Part 4
Staffing Activities: Selection
Chapter 08:
External Selection I
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Staffing Organizations Model
Organization
Mission
Goals and Objectives
Organization Strategy
HR and Staffing Strategy
Staffing Policies and Programs
Support Activities
Core Staffing Activities
Legal compliance
Planning
Recruitment:
Selection:
External, internal
Measurement, external, internal
Job analysis
Employment:
Decision making, final match
Staffing System and Retention Management
8-2
Chapter Outline
Preliminary Issues
Logic of Prediction
Nature of Predictors
Development of the
Selection Plan
Selection Sequence
Initial Assessment
Methods
Resumes and Cover
Letters
Application Blanks
Biographical
Information
Initial Assessment
Methods
References and
Background Checks
Handwriting Analysis
Literacy Testing
Genetic Testing
Initial Interview
Choice of Methods
Legal Issues
8-3
Learning Objectives for This Chapter
Understand how the logic of prediction guides the
selection process
Review the nature of predictors—how selection
measures differ
Understand the process involved in developing a
selection plan, and the selection sequence
Learn about initial assessment methods and
understand how these methods are optimally used in
organizations
Evaluate the relative effectiveness of initial
assessment methods to determine which work best,
and why
Review the legal issues involved in the use of initial
assessment methods, and understand how legal
problems can be avoided
8-4
Discussion Questions for This Chapter
A selection plan describes which predictor(s) will be used to
assess the KSAOs required to perform the job. What are the
three steps to follow in establishing a selection plan?
In what ways are the following three initial assessment methods
similar and in what ways are they different: application blanks,
biographical information, and reference and background checks?
Describe the criteria by which initial assessment methods are
evaluated. Are some of these criteria more important than others?
Some methods of initial assessment appear to be more useful
than others. If you were starting your own business, which initial
assessment methods would you use and why?
How can organizations avoid legal difficulties in the use of
preemployment inquiries in initial selection decisions?
8-5
Preliminary Issues
Logic of prediction
Nature of predictors
Development of the
selection plan
Selection sequence
8-6
Logic of Prediction: Past Performance
Predicts Future Performance
Not specific enough to make selection decisions
Job titles
Number of years of experience
What counts is the specific types of experiences
required and the level of success at each
8-7
Nature of Predictors
Content
Sign: A predisposition thought to relate to performance (e.g.,
personality)
Sample: Observing behavior thought to relate to performance
Criterion: Actual measure of prior performance
Form
Speed vs. power: How many versus what level
Paper / pencil vs. performance: Test in writing or in behavior
Objective vs. essay: Much like multiple-choice vs. essay
course exam questions
Oral vs. written vs. computer: How data are obtained
8-8
Development of the Selection Plan:
Steps Involved
1.
Develop list of KSAOs required for job
2.
3.
KSAOs are provided by job requirements
matrix
For each KSAO, decide if it needs to be
assessed in the selection process
Determine method(s) of assessment to
be used for each KSAO
8-9
Ex. 8.3 Assessment
Methods by Applicant
Flow Stage
•Initial assessment
methods
•Minimize the costs
associated with
substantive
assessment methods
by reducing the
number of people
assessed
8-10
Discussion questions
A selection plan describes which
predictor(s) will be used to assess the
KSAOs required to perform the job. What
are the three steps to follow in
establishing a selection plan?
8-11
Resumes and Cover Letters
Information provided is controlled by applicant
Major issues
Information needs to be verified by other predictors
to ensure accuracy and completeness
Large number received by organizations
Falsification and misrepresentation of information
Lack of research exists related to
Validity or reliability
Costs
Adverse impact
8-12
Overview of Application Blanks
Areas covered
Educational experience
Training
Job experience
Key advantage -- Organization dictates
information provided
Major issue -- Information requested should
Be critical to job success and
Reflect KSAOs relevant to job
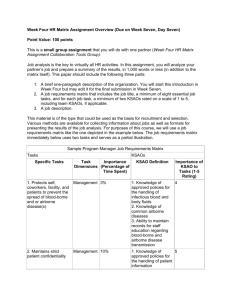
Sample application blank - Exh. 8.4
8-13
Sample Application for Employment
8-14
Application Blanks
Areas of special interest
Educational requirements
Level of education
GPA
Quality of school
Major field of study
Extracurricular activities
Training and experience requirements
Licensing, certification, and job knowledge
Weighted application blanks
Evaluation --> ŕ = .10 to ŕ = .20
8-15
Biographical Information / Biodata
Personal history
information of
applicant’s background
and interests
“Best predictor of future
behavior is past
behavior”
Past behaviors may
reflect ability or
motivation
Measures
Exh. 8.5: Examples of
Biodata Items
Biodata compared with
background checks
Background check
examines an
applicant’s
background
conducted through
records checks and
conversations with
references
Biodata
used to predict future
performance
information is
collected by survey
8-16
Exhibit 8.5 Examples of Biodata Items
8-17
Evaluation: Biographical
Information / Biodata
Test-retest reliability can be high: .77 to .90
Predictive validity moderate: r = .32 to .37
Issues
Generalizability beyond first group?
