Some Genodermatoses and Acquired Syndromes Part 2
advertisement

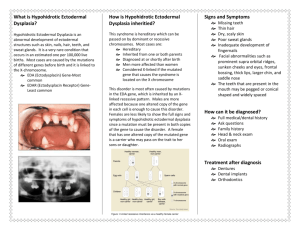
Some Genodermatoses and Acquired Syndromes Part 2 Rick Lin, DO MPH KCOM Dermatology Department Texas Division Sjogren-Larsson Syndrome Ichthyosis Spastic paralysis Oligophrenia MR Degenerative retinitis Flexural and lower abdominal accentuation Central face is spared Ectropion is unusual Palms and soles are involved Sjogren-Larsson Syndrome Autosomal recessive, localized to chromosome 17p11.2 Fibroblast and leukocyte deficiency in fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase (FALDH) Refsum’s Syndrome Ichthyosis with atypical retinitis pigmentosa Hypertrophic peripheral neuropathy Cerebellar ataxia Nerve deafness EKG changes Deficiency of phytanol-CoA hyroxylase localized in chromosome 10 Rud’s Syndrome Ichthyosis Hypogonadism Small stature Mental retardation Epilepsy Macrocytic anemia Retinitis pigmentosa AR KID Syndrome AKA congenital ichthyosiform syndrome with deafness and keratitis Extensive congenital ichthyosiform eruption Neurosensory deafness Hypotrichosis Partial anhidrosis Vascularization of cornea Nail dystrophy Tight heel cords CHILD Syndrome AKA Congenital Hemidysplasia with Ichthyosiform Erythroderma and Limb Defects (CHILD) X-linked, female only Unilateral ILVEN Erythrokeratodermia Variabilis AKA Medes da Costa, erythrokeratoderma variabilis, etc Keratoderma of palms and soles AD, 1p34-p35, coding for gap junction protein Histo: hyperkeratosis with parakeratosis and diminished granular layer Progressive Symmetric Erythrokeratodermia Rare, AD Symmetrically distributed on extremities, buttocks, and spare the trunk Treatment include keratolytics, corticosteroids, retinoids. Acquired Ichthyosis Similar to ichthyosis vulgaris clinically Develop any age with several systemic diseases Hodgkins Non-hodgkins lymphoma MF Multiple myeloma CA Hypothyroidism Pityriasis Rotunda Perfectly circular, hyperkeratotic and hypopigmented macules 2 forms: Type 1 found in blacks and Asians, has hyperpigmented lesions with less than 30 in numbers Type 2 occur in white patients, has hypopigmented lesions with more than 30 in numbers. There is slight psoriasiform hyperplasia with compact orthokeratosis and a diminished granular layer. Keratosis Pilaris AD condition Facial involvement may be mistaken for acne Keratolytic and topical vitamin D and topical retinoids are effective Follicular Atrophoderma Consist of follicular indentation 1mm wide, without hair Extensor surface of hands, legs, and arms Keratosis Pilaris Atrophicans Three syndromes Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei Atrophoderma vermiculata Keratosis pilaris follicularis spinulosa decalvans Keratosis Pilaris Atrophicans Faciei and Ulerythema Ophoryogenes Persistent erythema and small horny follicular papules onset during childhood On involution these leave pitted scars and atrophy with resulting alopecia Ulerythema Ophoryogenes describes involvement limited to the lateral third of the eyebrow KPAF involvement extent to the cheek and forehead Atrophoderma Vermiculata Symmetrical involvement of face by numerous closely crowded small areas of atrophy separated by narrow ridges. Honeycomb surface Worm eaten (vermiculata) Rambo Syndrome Grainy skin Multiple BCCs, triepitheliomas, hypotrichosis Perculiar cyanosis of the hands and feet 2 patients reported Examples of the entity I will chose to skip. Keratosis Follicularis Spinulosa Decavans KFSD begins on the face at any age up to adolescence Involve limbs and trunk Hyperkeratosis of palms and soles Follow by loss of hair and scarring Cicatricial alopecia of scalp and eyebrow is the hallmark of this disease Porokeratosis Heterogenous group of disorders Characterized by cornoid lamella on histology Porokeratosis of Mibelli Chronic progressive disease Atrophic patches surround by elevated border Predilection are the surface of hands and