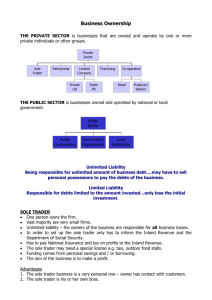
Shares in a private limited company
advertisement

Chapter 20 The importance of limited liability p96-99 Aims for today 1. Look at the difference between limited and unlimited liability 2. Appreciate the differences between sole traders and private limited companies Unlimited liability & Sole traders What does unlimited liability mean? Advantages of being a sole trader • Total control of the business by the owner. • Cheap and easy to start up – few forms to fill in and to start trading. ST just has to set up a bank account and inform the Inland revenue. • Keep all the profit – as the owner, all the profit belongs to the sole trader. • Business affairs are private – competitors cannot see what you are earning, so will know less about how the business works and how it succeeds. A sole trader may have one or more employees. It is the most common form of ownership in the UK. Disadvantages of being a sole trader • Unlimited liability • Can be difficult to raise finance • Can be difficult to enjoy economies of scale, i.e. lower costs per unit due to higher levels of production. Loosing out on bulk buying compared to larger companies • There is a problem of continuity if the sole trader retires or dies – what happens to the business next? Limited liability • A limited company is a business that is owned by its shareholders, run by directors and whose liability is limited. • Limited liability means that the investors can only lose the money they have invested and no more. This encourages people to finance the company....why? • If anyone claims against the company, “limited liability” means that they can only recover money from the existing assets of the business. They cannot claim the personal assets of the shareholders to recover amounts owed by the company. Limited companies • To set up as a limited company, a company has to register with Companies House and is issued with a Certificate of Incorporation. It also needs to have a Memorandum of Association which sets out what the company has been formed to do, and Articles of Association which are internal rules of the company. • Limited companies can either be private limited companies or public limited companies. The key difference between the two is that: • Shares in a public limited company (plc) can be traded on the Stock Exchange and can be bought by members of the general public. • Shares in a private limited company are not available to the general public; Task 1 • Answer questions on page 98 & 99 Differences between Private Limited Companies and Sole traders 1. Risk Limited liability means owing a company is less risky than being a sole trader. If a business goes wrong, then a sole trader could loose everything including personal assets (house, car) 2. Control A sole trader would be in sole control of his business as he owns all the shares. In a PLC if there is a majority shareholder, they have control. In a PLC where shareholder have a similar % of shares then no one has control. E.g 30%, 40% and 30% - Consider Dragons Den? Differences between Private Limited Companies and Sole traders 3. Profits Profits from a company are distributed depending upon the ownership of shares. Higher number of shares = more profits. Sole traders retain all their profits. 4. Privacy PLC must file their accounts each year with a government agency called COMPANIES HOUSE. These can be viewed by anyone for a small fee. Sole traders can kept their accounts private. Task 2 • Answer questions on page 99 Now for a quick quiz 1. Does a sole trader have limited or unlimited liability? 2. Who owns a PLC? 3. Why is limited liability important to attract investors? 4. State one disadvantage for setting up as a company? Paying for accounts to be audited, publishing accounts, loss of privacy 5. Are all businesses companies? 6. What are the advantages of being a sole trader?