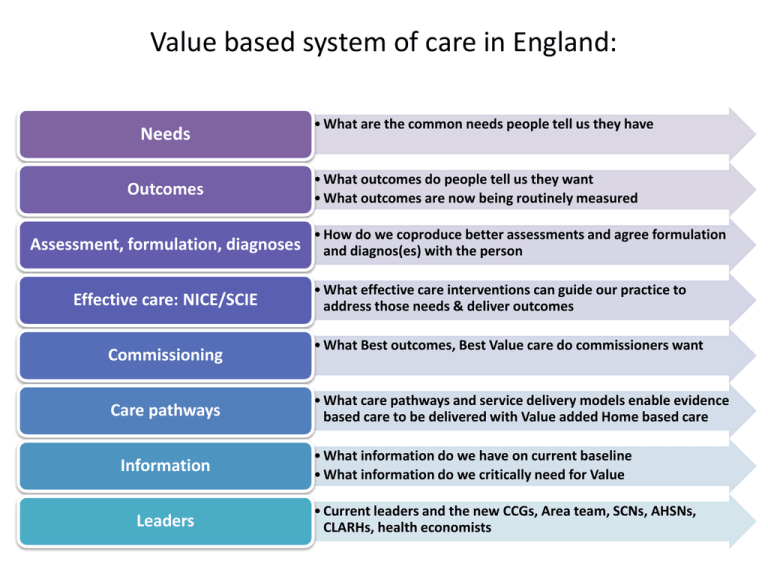
Value based system of care in England:
Needs
Outcomes
Assessment, formulation, diagnoses
Effective care: NICE/SCIE
Commissioning
Care pathways
Information
Leaders
• What are the common needs people tell us they have
• What outcomes do people tell us they want
• What outcomes are now being routinely measured
• How do we coproduce better assessments and agree formulation
and diagnos(es) with the person
• What effective care interventions can guide our practice to
address those needs & deliver outcomes
• What Best outcomes, Best Value care do commissioners want
• What care pathways and service delivery models enable evidence
based care to be delivered with Value added Home based care
• What information do we have on current baseline
• What information do we critically need for Value
• Current leaders and the new CCGs, Area team, SCNs, AHSNs,
CLARHs, health economists
Working together, mental health
can deliver social and wealth
capital for England
What Outcomes do our service users ask us
to achieve in partnership with them
Safety
“Will I be ok?”
From the
patient’s
perspective
Effectiveness
“Will it do me any
good?”
Experience
Efficiency
Was it fast, safe , near
home , back to work
asap
“Access, information &
treatment experience”
Professor Bruce Keogh, Medical Director of the NHS
Parity and equalities: Benchmark October 2013
There is a disparity in the number of people with mental illness in contact with
services, compared to physical health, yet it is a major cause of premature death
& lives lived in distress and misery
26% of adults with mental illness
receive care
92% of people with diabetes receive
care
By condition….
Anxiety and depression
PTSD
Psychosis
ADHD
Eating disorders
Alcohol dependence
Drug dependence
% in
treatment
24
28
80
34
25
23
14
Mental health problems are
estimated to be the commonest
cause of premature death
Largest proportion of the disease
burden in the UK (22.8%), larger
than cardiovascular disease (16.2%)
or cancer (15.9%)
People with schizophrenia die 15-25
years earlier
Depression associated with 50%
increased mortality from all disease
Value based system of care in England
Effective care:
NICE/SCIE
Commissioners
Care pathways
Information
Leaders
• What effective care interventions can guide our practice to
address those needs & deliver outcomes
• What Best outcomes, Best Value care do commissioners want
• What care pathways and service delivery models enable
evidence based care to be delivered with Value added
• And to increase access and self management
• What information do we have on current baseline
• What information do we critically need for Value
• Economic remodelling
• Current leaders and the new CCGs, Area team, SCNs, s
NICE Guidelines 2013
Alcohol dependence & harmful use &
clinical management
Antenatal and postnatal mental healthCompleted public health guidance
Antisocial personality disorder
Anxiety disorders
Brief interventions and referral for
Attention deficit hyperactivity disordersmoking cessation
(ADHD)
Interventions to reduce substance
Bipolar disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) misuse among vulnerable young
people
Dementia
Depression in adults
Depression in children and young people
Mental wellbeing and older people
Depression with a chronic physical health
Needle and syringe programmes
problem
Drug misuse: opioid detoxification
Preventing the uptake of smoking by
Drug misuse: psychosocial interventions
children and young people
Eating disorders
School-based interventions on alcohol
Medicines adherence
Smoking cessation services
Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) and
body dismorphic disorder (BDD) Social and emotional wellbeing in
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) primary education
Schizophrenia (update)
Social and emotional wellbeing in
Self-harm
secondary education
Violence
Workplace interventions to promote
When to suspect child maltreatment
smoking cessation
Autism spectrum disorders in children and
young people
