Slide Show-Cellular Respiration
advertisement

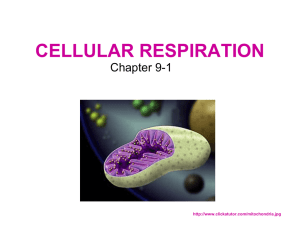
Cellular Processes Cellular Respiration Review I Can I can describe the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs I can describe the events that occur during cellular respiration. I can describe the role that mitochondria play in cellular respiration. Characteristic of Living Organisms Fungi Plants All living things obtain and use energy Animals Absorbing from the soil Absorbing from the sun How do living organisms obtain energy? Consuming other organisms Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs An organism that makes its own food. An organism that CANNOT make its own food. Example: Example How does food provide energy? We eat glucose What is glucose? Where does it come from? When we digest food, the energy is released Energy What kind of energy comes from food? The energy released from food is called ATP. What is cellular respiration? It is the process by which glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water and energy is released. Where in the cell does respiration occur? IN the MITOCHONDRIA! CELLULAR RESPIRATION Where? In the mitochondria What? The glucose molecules are broken down even more and ENERGY is released. How Heterotrophs Obtain Energy… Bloodstream Mitochondria Digestive system Cells Equation Vocabulary Raw material: the “stuff” (or materials) you need to start the process. Product: the “stuff” that you end up with (is produced as a result of the process). What do we need to start cellular respiration? 1. Sugars (glucose) 2. Oxygen What do we need to start cellular respiration? C6H1206 + 602 Glucose Oxygen “yields” What are the products of cellular respiration? 6C02 + 6H20 + ATP Carbon Dioxide Water Used to power cells. What is the equation for respiration? C6H12O6 +6O2 Glucose Oxygen 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP Carbon dioxide Water Energy Brain Pop Now we are going to watch the Cellular Respiration BrainPOP http://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/cellularrespiration/ Yeast Lab Background “An Investigation of Cellular Respiration” What are yeast? Yeast are micro eukaryotic organisms that have been used in baking for thousands of years Yeast Conduct cellular respiration What does cellular respiration need? What does cellular respiration create? Yeast Conduct fermentation Does not require oxygen Still produces energy Yeast Lab Set Up and Background Investigation of Cellular Respiration In your group: Read the “Purpose” and “Background Information” Sections Answer the “Background Questions” TIME IS UP!!!!!! Hypothesis We are going to increase the levels of glucose in the bottles. Do you think that this will INCREASE or DECREASE the level of ATP? Will this INCREASE or DECREASE the level of CO2? Why? Setting up the Lab LISTEN and follow all directions the first time they are given. Data Fill in your Data Table Yeast Preparation Active dry yeast needs to be reactivated with water Why? Key Idea Most chemical reactions within cells could not take place without water. Other than the water, what other items were in the bottle? Sugar Yeast Air What caused the balloon to blow up? Carbon Dioxide!!! But where did the carbon dioxide come from? Cellular Respiration (and fermentation!) Conclusion Make your final Conclusions Exit Slip