Scar Tissue & Remodelling
advertisement

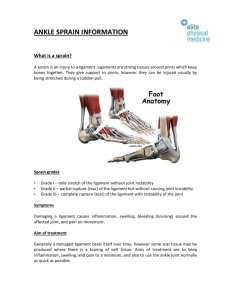
Task 1… • Complete the previous Injury sheet, it will help you for the assessment tasks later in the session. INFLAMMATION Inflammation is a protective attempt by the body to remove harm and to initiate the healing process It occurs within a few minutes to hours of injury The 5 key characteristics of inflammation are: •Pain •Redness •Swelling •Heat •Immobility (loss of function) THE INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE Injury causes tissue damage The damaged tissue releases chemicals Blood vessels dilate (widen) allowing increased blood flow to the injured area. This causes; HEAT PAIN REDNESS BLEEDING SWELLING LOSS OF FUNCTION THE CLOTTING MECHANISM (COAGULATION) Clotting, also known as “coagulation”, occurs almost immediately after injury to a blood vessel. It is the process of blood changing from its usual liquid state to a solid form. There are 3 stages; •Formation of Prothrombinase When liquid blood comes into contact with certain molecules (or foreign objects) it stimulates the formation of an enzyme called Prothrombinase. •Prothrombin is then converted to Thrombin The enzyme Prothrominase converts Prothrombin into Thrombin (another enzyme) •Fibrinogen is converted into Fibrin Thrombin converts Fibrinogen into Fibrin which forms the tread-like scaffolding structures that form a clot. HERE IS A LINKS TO A VIDEO ANIMATION OF INFLAMMATION & COAGULATION WHICH MAY HELP YOUR UNDERSTANDING! A cartoon animation of the full coagulation process in detail including all the info you need http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9QVTHDM90io SCAR TISSUE & REMODELLING A scar is a result of the body's repair mechanism after injury on many tissues. Scar tissue replaces normal tissue after it is damaged. Scar tissue is the formation and laying down of a protein called “collagen”. This is a fibrous tissue that replaces the tissue that has been damaged. It is not as elastic and pliable as skin and muscular tissue which makes it a lower quality tissue and less effective and efficient at doing its job. SPRAINS AND STRAINS Sprains and Strains are overstretching or tearing of tissue. Sprains involve ligamentous tissue and strains involve muscular tissue. Both involve pain and discomfort , deformity, swelling, bruising, impaired movement and loss of function. STRAIN A stretching or tearing of muscle/tendon SPRAIN A stretching, or tearing, of one or more ligaments. Sprains and Strains can be classified as first, second and third degree, depending on the amount of fibres involved. GRADES OF INJURY LIGAMENT SPRAIN MUSCLE STRAIN Degree / Severity Fibre Damage Signs and Symptoms Grade I (mild) few fibres Minimal discomfort swelling / tenderness movement slightly impaired / functional. Grade II (moderate) many fibres Significant pain / discomfort / noticeable swelling / tenderness / impaired movement / function impaired. Grade III (severe) total rupture Pain / significant swelling / bruising / tenderness / impaired movement / joint unstable / loss of function. HAEMATOMAS (INTER/INTRA) A haematoma, is a localized collection of blood outside the blood vessels, usually caused by trauma (in this case a muscle). It is different from a bruise, which is the spread of blood under the skin in a thin layer. •There are 2 types of haematoma; •Intramuscular This injury only effects the muscle fibre tissue and therefore bleeding is contained within the sheath that surrounds the muscle. Pressure within the muscle builds up which can become very painful. The fluid is unable to escape as the muscle sheath prevents it, acting like a balloon. Healing takes longer as bleeding stays in one area and has to be broken down. You are less likely to see visible bruising. •Intermuscular This type of injury includes the muscle and also the muscle sheath and therefore bleeding is not contained and can spread (for example with gravity). Initial bleeding can last longer, however recovery is often faster than intra muscular as the blood and fluids can flow away from the site of injury. You are more likely to see bruising. P3 What you guys can do… • Design a leaflet that describes in a informative manner the following points: · · · Inflammation The Clotting Mechanism Scar Tissue Signs and Symptoms a coach should look out for to identify; o A sprain o A strain •A haematoma (Including the severity and type grading system)