finger and the feet and ankle Onset early in life and persist indefinitely Treatment: 5FU, Cryo, CO2 Disseminated Superficial Actinic Porokeratosis DSAP is numerous superficial annular keratotic brownish red papules More common in women Assn with AIDS, cirrhosis, Crohn’s, immunosupression Cryo and 5-FU Linear Porokeratosis Porokeratosis following lines of Blaschko Porokeratosis Palmaris, Plantaris, et Disseminata Palms and sole or both Darier’s Diseases AKA Keratosis Follicularis Dirty, warty, papular excrescences tend to coalesce into patches Punctate keratosis V-nicking and red white banding Worse in summer AD 1:100,000 Corps ronds and grains Treatment: Tazarac and Accutane. Acrokeratosis Verruciformis of Hopf Numerous flat verrucous papules on back of the hands, knees, and elbows AD Pachyonychia Congenita Excessively thickened nails of all fingers and toes Palmar and plantar hyperkeratosis Follicular keratosis Painful friction blisters may develop 4 types have been described. Type one most common Dyskeratosis Congenita Atrophy and reticular pigmentation of sky Dystrophy of the nails Leukoplakia Hyperhidrosis of palms and soles Skeletal anomalies and esophageal stricture X-linked recessive traint Xq28 locus Congenital Ectodermal Defects Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia And tons of other ones Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia and Anhidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia Hypotrochosis Anodontia Hypohidrosis to anhidrosis Absent or reduce sweating Eccrine glands are absent or rudimentary on biopsy Facies suggest congenital syphilis X-linked recessive Note the peg-shaped teeth, hypodontia, periorbital hyperpigme ntation and sebaceous hyperplasia. Note the flat nasal bridge, depressed nasal tip, sparse hair (scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes), pegshaped teeth, full lips and sebaceous hyperplasia. Also note the normal secondary hair in adults. Hidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia Clouston’s syndrome Active eccrine sweat gland Facial feature normal AD Alopecia, nail dystrophy, palmoplantar hyperkeratosis Cataracts and strabismus 13q11-q12.1 Bunch of the entities I skip EEC S. Rapp-Hodgkin Ectodermal Dysplasia s. Ectodermal dysplasia with corkscrew hair s. Odonto-tricho-ungual-digital-palmar s. Costello s. Lenz-Majewski s. Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn s. CHIME s. Pachydermoperostosis Ladd-Lin s. Cutis Verticis Gyrata Folds and furrows on the scalp Vertex is involved M:F=6:1 90% patient developed by age 30 Assn with MR and schizophrenia Aplasia Cutis Congenita Congenital defect of the skin Absence of skin and subcutaneous tissue of the cranium Focal Dermal Hypoplasia AKA Goltz’s Syndrome Syndactyly, oligodactyly, and adactyly Multiple abnormality of mesoderma and ectodermal tissues Yellowish brown nodules on buttocks, axillae, and thighs X-linked dominant Cockayne’s Syndrome Dwarfism Retinal atrophy Deafness Photodermatitis Telangiectasia Microcephaly, sunken eyes, and characteristic facial appearance Werner’s Syndrome Aka adult progeria Premature-aging syndrome Growth arrest at puberty Senile cataracts in late 20 Premature graying and balding at 30’s High rate of malignancy Progeria AKA Hutchinson-Gilford Syndrome Dwarfism Alopecia Generalized atrophy of the skin Enlarge head Fatal by second decade Congenital Auricular Fistula Anomaly occurs in preauricular region Anterior to external ear there is a small dimple, pore, or fistulous opening Scrofuloderma or EIC may develop Branchial Cleft Cyst Developmental anomaly Exude sebum like material AD with incomplete penetrance Popliteal Pterygium Syndrome Pterygia or skinfold may extend from thigh down to heel thus prevent extension or rotation of the legs AD Other Congenital Anomalies that we will all miss together on the board…. Franceschetti-Klein syndrome Apert’s Syndrome Whistling Face syndrome