Why out classroom
advertisement

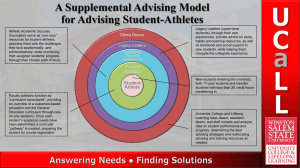
Approaches for students engagement outside the classroom Learning out of the classroom is the name given to all events/activities that occur outside the classroom both on and off the college site .this includes short visits into the community as well as visits to factories, offices, neighbourhood science centres as well as sport like football, basketball.....etc Learning out of the classroom is important. But why? • • • • • • Expensive Difficult Special skills Safety Time Environment So why do we do it? Reasons: • There are some things students need to learn that can only be learnt out of the classroom. • There are some things that students need to learn that are better learnt out of the classroom in terms of knowledge/understanding, skills, values. But is this TRUE ? Why should we learn out of the classroom? So – out of classroom learning • Can be better • Provides a unique context for learning • Is happening • Is supported • Has a policy But there is one big challenge Providing high quality learning When you take medical students outside the classroom it does not automatically mean they learn anything. A high quality lesson about immunization inside the classroom is better than a poor quality lesson in PHC . “The aim of teaching is simple: it is to make student learning possible” 10 I hear, and I forget I see, and I remember I do, and I understand. I hear, and I forget I see, and I remember I do, and I understand. Traditional Learning was Teacher-directed Direct Instruction Knowledge Content Basic Skills Theory Curriculum Individual Classroom Summative Assessed ( Giving only main point) Learning for School A Project Learning Classroom is Teacher-directed Direct Instruction Knowledge Content Basic Skills Theory Curriculum Individual Classroom Summative Assessed ( Giving only main point) Learning for School A Better Student-directed Collaborative Construction Skills Process Higher-order Thinking Practice Life Skills Group Community Formative Evaluation ( Continuous) Learning for Life Balance Medical Education in the Future Significant changes in the process of medical education 1. 2. 3. 4. Lectures decreased Students as instructors Use of small groups Teachers as facilitators Medical Education in the Future 5.Changes in evaluation methods 6.Texts updated 7.Information management skills 8.Interactive laboratories and clinical simulations Simulation in Action pictures Simulation in Action Simulation can be used to foster teamwork and focus on common educational objectives, thereby reducing duplication of cost and time associated with training. 85% agreed that the simulated training was useful or extremely useful and would return for more training. Two Components of Student Engagement 1. What students do -- time and energy devoted to educationally purposeful activities 2. What institutions do -- using effective educational practices to induce students to do the right things Two Components of Student Engagement Student Success Advising Student Engagement Curriculum Redesign Advising Advising Advising Critical Thinking Collaboration Self-Assessment Communication Student Engagement Student Engagement Curriculum Redesign Curriculum Redesign OBJECTIVES 1- To develop an awareness of the positive impact that experiences outside the classroom can have on Education for Sustainable Development; 2- To develop an understanding of the planning and risk management required for teaching and learning outside the classroom; 3- To identify appropriate strategies for teaching and learning outside the classroom. 4- students need to learn in a variety of context in order to gain the knowledge, skills, take responsibility for their own safety, form positive relation with teachers Activities of LEARNING OUTSIDE THE CLASSROOM 1-Approaches to learning outside the classroom 2- Planning for learning outside the classroom 3- Risk management Difficulties ON LEARNING OUTSIDE THE CLASSROOM 1-Organisational factors such as the difficulty of supervising a large group of students and providing them with the assistance they may need. 3-Time needed to plan a worthwhile field trip. 4-Cost of transport and accommodation, if required. 5- Lack of detailed knowledge of the locality. 6- Safety of the students. 7- Lack of necessary skills in students. Type of student engagement outside the classroom: A- On-site in the college ground e.g sports , painting B- Off-site short visit within college hours e.g:museum, art gallery.PHC,research center, blood bank,geriatric home…..etc. C- Off-site day trips which may extent out of college hours e.g Farm visit ,field trip, data collecting D- Off-site- residential multi-day trips e.g trip to another region Activity 1 :APPROACHES TO LEARNING OUTSIDE THE CLASSROOM Two common approaches are (i) Field Teaching and (ii) Field Research. Field Teaching A-Study of topic or theme in class. Teacher talk, textbook study, note taking, slide viewing, videos, etc. B-Field observations (often teacher directed). Recording of information in the field. Some field interpretation. C-Back in the classroom – further interpretation and explanation together – writing up field report. Field teaching can improve and influence: • attitudes, beliefs and self-perception: independence, confidence, self-esteem, self-control, personal effectiveness, • interpersonal and social skills: social effectiveness, communication skills, teamwork. Field Research 1-Identification of a problem as the result of direct observations; or from class work; or from special interests of students. 2-Formulation of an hypothesis as a result of reading, discussion, thinking. 3-Field activities to collect data to test hypothesis. 4- Data analysis – processing information. 5- Hypothesis testing – accept or reject. 6- Discussing and writing up of possible ways to solve the originally identified problem using information gathered in the field. This approach represents an inductive (life long)approach to learning. It involves observation, description and explanation with a problem solving focus. ACTIVITY 2: PLANNING FOR LEARNING OUTSIDE THE CLASSROOM. Generally there are three stages to effective learning outside the classroom: 1-Preparation in class (pre-field stage); 2- The fieldwork itself, (field stage); and 3- Follow-up in class (post-field stage). PREPARATION 1-Pre-visit the site(s). 2- Develop clear objectives for the study. 3- Plan pre-field study learning experiences and prepare students to see fieldwork as active learning. 4- Prepare fieldwork activities and resources. 5-Decide how much time is required for the tasks and for travel to and from the site. 6-Identify appropriate student/teacher ratio. 7-Identify all possible risks and manage them appropriately, ie. think through possible risks and how you will address them. ACTIVITY 3: RISK MANAGEMENT Planning to minimize risks to the health and safety of students is an integral principle for learning outside the classroom. Risk management is the name given to the identification, assessment and reduction of these risks. Being aware of potential risks helps us to think deeply about what we are planning to do, why we are doing it, and whether we have the skills to lead the activity safely. Key skills for reducing the level of risk before and during activities, include: A-Directive Leadership Use directive leadership in order to reduce the risks of certain activities. Always make sure any direction is accompanied with a reason so that individuals can learn from the experience. For example, it is appropriate to ask students to: 1-Move away from rock pools that are deep and have an unsafe walking area; 2-Put on extra clothing if they are cold and exposed to the wind; and/or 3-Work together in pairs and not to move away to other areas before checking with a supervisor. B-Talking About Potential Risk This is a very important technique for reducing risks both before and during activities. It is not sufficient for a teacher to be the only one possessing the knowledge of plans. Good leaders share with the students the planned activity , for example: 1-Telling the group the name of the place they will be going to for the day, and giving them maps of the area. 2-Tell students what they should do if they are separated from the party. 3-Tell students who is carrying emergency equipment and who has first aid skills. Take Some Risks! 39 4/13/2015