Chap 3 sect 1 cont.ppt
advertisement

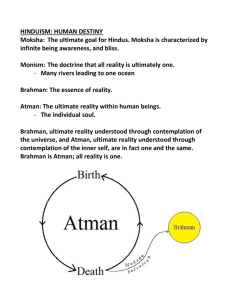
Hinduism Mr. Tackabury Hinduism Has no single founder, and no single sacred text Religion started when the Aryans (nomadic people) blended with the Indus valley people Many Gods, and many forms of worship Many gods-or one? Hindu thinkers came to believe that everything in the universe was part of a unchanging, all powerful spiritual force called Brahman Most important Hindu Gods: -Brahman- the creator -Vishnu- the preserver -Shiva- the destroyer *each represents aspects of the Brahman* Would you want any of this? The Goal of life: Every Hindu has an essential self called atman (really just another name for Brahman) The ultimate goal of existence is to achieve Moksha (union) with Brahman In order to accomplish this: -Individuals must free themselves from selfless desires -reincarnation-rebirth of the soul in another bodily form -allows people to work towards Moksha through several lifetimes Karma and Dharma Come closer to achieving Moksha by obeying the law of Karma Refers to all the actions in a person's life that will affect his/her fate in the next life To Hindus, all existence is ranked: -Humans are the closest to Brahman then comes animals, plants, and objects like rocks and water Live a good life, earn good Karma=rebirth into a higher level of existence Live a bad life= reborn into suffering Dharma- the religious and moral duties of an individual Duties depend upon a person's class, occupation, gender, or age Ahimsa (non-violence) To Hindus all people and things are aspects of Brahman and should therefore be respected