Communication and Culture
advertisement

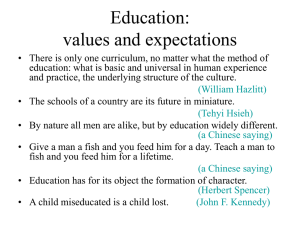
/ KING SAUD UNIVERSIT Y AUBURN UNIVERSIT Y SUMMER TEACHING INSTITUTE COMMUNICATION IN THE CLASSROOM ” C O M M U N I CAT I O N / T H I N K I N G S T Y L E S ” & “ C U LT U R E B U M P S ” JUNE 27, 201 2 Dr. Stacey Nickson COMMUNICATION? OVERVIEW CLASSROOM COMMUNICATION Communicatio n Channels Thinking Styles SelfInventory Thinking Styles Activity CULTURE BUMP Culture Bumps Brian and Aziz Negotiating Differences WHAT CAUSES COMMUNICATION BREAKDOWNS BETWEEN TEACHERS & STUDENTS? COMMUNICATION ISSUES IN YOUR CLASSROOM At your tables, identify issue in your classrooms between each of the following: Student to student Student to teacher Teacher to student Teacher to teacher WHAT IS COMMUNICATION? WHAT IS NOT COMMUNICATION? WHAT MAKES A PROFESSOR A GOOD COMMUNICATOR IN THE CLASSROOM? ARE YOU A GOOD COMMUNICATOR? WHY/WHY NOT THERE ARE THREE CHANNELS OF COMMUNICATION … It is clear that speaking and writing are one way that we communicate. This is verbal communication… SECOND CHANNEL OF COMMUNICATION Repeat the following: I live in a white house. President Obama lives in the White House. (Intonation) Shhh…be quiet GO AWAY! (Volume) Whajaeat lasnight? What did you eat last night? (Speed) This is paralanguage. LOOK AT THE PHOTOS AND COMPLETE THE SENTENCE FOR EACH ONE… I Am… QuickTime™ and a None decompressor are needed to see this picture. BASED ON THE PHOTOS… What is the third way that we communicate? Non-verbal language Dress Gestures Space/Time Posture Eye-contact THREE CHANNELS OF COMMUNICATION: VERBAL, NON-VERBAL AND PARALANGUAGE Research shows that __________provides 60% of the meaning in communication. Research shows that __________provides 38% of the meaning in communication. Research shows that __________provides 2% of the meaning in communication. WHY DO WE COMMUNICATE? To give information Or… LET’S LOOK AT TWO REASONS IN THE CLASSROOM To instruct, to give information To connect, to form teacher/student relationships ST YLES OF THINKING THE WAY WE THINK AS TEACHERS WILL INFLUENCE HOW We teach - THINKING ST YLES TEST Complete the Thinking Styles Test A. Score the results (see the guide) B. Graph the results (if time permits) THINKING ST YLES GROUPS Af ter completing the Thinking Styles test to determine your own dominate thinking style... Briefly Go To The Table for Your Thinking Style In Your “Thinking Style Group” Discuss the Following: 1.How does your thinking style influence your learning style? 2. How does your thinking style influence your teaching style? Return to your original tables/groups THINKING ST YLES BOARD Likes: - Order, predictability - Logical sequence - Following directions Learns best with: - Structured environment Dislikes: - Incomplete or unorganized - Questions without right/wrong Makes sense - Step-by-step - A schedule to follow Concrete Sequential Likes: - Their points to be heard - Analyzing before deciding - Applying logic Learns best with: - Able to work alone Dislikes: - Expressing their emotions - Too little time to be thorough Makes sense: - Well researched information - Work through ideas thoroughly Abstract Sequential Likes: - Experimenting - Take risks - Independent problem solving Learns best with: - Trial-and-error approaches Dislikes: - Restrictions and limitations - No options Makes sense: - Try it - Concrete examples Concrete Random Likes: - Listen to others - Group harmony - Healthy relationships with others Learns best with: - Group activities Dislikes: - Criticism - Focusing on one thing at a time Makes sense: - From the heart not the head - Personal examples Abstract Random STUDENT NAME CARDS Monira Farid Abdullah Alanoud EXERCISE: MATCH THE STUDENTS AND THEIR THINKING ST YLES Part I Student Name Cards... A. Briefly discuss the thinking styles described in the four quadrants on the Thinking Styles Board. B. Read each student’s card aloud and identify the thinking styles of each of the students. Place their name card in the appropriate quadrant on the Thinking Styles Board. MONIRA IS… Monira loves socializing. Her professors noticed she was the friendliest girl on campus, but thought if she would just stop talking she would become an accomplished student. They did, however, notice that with group projects she got the group to work well together and make the project fun. Monira’s thinking style is_____________ FARID IS… Farid is considered by many to be unorganized, but that is because he has his own way of doing things. He comes to life when he has the freedom to complete a project his own way, rather than using the standard methods the teacher expects him to follow. He enjoys doing hands-on science projects and especially enjoys doing anything others find “impossible”. Farid’s thinking style ABDULLAH IS… Abdullah is considered a model student. He is well organized. He has the nicest handwriting and his papers are neat and precise. He likes it when the professor tells him what is needed and gives him time to work on it. He consistently follows the proper procedures and is not afraid to ask questions to find out how to do assignments and projects right in order to meet due dates. ALANOUD IS… Alanoud barely graduated from high school even though she is really smart. She could never understand why she had to do the homework. However, when her professor let her select her own topic for her term paper and she got to research and write about “horses”, things were different. Alanoud easily wrote over 20 pages of information, did an outstanding job, and received the highest grade in the class. “THINKING ST YLES” REFLECTION 1. What did you learn about yourself as a “thinker” and how that impacts your teaching? 2. What did you learn about your students as “thinkers” and changes you can make so they are better able to learn from you? CULTURE BUMP THE CULTURE BUMP SYSTEM THEORY, APPROACH AND APPLICATION HANDBOOK ON COLLEGE AND UNIVERSIT Y TEACHING…A GLOBAL PERSPECTIVE CULTURE BUMP Is… Can Apply To… Simply a cultural difference that occurs when people have different expectations about behavior National culture Regional differences Ethnic differences Gender differences Generational differences Socio-economic differences Religious differences OTHER ? A r c h e r ( 1 9 91 ) A DRAMATIZATION OF CULTURE BUMPS… “BRIAN AND AZIZ” The Movie Synopsis: Two young men who study together at an American university, meet outside of class for the first time. Brian and Aziz are classmates in a sociology class… AS YOU WATCH THE MOVIE… At Alternating Tables List and Discuss the Following: Identify the Culture Bumps for Brian Identify the Culture Bumps for Aziz GO TO THE BOARD WITH YOUR GROUP List all of the Culture Bumps You Identified CULTURE BUMP SKILLS 1.Identify and describe culture bumps 3. Find common ground in the situation 2. Recognize and manage your emotional response to the bump 4. Describe exactly what you expect in the situation and the meaning BRIAN AND ND AZIZ…2 ENDING As you watch the second ending…. 1. Look at how Brian manages his emotions differently than before? 2. What is the question that moves them to common ground? 3. Who asks the question that moves them to common ground? 4. What does Aziz say that helps Brian’s expectations to be met? 5. Identify a “new” Culture Bump” in the nd 2 ending? “THE TOOLKIT”…FREE ON CULTUREBUMP.COM