Although predictive validity exists, it is not
clear
what these inventories assess
Falsification can be a big problem
8-18
Reference Reports:
Letters of Recommendation
Problems
Inability to discern more-qualified from
less-qualified applicants
Lack of standardization
Suggestions to improve credibility
Use a structured form
Use a standardized scoring key
8-19
Reference Reports: Reference Checks
Approach involves verifying applicant’s
background via contact with
Prior immediate supervisor(s) or
HR department of current of previous companies
Roughly 8 of 10 companies conduct reference
checks
Problems
Same as problems with letters of recommendation
Reluctance of companies to provide requested
information due to legal concerns
Exh. 8.7: Sample Reference Check
8-20
Reference Reports: Background Testing
Method involves assessing reliability of applicants’
behavior, integrity, and personal adjustment
Type of information requested
Criminal history
Credit information
Educational history
Employment verification
Driver license histories
Workers’ compensation claims
Key issues
Limited validity evidence
Legal constraints on pre-employment inquiries
8-21
Evaluation of Reference Reports
Predictive validity limited: r = .16 to .26
Validity depends on source providing
information
HR department, coworker, or relative
Supervisors
What sources do you think work best?
Cost vs. benefit of approach must be
considered
8-22
Genetic screening
Done to screen out people who are susceptible to
certain diseases (e.g., sickle cell anemia) due to
exposure to toxic substances at work
Genetic screening is not widespread, companies such
as Du Pont and Dow Chemical experimented with it to
protect their employees
Court decisions have ruled that genetic screening is
prohibited under the Americans With Disabilities Act
(ADA)
genetic testing is permissible only when consent has been
granted by the applicant or when test results directly bear on
an applicant’s ability to perform the job
8-23
Initial Interview
Characteristics
Begins process of necessary differentiation
Purpose -- Screen out most obvious cases
of person / job mismatches
Limitation -- Most expensive method
of initial assessment
Video and computer interviews
Offers cost savings
8-24
Evaluation of Initial Interview
Minimal evidence exists regarding
usefulness
Guidelines to enhance usefulness
Ask questions assessing most basic KSAOs
Stick to basic, fundamental questions
suitable for making rough cuts rather than
subjective questions
Keep interviews brief
Ask same questions of all applicants
8-25
Choice of Initial Assessment Methods
8-26
Discussion questions
In what ways are the following three initial
assessment methods similar and in what ways
are they different: application blanks,
biographical information, and reference and
background checks?
Describe the criteria by which initial
assessment methods are evaluated. Are some
of these criteria more important than others?
Some methods of initial assessment appear to
be more useful than others. If you were
starting your own business, which initial
assessment methods would you use and why?
8-27
Legal Issues
Disclaimers - Organization clearly identifies
rights it wants to maintain
Employment-at-will
Verification consent
False statement warning
Reference checks
Preemployment inquiries
Federal laws and regulations
EEOC Guide to Preemployment Inquiries
ADA regulations
State laws and regulations
8-28
Legal Issues
Bona fide occupational qualifications - BFOQs
Discrimination based on sex, religion, or national
origin, but not race or color, is permitted if it can be
shown to be a BFOQ “reasonably necessary to the
normal operation” of the business
Employer justifications
Inability to perform
Same-sex personal contact
Customer preference
Pregnancy or fertility
8-29
Discussion questions
How can organizations avoid legal
difficulties in the use of preemployment
inquiries in initial selection decisions?
8-30
Ethical Issues
Issue 1
Is it wrong to “pad” one’s résumé with information
that, while not an outright lie, is an enhancement?
For example, would it be wrong to term one’s job
“maintenance coordinator” when in fact one simply
emptied garbage cans?
Issue 2
Do you think employer have a right to check into
applicants’ backgrounds? Even if there is no
suspicion of misbehavior? Even if the job poses no
security or sensitive risks? Even if the background
check includes driving offenses and credit
histories?
8-31