Trade defined: - High School Geography
advertisement

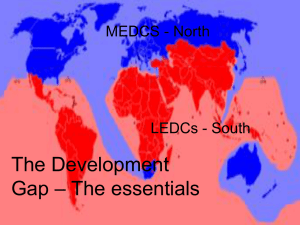
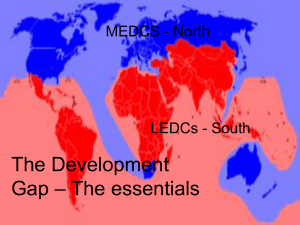
Trade Mini Peer Presentations Group 1: Definition & Why is trade necessary? Trade balance, surplus & deficit Group 2: Problems faced by LEDC countries & trade imbalance Group 3: Trade blocs, tariffs, quotas Group 4: Free trade & Arguments for and against Activity: Each group will present on their section – it is also really important to take notes throughout these presentations - this is all really crucial information or the semester exam Come up with 5 questions to make sure everyone has understood your presentation – you will ask these at the end Presentation points to remember: Engage the audience Try not to use notes Everyone in the group must participate Think of an interactive and imaginative way to get the information across Trade defined: The exchange of goods and services for money Discuss with a partner, and write a few sentences explaining why trade is necessary Why trade is necessary ? No country is self sufficient in the full range of raw materials that are needed by its inhabitants. To try to achieve this, countries must trade with each other Trade is the flow of commodities from producers to consumers, and it is important in the development of a country. Countries that trade with other countries are said to be interdependent Trade Surplus & Deficit If the value of a countries exports is more than its imports it has a trade surplus and if the value of the imports is more than the exports then it is a deficit Trade balance is the difference in value between a countries imports and exports Activity: Work out the trade balance for countries A, B, C & D, and state whether they have a trade surplus or deficit 1) Country A exports $560 billion worth of goods to its trading partners each year. In return it imports $290 billion worth of goods each year. Calculate the trade balance of this country. __________________________ What sort of balance of trade will this country have?____________________ 2) Country B exports $200 billion worth of goods to its trading partners each year. In return it imports $290 billion worth of goods each year. Calculate the trade balance of this country. __________________________ What sort of balance of trade will this country have?____________________ 3) Country C exports $720 billion worth of goods to its trading partners each year. In return it imports $400 billion worth of goods each year. Calculate the trade balance of this country. __________________________ What sort of balance of trade will this country have?____________________ Trade deficits & surpluses Trade deficits – does it damage a countries economy? The successful American business man and investor Warren Buffett was quoted in the Associated Press (January 20, 2006) as saying "The U.S trade deficit is a bigger threat to the domestic economy than either the federal budget deficit or consumer debt and could lead to political turmoil... Right now, the rest of the world owns $3 trillion more of us than we own of them." If a country has a deficit – then it is paying other countries a lot of money- then those countries can use that money to buy shares in companies from the country they have traded with Trading relationships should be balanced…… According to the economist, John Maynard Keynes - "If the economic relationships between nations are not, by one means or another, brought fairly close to balance, then there is no set of financial arrangements that can rescue the world from the impoverishing results of chaos." Difficulties faced by LEDCs What are the trade problems for LEDCs? Countries that relay on one commodity can be a problem because: Prices and demand for these products fluctuate annually – and the price paid for these commodities is often fixed by MEDCs Overproduction or world recession can also impact prices of these goods, also stocks of that particular commodity (e.g. a mineral) can also become exhausted Most exports are bought by TNC’s (transnational corporations) so the profits don’t go back to the producers (its not fair trade) LEDCS are not selling high value goods – there is very little value added to the good through secondary sector industry (manufacturing the goods) Reasons for imbalance of trade between MEDC and LEDC counties MEDC’s process primary goods – and add value to them -MEDCs then export these manufactured goods – which are high in value, whereas LEDCs only have limited primary goods to sell MEDCs also have the high tech quaternary industries, and possess the skills and technology to develop high value products MEDCs retain profits within their countries and the profits don’t go back to the LEDCs LEDCs often only relay on the export of two or three products Trade is hindered by poor internal transport networks Who has the largest share of the worlds trade? Examples of countries imports and exports You can clearly see that Sierra Leone – an LEDC really relies on the export of minerals, whereas MEDCs exports and imports are more similar to each other Trading Blocks Nations belonging to a mutual trade pact and agree to give each other reduced trade tariffs while imposing trade barriers and restrictions to nonmember nations. Some trade blocks such as the EU have also developed close political ties, as well as a common currency, the Euro Within these trading blocks countries trade with each other freely. This makes for a large market, increasing the number of customers for businesses, and strengthen the alliances between those nations An alliance is an agreement between two or more parties, made in order to advance common goals and to secure common interests Trading Blocks Make sure you know some of these trading blocks! Tariffs & Quotas Tariffs are taxes or custom duties paid on imports. The exporter has to pay a percentage of the value of the goods to the importer. Tariffs can be used to raise money, and they increase the price of imported goods in order to make them more expensive, and less competitive Tariffs increase the costs of imports (they may be imposed to by countries to encourage a trade balance) or protect home made products Quotas limit the amount of goods that can be imported. Quotas tend to restricted to primary goods to they work against LEDCs These both go against free trade Free Trade Free trade: Trade between nations without protective customs tariffs and quotas. Discuss the arguments for and against free trade Arguments for free trade Arguments against free trade Free Trade: Arguments for and against Free trade: Trade between nations without protective customs tariffs and quotas. Arguments for free trade Arguments against free trade 1) It's important to protect the economy of your country – free trade can mean that products will 1) It will deliver the greatest be bought from overseas rather than made at Good to the greatest amount home Of people (the utilitarian argument) 2) Other nations might treat their workers who 2) Countries that depend on make products they export unfairly – their rights each other for trade, rarely go cannot be guaranteed. to war ( this is called the Dell Theory 3) Foreign companies can buy up companies of Conflict Prevention) within ones own country- this could be seen as a threat to national security 3) Countries can develop through Trading- exporting what they have, 4) Free trade does not mean fair trade- and And importing what they don’t have countries producing primary products don’t benefit as much as the countries manufacturing them The world is spiky! Check out the distribution of indicators throughout the world: E:\CURRENT\IB Psych\IB Psy G 12 08_09\comparitive http://creativeclass.com/rfcgdb/articles/other-2005The%20World%20is%20Spiky.pdf Quick Quiz 1) Why can trade deficits be a big problem for nations? 2) What did John Maynard Keynes say about the importance trade balance? 3) Who has the largest share of the worlds trade? 4) What are tariffs? 5) What are quotas? 6) What are trading blocks? 7) Identify three trade blocks 8) Identify two arguments in support of free trade and three arguments against free trade