Graphing Sequences
advertisement

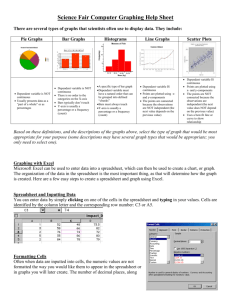
Graphing Sequences Section 1.4 There is more than one way to represent a sequence. Tables Graphs Other kinds of formulas Match each table with a recursive formula and a graph that represent the same sequence. Think about similarities and differences between the sequences and how those similarities and differences affect the tables, formulas, and graphs. Write a paragraph that summarizes the relationships between different types of sequences, recursive formulas, and graphs. What generalizations can you make? What do you notice about the shapes of the graphs created from arithmetic and geometric sequences? Setting Up a Spreadsheet with a Sequence 1. Open a new document and start with a List and Spreadsheet. 2. Label column A xcoord 3. Label column B ycoord 4. Fill the first two cells in column A with1 and 2. Press the Caps key and the down arrow to highlight the two cells. Press MENU, choose DATA, choose Fill. Cursor down to highlight the first 10 cells and press ENTER. 1. Move to the box under ycoord to enter a command to make a sequence. 2. Press Menu, 3 Data, 1 Generate Sequence. Fill in the formula for the sequence, the initial terms, n(), nMax. 1. To create a graph of the data in your spreadsheet, press HOME, add a Data and Statistics page. 2. Move to the edge with the cursor and select xcoord for the bottom axis and ycoord for the vertical axis The general shape of the graph of a sequence’s terms tells you about the type of sequence you have generated. u1 1 un un 1 2 This is an arithmetic sequence The general shape of the graph of a sequence’s terms tells you about the type of sequence you have generated. u1 90 un (1 .2) * un 1 This is a geometric sequence.