states of consciousness revision
advertisement

CHAPTER 2
Cribb, Gridley, McKersie, Rice & Anin (2004)
‘…the awareness of objects and
events in the external world and
of our own existence and mental
experiences at any given
moment.’
Your consciousness is changing
and shifting depending on your
attention.
consciousness {p96} as a psychological construct
informed by the work of
René Descartes {p97} and William James {p100}
• Dualism
• The mind & the body are 2 different
things.
• Mind: non-physical spiritual entity (soul)
• Body: physical, fleshy structure (matter)
• Mind and body come interact through the
pineal gland.
‘…consciousness is
constantly changing.’ It
is like a stream, a
continual flow of
‘thoughts, feelings,
perceptions, images,
sensations and so on.’
States (levels) of consciousness
Total Awareness
Normal Waking
Consciousness
2/3 of day in
this state
State of focused attention
Divided attention
Daydreaming state
Meditative state
Hypnotic state
Sleep state
Anaesthetised
State of unconsciousness (coma)
Complete lack of
awareness.
Altered state of
Consciousness
‘…refers to the states of
consciousness associated
with being awake and aware
of our thoughts, memories,
feelings and the sensations
Stroop
we are experiencing from
effect
the outside world.’
‘Attention in a
concentration of mental
activity that involved
focusing on specific
stimuli while ignoring
other stimuli.’
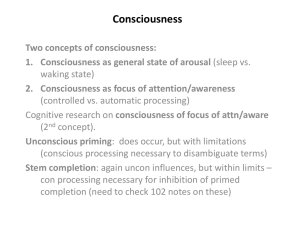
concepts of normal waking consciousness {p105}
and
altered states of consciousness {p115}, including
daydreaming, meditative and alcohol-induced, in terms
of levels of awareness, content limitations, controlled
and automatic processes, perceptual and cognitive
distortions, emotional awareness, self-control and time
orientation
‘…used to describe any state of consciousness
that is distinctly different from normal waking
consciousness…’
Tendency is to automatically read the word
Reading is an automatic process
Takes much longer to state the colour of the
ink as we have to prevent automatic
processing and impose controlled processing
Conclusion – automatic processing takes
precedence over controlled processing
Disturbed sense of time
In an ASC time is experienced at a
different speed than in NWC. Eg
sleeping, daydreaming
Changes in self control
• Our ability to maintain self control may
be raised or lowered during an ASC
• Lowered inhibitions displayed by
people affected by alcohol.
• May gain greater self control under
hypnosis e.g. conquering addictions.
Cribb, Gridley, McKersie, Rice & Anin (2004)
Electroencephalograpg (EEG)
‘detects, amplifies and
records general patterns of
electrical activity of the
brain.’
methods used to study the level of alertness in normal
waking consciousness and the stages of sleep:
– measurement of physiological responses including
electroencephalograph (EEG) {p133},
electrooculargraph (EOG) {p135}, heart rate, body
temperature and galvanic skin response (GSR) {p124}
– the use of sleep laboratories, video monitoring and
self reports
Measures eye
movements or
eye positions
through activity
in eye muscles
Galvanic skin response
‘…a physiological response
that indicates the change in
the resistance of the skin to
an electrical current.’
Alpha:
high frequency, low amplitude (slightly
larger than beta). Relaxed or meditative
state.
Renaé Descartes’ theory of consciousness as a
psychological construct relies on the concept that
a)
b)
c)
d)
The mind and body are separate entities
Interactions between brain neurons influence our
consciousness
Consciousness is an everchanging stream of ideas and
occurs only in the brain
Consciousness is produced by the soul and is located
in organs such as the liver and heart
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q1), 2011
Hilary has been knitting for twenty years. She is able to
knit quickly and accurately while she watches television.
Her granddaughter, who is just learning how to knit,
makes many mistakes if she tries to knit and watch
television at the same time.
This is because
a)
Hilary is in an altered state of consciousness when she
is knitting
b)
Knitting is a controlled process for Hilary and an
automatic process for her granddaughter
c)
Hilary is able to divide her attention while her
granddaughter is unable to divide her attention
d)
Hilary is able to use selective attention to know while
her granddaughter needs to use divided attention
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q2), 2011
Paulette meditates to reduce her stress levels.
