
• Loss of status/job security
• Peer pressure
• Past success
Change Agent Characteristics &
Resistance
• Disruption of culture or group relationships
• Personality conflicts
• Lack of tact or poor timing
• Leadership style
• Failure to legitimize change
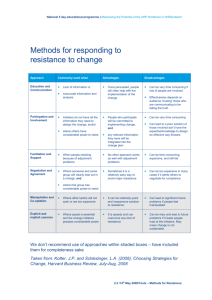
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Approach
Education and
Communication
Participation and
Involvement
Facilitation and Support
Commonly Used in
Situations Where:
Advantages Drawbacks
There is a lack of information or inaccurate information & analysis
The initiators do not have all the information they need to design the change & others have considerable power to resist
Once persuaded, people will often help with implementation of change
People who participate will be committed to the implementation of change
People are resisting because of adjustment problems
No other approach works as well with adjustment problems
Can be very time consuming if lots of people are involved
Can be very time consuming if participators design an inappropriate change
Can be very time consuming, expensive and still fail
18-14
Table 18-3
Overcoming Resistance to Change
Approach
Negotiation and
Agreement
Manipulation and
Co-optation
Explicit and Implicit
Coercion
Commonly Used in
Situations Where:
Advantages Drawbacks
Someone or some group will clearly lose out in a change and where that group has considerable power to resist
Sometimes it is a relatively easy way to avoid major change
Other tactics will not work or are too expensive
It can be relatively quick and inexpensive
Can be too expensive in may cases if it alerts other to negotiate for compliance
Can lead to future problems if people feel manipulated
Speed is essential and where the change initiators possess considerable power
It is speedy and can overcome any kind of resistance
Can be very risky ad leave people mad at the initiators
18-15
Stress
• An adaptive response to an environmental stimulus that places special demands on the individual
• Fight-or-flight response
– Physiological changes
– Physiological reactions
• Eustress vs. Distress
• Stressors – factors that cause stress
Stress and Performance
Stress
Coping Strategies
• Control strategy
– Aggressively try to solve problem
• Escape strategy
– Avoid problem
• Symptom Management strategy
– Deal with symptoms (drinking, meditating, etc.)
Mitigating Factors
• Social Support
– Esteem support
– Informational support
– Social companionship
– Instrumental support
• Hardiness
– Challenges vs. stressors
– Internal locus of control
Personality & Stress
• Type A personality
– Never ending struggle to achieve more and more in less and less time
– Sense of urgency about time
– Competitive
– Aversion to idleness
– Type A’s tend to:
• Speak rapidly
• Answer questions quickly
• Be sarcastic (hide rudeness in humor)