PPT: Hinduism
advertisement

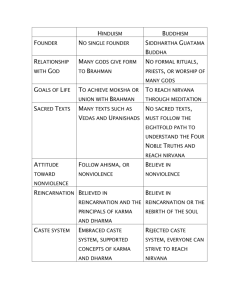
Of the five major religions; Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism place in chronological order in which they first appeared http://www.mapsofwar.com/ind/history-of-religion.html • Aryans • 2000 B.C. – 1500 B.C. • Migrated to the Indian Subcontinent from Europe • Aryans settled and gave up their nomadic ways • Created a civilization around the Indus and Ganges Rivers http://www.mrsk.net/harappan%20civilization.html • Vedas- hymns, chants, religious teachings which helped us understand the Aryans • Nomadic herders • Warriors on chariots • Loved food, drink and dice games http://veda.wikidot.com/hinduism • Polytheistic – Gods & Goddesses embodied natural forces • Indra (God of war) • Varuna (God of order and creation) • Agni (God of fire & the messenger) Aryan Religion started to change…. Brahman A single spiritual power that resided in all things and was above the gods of the Vedas Mystics Seek direct communication with divine beings through meditation & yoga Aryans started to encounter other people and their traditions/culture The cultures started blend which is called acculturation http://blogs.discovermagazine.com/gnxp/tag/population-genetics/ Stories helped blend the cultures Together Mahabharata Epic battle over the Ganges River Moral lesson: Importance of duty over personal desires & ambitions http://www.indianetzone.com/2/lord_indra.htm Ramayana The fantastic deeds of Rama & his wife Sita Moral lesson: virtue & loyalty Apply the five themes of geography to the Indus and Aryan Civilizations Relative Location India Subcontinent, Southern Asia Place Mountains, Rivers, Plateaus Polytheistic, Farmers, Traders Movement Walking, Boat, Nomads at first Human Environment Interaction Farming Region Himalayan Mountain Region, India First organized religion http://eslsocialstudiesexploratorium.blogspot.com/2010/12/aim-what-are-origins-of-hinduism-and.html Brahman-the one true god, supreme spirit • Present in all creations • Formless • Concrete forms of Brahman • Brahma, the creator • Vishnu, the preserver • Shiva, the destroyer 6. Moksha 5. Death Moksha is the main goal of existence (Heaven) • Union with Brahman • Cannot be achieve in one lifetime • Reincarnation- rebirth of soul in another bodily form 1. Reincarnation 3. Karma • To help achieve goal one must obey the laws of Karma • All actions of a person’s life affects his or her fate in the next life • Wheel of Fate---continuous reincarnation Escaping the Wheel of Fate • Dharma- Religious and moral duties of an individual 6. Moksha 5. Death • Ahimsa- Practice of non violence 1. Reincarnation 4. Ahimsa 2. Dharma 3. Karma Scriptures • Vedas • Epic Stories • Other literature Hindu Caste System http://akarlin.com/2012/08/14/the-puzzle-of-indian-iq-a-country-of-gypsies-and-jews/