Common Collective Dilemmas
advertisement

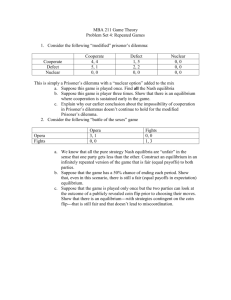
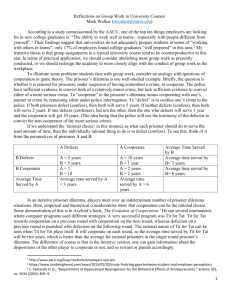
Common Collective Dilemmas Jamie Monogan University of Georgia August 20, 2014 Objectives By the end of this meeting, participants should be able to: •Explain the premise behind several common games: the collective-action problem, the coordination game, the prisoner’s dilemma, the free-rider problem, the tragedy of the commons, and the principal-agent problem. •Describe the role of institutions in resolving collective dilemmas. Prisoner’s Dilemma • Strategic interaction where each actor is better off with cooperation, but each is incentivized to not cooperate A Political Campaign Prisoner’s Dilemma Collective-Action Problems • Large-scale Prisoner’s Dilemma • People want to see public good provided – Public vs. private goods • Individuals have no incentive to provide it: free-riding occurs (e.g., the free-rider problem is a synonym) • Effective enforcement is required to solve problem • Danny DeVito summed this up in Tin Men • Special case: the Tragedy of the Commons Coordination Problems • Group wants to act in common, but cannot agree on solution – Where to meet for lunch? – Which side of the road to drive on? – Which candidate to support? Unstable Coalitions • Collective agreements can be undermined in the face of competition • Losers in original coalition have incentives to make “better” offer to some coalition members • Minimum winning coalitions are more susceptible to coalition “raiding” Unstable Coalitions • Unstable coalitions can undermine collective decision making – No final decision ever made • Agenda setters can help by restricting options available to the group Principal-Agent Problems • Principals hire agents to do some task for them – Car mechanic – Doctor • Principal cannot be sure agent is acting faithfully – Information asymmetry exists between principal and agent Principal-Agent Problems • These problems also exist in government • All elected officials are agents of the voters • Elected officials delegate tasks to bureaucrats and bureaucratic agencies Institutions • Institutions are formal constraints on behavior • Can be large and complex or a rule within a larger institution • Institutions help solve collective dilemmas – How does the mafia affect the prisoner’s dilemma? – How do committee chairpersons affect unstable coalitions? – Thomas Hobbes: Government solves “war of all against all.” – Institutional design affects distribution of benefits in society – Can be inequitable: large vs. small states Institutions Assignments • For Friday: Read Bullock & Gaddie, Interlude: votefordanae.com • Be prepared to talk about this reading in your discussion section. • For Monday: Read Kollman, pp. 3150.