Delirium
Identification and care pathways for common
mental health disorders
Psychosis with substance misuse
Self-harm (longer term management)
Public health guidance in
development
Alcohol-use disorders (prevention)
Home-based approaches to promoting
children's wellbeing
Looked after children
Personal, social and health education
focusing on sex and relationships and
alcohol education
Pre-school approaches to promoting
children's wellbeing
Preventing domestic violence
Quitting smoking in pregnancy and
following childbirth
School-based interventions to prevent
smoking
Value in mental health NICE/SCIE
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Right information
Right physical health care
Right medication
Right psychological therapies
Right rehabilitation, training for employment
Right care plan addressing housing, work, healthcare, self management
Right crisis care
Mental health : Is the problem that we have no evidence or value based guidance?
Mental health has over 100 NICE Health Technology appraisals, NICE
guidelines, Public health related guidelines and Quality standards…..
The problem is not lack of guidance
The problem is that we have not focused on how we learn and disseminate from
those that can and have implemented
Can the FT network lead a new NHS Change model?
8
“Crossing the Quality Chasm”
Ohio State Psychiatry Grand Rounds
12.05.2012
9
National Audit of Sschizophrenia
Physical Health
•
•
Significant premature mortality among those with a diagnosis of schizophrenia
(M=20yrs; F=15yrs).
Only 29% had all 5 risk factors monitored only 25% had treatment for elevated BP
Medicines
•
10 fold variation among trusts in relation to adherence to safe, effective medicines
practice
Psychological Therapies
• The range of those offered psychological therapies varied from 0% to
94%.
What are the reasons for increased Length of stay
Comorbidities: physical ill health, substance misuse, PD
Detentions under the mental health act
Implementations of NICE/SCIE evidence based care
Workforce capacity and competence
• People with SMI die 15-25 years younger due to 5-12 times increased levels
of un assessed and untreated COPD, Diabetes, High BP, Cancer
• Substance misuse is 6+ times more common in people with SMI
• Workforce strategies and training programmes need to be provide training
in evidence based treatments
Co-morbidity is the norm
Lancet, Barnett, Mercer et al 2012
5. Integrated physical and mental health care Long term conditions
Mental health raises costs in all sectors
Chris Naylor, Kings fund
• Between 12% and 18% of
all expenditure on longterm conditions is linked
to poor mental health and
wellbeing – at least £1 in
every £8 spent on longterm conditions.
180%
160%
% increase in annual per patient costs
(excluding costs of MH care)
• Overall, international
research finds that comorbid MH problems are
associated with a 45-75%
increase in service costs
per patient
(after controlling for
severity of physical illness)
140%
120%
100%
80%
Depression
Anxiety
60%
40%
20%
0%
Mental health has the capacity to improve
England's social and wealth capital
Economic remodelling programmes
• Unplanned care pathways
• Psychosis pathways
• Children and Young people pathways
• Integrated physical and mental health care pathways
Prevention and Early intervention (Knapp et al, 2011)
highly effective treatments: major economic benefit
For every one pound spent the savings are:
Parenting interventions for families with conduct disorder : £8
Early diagnosis and treatment of depression at work: £5 in year 1
Early intervention of psychosis £18 in year 1
Screening & brief interventions in primary care for alcohol misuse £12 Yr 1
Employment support for those recovering from mental illness: Individual
Placement Support for people with severe mental illness results in annual savings
of £6,000 per client (Burns et al, 2009)
Housing support services for men with enduring mental illness: annual savings:
£11,000–£20,000 per client (CSED, 2010).
Outcomes in Mental health












