3. Energy Efficiency - science
advertisement

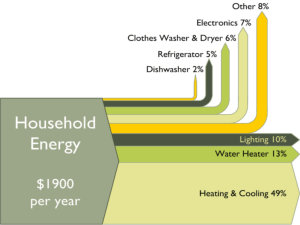
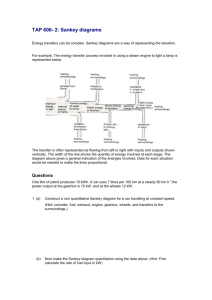
13 April, 2015 Energy Transformations Objectives Understand that energy can change form and be able to draw diagrams to represent this. HSW: AF3: Select appropriate methods for presenting scientific data. Used before in: lesson 1 – Energy Types Will use again in: PLTS: Used before in: Will use again in: Keywords Energy, Transfer, Transformation, Sankey, Useful, Wasted. 1 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2006 Outcomes: All students should be able to: • Draw energy transfer diagrams that describe energy transformations. • Interpret Sankey diagrams and label useful and wasted energy. Most students should be able to: • Use Sankey diagrams to work out the amount of energy transformed by a device into different types. • Draw accurate Sankey diagrams using graph paper. Some students should be able to: • Use a Sankey diagram to calculate the efficiency of a device. 2 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2006 3 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2006 Energy transfer in a television An energy transfer diagram shows the input and output energies for a device. This includes all the useful and wasted forms of energy. For example, in a television: light electrical sound heat 4 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2006 Energy transfer in a radio What are the main energy transfers in a radio? (Don’t forget the wasted energy.) electrical 5 of 35 sound heat © Boardworks Ltd 2006 Energy transfer in a car engine What are the main energy transfers in a car engine? (Don’t forget the wasted energy.) kinetic chemical sound heat 6 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2006 Identifying energy transfers 7 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2006 How can we represent energy transfers? All the energy transfers (useful and wasted) that are associated with a device can be represented by a Sankey diagram. A Sankey diagram uses arrows to represent all the output energies. Filament light bulb 100 J 10 J electrical light energy energy (input) (output) 90 J heat energy (wasted) The thickness of each arrow is proportional to the amount of energy involved at that stage. Energy efficient light bulb 20 J 10 J electrical light energy energy (input) 10 J (output) heat energy How does the energy use in (wasted) these light bulbs compare? 8 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2006 TASKS ALL 1) Use the keywords to copy and complete the following: • Energy ………… diagrams can show how energy moves from one place to another and ……… type. They can also show the useful and …… energies. • Sankey Diagrams show ……… that represent the amount of energy being transformed so that you can easily see the …………. of useful and wasted energy and calculate the …………. of a device. wasted transfer efficiency arrows changes percentage MOST 2) Draw an energy transfer diagram for a car engine and label the useful and wasted energies. Use the following words to help: Chemical, Heat, Sound, Kinetic 3) Do questions 1 – 3 on pages 46 & 47 of Milner Text Book SOME 4) Do question 4 and 5 on page 47 of the Milner Text book and calculate the efficiency of each engine. Can you think of a good way of displaying this data? 9 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2006 Plenary – The Big Q: How efficient is a Power Station? • • • Describe the following energy transfer using appropriate diagrams and calculations. Burning Coal produces 100 Mega Joules of Energy. 65 Mega Joules is transformed into electrical energy in a power station but the rest is wasted as heat. All students should be able to: • Draw energy transfer diagrams that describe energy transformations. C Most students should be able to: • Use Sankey diagrams to work out the amount of energy transformed by a device into different types. • Draw accurate Sankey diagrams using graph paper. B Some students should be able to: • Use a Sankey diagram to calculate the efficiency of a device. • A Now swap with your partner and mark it. 10 of 35 © Boardworks Ltd 2006





![Direction_and_Scale[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005432475_1-80ce3065f13008250a8cdec135db9846-300x300.png)