Evidence that Paulette is in a meditative state could include
a)
b)
c)
d)
Reduced heart rate, alpha waves, lowered temperature
Increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, beta waves
Reduced heart rate, beta waves, low galvanic skin
response
Alpha and beta waves, reduced breathing rate, increased
muscle activity
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q3), 2011
Psychological measures such as those in Question 3 are
useful for measuring an individual’s state of consciousness.
However, it should not be assumed that a person is an altered
state of consciousness on the bias of these measures alone
because
a)
b)
c)
d)
These measures re not as accurate as self-report
An increase or decrease in heart rate is possible as a
result of meditation
Psychological measures are subjective measures of a
person’s state of consciousness
Changes in psychological responses may be due to a
range of reasons other than a person’s state of
consciousness
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q4), 2011
Petra was completing her psychology examination.
At the beginning of the examination, various thoughts were
active in her mind such as how to fill in the multiple-choice
answers, whether she should attempt the short answer
questions first, and that the room was a little cold.
Petra’s state of consciousness is best described as
a)
b)
c)
d)
Dualism
Selective attention
Normal waking consciousness
An altered state of consciousness
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q5), 2011
Petra was completing her psychology examination.
Petra’s thoughts then began to drift onto other things while
completing the examination, such as what she will wear at
her school formal, what everyone else will be wearing,
whether the boy she likes will notice her.
The term that most accurately explains Petra’s experience at
this time is
a)
b)
c)
d)
Daydreaming
Meditative state
Content limitations
Automatic processing
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q6), 2011
Renaé Descartes’ theory of consciousness as a
psychological construct relies on the concept that
a)
b)
c)
d)
The mind and body are separate entities 89%
Interactions between brain neurons influence our
consciousness 3%
Consciousness is an everchanging stream of ideas and
occurs only in the brain 6%
Consciousness is produced by the soul and is located
in organs such as the liver and heart 2%
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q1), 2011
Hilary has been knitting for twenty years. She is able to
knit quickly and accurately while she watches television.
Her granddaughter, who is just learning how to knit,
makes many mistakes if she tries to knit and watch
television at the same time.
This is because
a)
Hilary is in an altered state of consciousness when she
is knitting 1%
b)
Knitting is a controlled process for Hilary and an
automatic process for her granddaughter 5%
c)
Hilary is able to divide her attention while her
granddaughter is unable to divide her attention 88%
d)
Hilary is able to use selective attention to know while
her granddaughter needs to use divided attention 7%
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q2), 2011
Paulette meditates to reduce her stress levels.
Evidence that Paulette is in a meditative state could include
a)
b)
c)
d)
Reduced heart rate, alpha waves, lowered temperature 70%
Increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, beta waves 1%
Reduced heart rate, beta waves, low galvanic skin response
25%
Alpha and beta waves, reduced breathing rate, increased
muscle activity 4%
Paulette would be most unlikely to show beta-waves in a meditative
state. The meditative state is sometimes referred to as the ‘alpha state’.
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q3), 2011
Psychological measures such as those in Question 3 are
useful for measuring an individual’s state of consciousness.
However, it should not be assumed that a person is an altered
state of consciousness on the bias of these measures alone
because
a)
b)
c)
d)
These measures re not as accurate as self-report 1%
An increase or decrease in heart rate is possible as a
result of meditation 4%
Psychological measures are subjective measures of a
person’s state of consciousness 9%
Changes in psychological responses may be due to a
range of reasons other than a person’s state of
consciousness 86%
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q4), 2011
Petra was completing her psychology examination.
At the beginning of the examination, various thoughts were
active in her mind such as how to fill in the multiple-choice
answers, whether she should attempt the short answer
questions first, and that the room was a little cold.
Petra’s state of consciousness is best described as
a)
Dualism 5%
b)
Selective attention 11%
c)
Normal waking consciousness 80%
d)
An altered state of consciousness 4%
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q5), 2011
Petra was completing her psychology examination.
Petra’s thoughts then began to drift onto other things while
completing the examination, such as what she will wear at
her school formal, what everyone else will be wearing,
whether the boy she likes will notice her.
The term that most accurately explains Petra’s experience at
this time is
a)
b)
c)
d)
Daydreaming 95%
Meditative state 1%
Content limitations 2%
Automatic processing 2%
VCAA Psychology Exam 1, (q6), 2011