Chapters 31 and 34 - Nervous Endocrine
advertisement

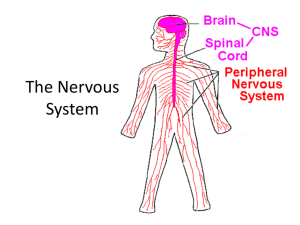
The HUMAN BODY Chapters 31 and 34 Nervous and Endocrine Systems Chapter 31.1 The Neuron • Objectives – Identify the functions of the nervous system – Describe the function of neurons – Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted NERVOUS SYSTEM • Function: – Send and receive messages within the body – Respond to stimuli Systems: -Central Nervous System -Peripheral Nervous System Nerve Cells AKA Neurons • Neuron- basic unit of structure and function of the nervous system • Bundles of neurons form nerves Parts of a Neuron: -Dendrite -Cell Body -Axon -Myelin sheath (speeds up impulses) -Axon Terminals Types of Neurons • Sensory Neurons: Impulse from sense organ to spinal cord/brain • Motor Neurons: Impulse from brain/spinal cord to muscles and glands • Interneurons: Connect sensory and motor neurons Nerve Transmission • Messages are electrical and chemical signals • An electric charge is conducted down a neuron (Dendrite to axon) – Axon is covered in an insulating layer called a myelin sheath to speed up impulses • As it reaches the end of the axon, chemicals (neurotransmitters) are released across the synapse (gap between neurons) to the next neuron • The message continues neuron to neuron Nerve Impulse Videos Neurons: Nerve Cells Describe the path of nerve transmission that allows the batter to hit a ball. Reflexes How is a reflex different from the example of the batter hitting a ball in the previous video clip? Check-in • What is the function of the nervous system? – Send and receive messages and respond to stimuli • Basic unit of structure and function of nervous system – Neuron (nerve cell) • Part of neuron that receives the impulse – Dendrite Check-in • Type of neuron that sends message from sense organ to spinal cord/brain – Sensory neuron • Type of neuron that connects sensory and motor neurons – Interneuron Chapter 31.2 Central Nervous System • Objectives – Discuss the functions of the brain and spinal cord – Discuss the effects of drugs on the brain Central Nervous System • Brain- control center; transmits and receives messages – Cerebrum – Cerebellum – Brain Stem (midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata.) • Spinal Cord- connects brain with rest of the nervous system Brain function fun! • The Brain Addiction and the Brain • Dopamine – neurotransmitter released with pleasurable activities • Addictive drugs cause large release of dopamine (resulting in “high”) • Brain reacts by reducing number of receptors for dopamine normal activities no longer produce the pleasure they once did Check-in • Part of brain that controls balance – Cerebellum • Part of brain that controls heart rate – Brain stem (medulla oblongata) • Part of brain that controls thinking – Cerebrum (frontal lobe) • Part of brain that controls body temperature – Hypothalamus Check-in • Neurotransmitter associated with pleasure – Dopamine • Why do addictive drugs create a cycle in which more and more is needed to get the “high”? – Because brain responds to excess dopamine released when they are taken by decreasing the number of dopamine receptors Chapters 31.3 and 31.4 Peripheral Nervous System & Senses • Objectives – Discuss the functions of the sensory division of the peripheral nervous system – Identify the five sense organs and the sensory receptors associated with each – Discuss the functions of the motor division of the peripheral nervous system Peripheral Nervous System • Link between the central nervous system and the rest of the body – Network of nerves throughout the body *Made of many neurons Sensory Division • Transmits impulses from sense organs to central nervous system • Uses sensory receptors – – – – – Chemoreceptors Photoreceptors Mechanoreceptors Thermoreceptors Pain receptors SENSES • Vision- eyes • Hearing and Balanceears • Smell and taste- nose and mouth • Touch- skin Motor Division • Transmits impulses from central nervous system to muscles or glands Somatic nervous system: Autonomic nervous system: regulates activities under regulates activities that are conscious control automatic or involuntary Check-in Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Division Motor Division Impulses from sense organs to CNS Impulses from CNS to muscles/glands Somatic Autonomic Conscious control Involuntary control Check-in • Hearing/balance • Chemoreceptor • Smell • Mechanoreceptor • Taste • Pain receptor • Touch • Photoreceptor • Vision • Thermoreceptor Chapter 34.1 and 34.2 Endocrine System • Objectives – Describe the structure and function of the endocrine system – Identify the functions of the major endocrine glands ENDOCRINE SYSTEM • Function- produce chemical messengers (hormones) from glands to regulate certain body activities What are hormones? Glands? • Hormone: chemical messenger • Gland: organ that produces and releases a substance Exocrine: release substances out of body or into digestive tract Endocrine: release hormones directly into blood Glands of Endocrine System Head Region: -Pituitary: controls other glands -Pineal Gland: regulates sleep and wake cycle, along with other basic functions -Hypothalamus: controls secretions of the pituitary gland (link between endocrine and nervous system) Glands of the Endocrine System Neck Region: -Thyroid: regulates metabolism (rate at which food is turned into energy) -Parathyroids: maintains homeostasis in blood calcium levels Glands of the Endocrine System Abdominal Region: -Adrenals: helps body prepare for and deal with stress (fight or flight) -Pancreas: Releases insulin and glucagon to regulate level of glucose in blood Glands of the Endocrine System Reproductive Region: -Ovaries (females): produce eggs and estrogen to create female characteristics -Testes (males): produce sperm and testosterone to create male characteristics Check-in • Controls the pituitary gland – Hypothalamus • Regulates metabolism – Thyroid • Regulates sleep/wake cycle – Pineal • Controls other glands – Pituitary Check-in • Produces eggs and estrogen – Ovary • Helps deal with stress (fight or flight) – Adrenal • Maintain blood calcium levels – Parathyroid • Regulates blood glucose/sugar levels – Pancreas