Buddhism and Hinduism
advertisement

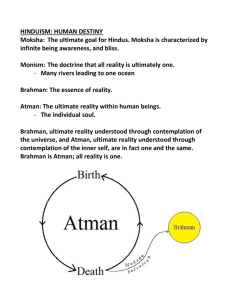
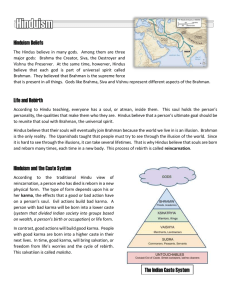
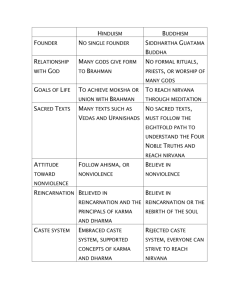
Hinduism Background Hindu practices come from the beliefs of many groups in India Aryans migrated to India brought a collection of myths of their gods Aryan priests could sing long hymns from memory, each hymn for a different ritual 837 million followers worldwide (13 %) Over 80 % of India’s population Older than Christianity, Buddhism, & Islam No single founder Unique to India Why didn’t it spread? Geographical Barriers Doesn’t seek converts Monotheistic or Polytheistic God is one-but goes by many names Brahman-all of the universe is a part of Brahman All other divinities are aspects of the absolute and unknowable Brahman. All these deities are but Manifest forms (attributes and functions) of the impersonal Brahman Hindu Trinity Brahma – Creator Vishnu – Preserver Shiva - Destroyer Sacred Texts Priests gathered the hymns into four collections called Vedas Rig-Veda - most ancient and most important (has 1028 hymns of praise) Upanishads - collection of essays that try to interpret and explain the Vedic hymns Bhagavad Gita – ethical ideas central to Hindus Basic ideas of the Upanishads One true reality is Brahman mighty spirit that creates and destroys unchanging all powerful, spiritual force Power beyond many gods Too complex for people to understand Brahman is a unifying and all powerful spirit One aspect of Brahman is the Self (soul) called Atman Atman is everywhere Atman is your essential self Nothing that lives ever dies entirely when a living thing dies, its inner self is reborn into another form (reincarnation) Reincarnation = Rebirth (samsara) All wise Hindus must seek to reach a state of perfect understanding called moksha the inner self that reaches moksha will never suffer another reincarnation In moksha, the self disappears to merge with Brahman Maya The power of Brahman, the creative aspect of God This world Senses, pain, suffering Cosmic Illusion Karma and Dharma Hindus believe in an ethical law of cause and effect called Karma Moral behavior in one life guaranteed rebirth into a higher class Immoral behavior would drop a soul to a lower class Good karma = performing your dharma Dharma - set of duties and obligations of each caste Caste System According to the Rig-Veda, four different groups of people were created from the body of a Hindu God Brahmins Kshatriyas Vaishyas Shudras Brahmins created from the God’s mouth priestly class and highest group in Indian society Kshatriyas created from the God’s arm ruler and warrior class Vaishyas created from the God’s leg landowners, merchants and artisans Shudras created from the God’s feet servants and slaves Hindus call these groups within society jatis (castes) Ritual purity was the basis for rankings the castes Higher castes are purer than lower castes Lowest group in society were outside the caste system (called untouchables or outcastes) And we too are manifest forms of God! “We are not human beings having spiritual experiences; We are spiritual beings having a human experience!” “That art Thou” Hinduism is about recognizing the all pervasiveness of the divine