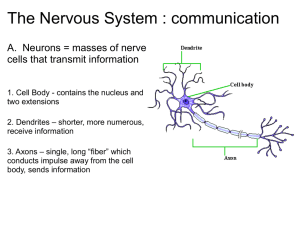
Branches of Vagus Nerve
advertisement

NERVES OF THE NECK Main Nerves of the neck Vagus nerve. Accessory nerve. Hypoglossal nerve. Cervical part of sympathetic trunk. 5. Cervical plexus. 6. Phrenic nerve. 1. 2. 3. 4. Vagus Nerve It is a mixed nerve, it leaves the skull through the jugular foramen. It has two sensory ganglia (superior and inferior ganglia). At its beginning, it is joined by the cranial part of accessory nerve (having motor fibers to pharynx and palate). It descends in the neck within the carotid sheath in between carotid artery and internal jugular vein. It descends in front of the 1st part of subclavian artery, then enters the thorax. Branches of Vagus Nerve 1. Meningeal branch: for posterior cranial fossa. 2. Auricular branch: sensory for the medial surface of auricle, floor of external auditory meatus and adjacent parts of outer surface of tympanic membrane. 3. Pharyngeal branch: (its fibers come from cranial part of accessory nerve). It passes between ext. and int. carotid arteries, and shares in pharyngeal plexus around the wall of pharynx. It supplies all muscles of palate (except tensor palati) and all muscles of pharynx (except stylopharyngeus). Branches of Vagus Nerve 4. Superior laryngeal nerve: Descends toward the larynx and divides into: A. External laryngeal nerve that accompanies the superior thyroid artery then deep to the thyroid gland to supplies the cricothyroid muscle. B. Internal laryngeal nerve that pierces the thyrohyoid membrane and supplies the mucosa of the piriform fossa of pharynx and mucosa of larynx above the level of vocal fold. 5. Cardiac branches: 2-3 nerves that share in formation of cardiac plexus. Branches of Vagus Nerve 6. Right recurrent laryngeal nerve: arises from the right vagus as it crosses the first part of the subclavian artery. It hooks backward and upward behind the artery, then ascends in the groove between the trachea and esophagus. It passes deep the thyroid gland with accompany of inferior thyroid artery. It enters the larynx and supplies all its intrinsic muscles (except cricothyroid) and mucosa of the larynx below the level of the vocal folds and upper part of trachea. (left recurrent laryngeal nerve begins in the thorax). Accessory Nerve It is a motor nerve and consists of cranial and spinal (upper 5 cervical segments) parts. It leaves the skull through the jugular foramen, then the two parts separate again, the cranial part joins the vagus nerve at its inferior ganglion and it is distributed through it (mainly in the pharyngeal plexus and recurrent laryngeal nerve). The spinal part runs downward and laterally, crosses the internal jugular vein, enters deep to sternocleidomastoid, then crosses the posterior triangle (on the levator scapulae muscle) and enters deep to the trapezius muscle. It supplies sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. Hypoglossal Nerve It is a motor nerve that supplies all muscles of the tongue (except palatoglossus). It leaves the skull through the hypoglossal canal, then it has a short course in the carotid sheath (with internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein, glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory nerves). It passes between the internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein (covered by the posterior belly of digastric). It then curves up and anteriorly crossing the first part of lingual artery and is distributed to the lingual muscles. At its beginning, it is joined by branch from the cervical plexus (containing fibers from C1) which supplies some muscles. Branches of Hypoglossal Nerve 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Meningeal branch: for posterior cranial fossa. Descending branch: Containing C1 fibers. It is also called (descendens hypoglossi) and form the superior root of ansa cervicalis. Nerve to thyrohyoid: also contains C1 fibers and supplies the thyrohyoid muscle. Nerve to geniohyoid: also contains C1 fibers and supplies the geniohyoid muscle. Muscular branches of the tongue: supplies all intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue except palatoglossus (from pharyngeal plexus). Cervical sympathetic trunk It extends upward till the base of the skull and below to the neck of the first rib where it continues in the thorax. It lies behind the common and internal carotid arteries (posterior to the carotid sheath). It possesses three ganglia; superior, middle and inferior. Superior ganglion is the larger and longer and lies just below the skull. Middle ganglion lies at the level of the cricoid cartilage (6th cervical vertebra). Inferior ganglion may fuse with 1st thoracic to form stellate ganglion and it lies in front of the neck of the 1st rib. Branches of superior ganglion 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Internal carotid nerve: accompanies the internal carotid artery and enters the carotid canal and form the plexus around the artery. Gray rami communicantes: to upper four anterior rami of the cervical nerves. Arterial branches: with form plexus around the common and external carotid arteries and are distributed with them. Branches to the cranial nerves: join the glossopharyngeal, vagus and hypoglossal nerves. Pharyngeal branches: to the pharyngeal plexus. Superior cardiac branch: to the cardiac plexus in thorax. Branches of middle ganglion 1. 2. 3. 4. Gray rami communicantes: to the anterior rami of the 5th and 6th cervical nerves. Arterial branches: with form plexus around the inferior thyroid artery to be distributed to the thyroid gland. Middle cardiac branch: to the cardiac plexus in thorax. Ansa subclavia: descends in front of the first part of subclavian artery then rotates around it and ascends again to join the inferior cervical (or stellate) ganglion. Branches of inferior ganglion 1. 2. 3. 4. Gray rami communicantes: to the anterior rami of the 7th and 8th cervical nerves. Arterial branches: with form plexus around the subclavian and vertebral arteries to be distributed along them. Inferior cardiac branch: to the cardiac plexus in thorax. Ansa subclavia: mentioned before. Cervical plexus 1. 2. 3. Formed by the anterior rami of the upper cervical nerves. Lies in front of the origin of levator scapulae and scalenus medius muscles. It is covered by the prevertebral fascia. Branches: Cutaneous branches: lesser occipital, great auricular, transverse cervical and supraclavicular nerves. Muscular branches: to prevertebral muscles, sternocleidomastoid & trapezius (proprioceptive), levator scapulae, geniohyoid & thyrohyoid (through C1 fibers that join hypoglossal nerve and infrahyoid muscle (through ansa cervicalis). Phrenic nerve: to the diaphragm. Phrenic nerve It is the only motor nerve supply to the diaphragm. It also contains sensory and sympathetic nerves. It supplies the pleura and peritoneum on both surfaces of diaphragm, mediastinal pleura, pericardium and proprioceptive sensation of the diaphragm. It arises from C3,4,5 and runs over the scalenus anterior muscle (from its lateral to medial borders) and covered by prevertebral fascia and enters the thorax by passing in front of the subclavian artery.