GCSE Business Studies
advertisement

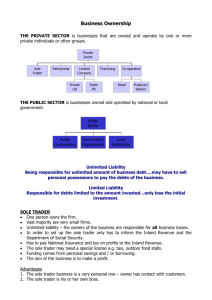
GCSE Business Studies Unit 1 Introduction To Small Businesses GCSE Business Studies • Types of Business 1.4 Making the Start- Up Effective • To understand the difference between sole traders, partnerships, franchises, ltd companies and PLCs. • To be able to identify benefits and disadvantages of each 1.2 Making the start-up effective GCSE Business Studies Unit 1 Introduction To Small Businesses Lesson Objectives • Recap what a Sole Trader and a PLC is by answering the true or false questions A-10/10 correct B – 8 – 9 correct C -6-7 correct 1.2 Making the start-up effective GCSE Business Studies Unit 1 Introduction To Small Businesses In your booklets Public Limited Company (PLC) Private Limited Company (Ltd) Partnership Franchise Which of these do you already know? 1.2 Making the start-up effective Types of business GCSE Business Studies Unit 1 Introduction To Small Businesses Sole Trader • Use the internet to research the 5 different types of business. Fill in the table in your booklets. 1.2 Making the start-up effective GCSE Business Studies Unit 1 Introduction To Small Businesses Task 1: Sole Trader -Summary A sole trader (sole proprietor, sole proprietorship or sole owner) is a business that is owned and run by one person. Most small businesses are run as sole traders. Sole traders have unlimited liability. They are in complete control of their business, and take all of the profits They usually use personal savings to start their business, although bank loans and overdrafts are often used too. Partnership - Summary A partnership is a bit like two or more sole traders trading together. A partnership is owned and controlled jointly by the partners. Partnerships suit the professions such as doctors, lawyers, accountants and architects. However partnership can exist in any line of work, e.g. a painter and decorator may become partners. Partnerships generally have unlimited liability, although liability is shared between the total number of partners therefore it is less risky than being a sole trader. Finance is usually raised through personal savings and bank loans, just like Sole Traders. Partners split profits depending on their own share agreements. Private Limited Company The ‘private’ in ‘private limited company’ means that the shares can only be sold privately – they cannot be offered for sale to the general public. All the shareholders must agree to the sale. Often the shareholders are all members of the same family. Private limited companies have Ltd. or Limited after their name. Private limited companies are generally smaller than plc’s. They have more control over the fate of the company since they control the sale of the shares. Public Limited Company The ‘public’ in ‘public limited company’ means that the public can buy shares in the company if they are offered for sale. Companies usually become a plc due to major growth. Becoming a plc brings a lot of capital into the business which allows further growth. Shares are traded on the stock market, where anyone can buy them at the current market price. Shares can go up and down in value based on company performance, economic factors or world events Public limited companies have plc after their name. Franchise Franchising is essentially the 'hiring out' or licensing of the use of 'good ideas' to other companies. Companies like McDonalds, Specsavers and Starbucks are all franchises. A franchise has limited liability. The franchisee pays a start up fee to use the name, business plan, materials etc of the franchisor. The franchisee then must make regular payments, usually based on a percentage of the profits. Public limited companies have plc after their name. Over to you A – 14 to 15 marks B – 12 to 13 marks C – 9 to 11 marks Answer the exam style questions in your books.