Transportation Planning Lecture
advertisement
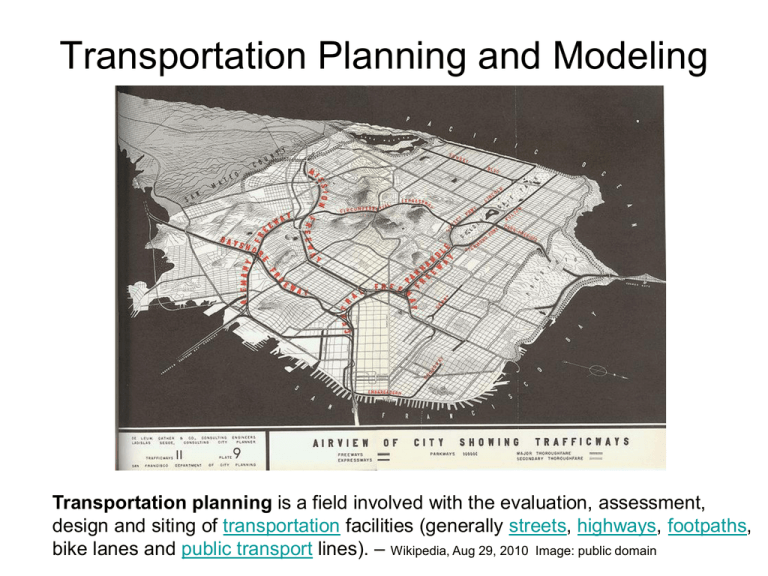
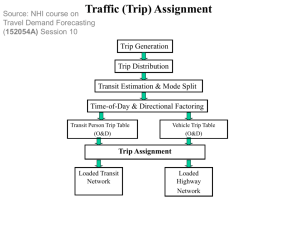
Transportation Planning and Modeling Transportation planning is a field involved with the evaluation, assessment, design and siting of transportation facilities (generally streets, highways, footpaths, bike lanes and public transport lines). – Wikipedia, Aug 29, 2010 Image: public domain Rational Planning Method – defining goals and objectives, – identifying problems, – generating alternatives, – evaluating alternatives, and – developing plans Image: GNU Free Documentation License Daniel Schwen, the copyright holder Des Moines MPO http://www.dmampo.org/ Planning Options • Short run – – – – TSM TDM Access Mgmt. Congestion Mgmt. • Long Run – Construction – Land use • Future? – Pricing – Technology (ITS, fuels) Congestion Pricing • http://www.streetfilms.org/archives/campaign-for-new-yorks-future-congestion-pricing/ Why we don’t use congestion pricing: http://planningresearch.blogspot.com/2007/03/m anville-on-why-we-dont-use-congestion.html Travel demand modeling • Evaluating alternatives requires – Estimated travel demand (trips) – Estimated trip lengths – Estimated modal shares – Estimated travel speeds – Estimated travel delays – Estimate air quality, noise and energy impacts • Need a systematic process “Four” step model sometimes omitted optional Data collection • Demographic/Socioeconomic • Transportation system • Travel behavior/propensity/desires – Surveys Study area/zone slide Travel Demand Modeling (Forecasting) • What is travel “demand”? • Three factors – Land use – Socioeconomics and demographics – Transportation services (TTYP name 3 characteristics of these factors that affect demand) Trip Generation • Determine number of “trip ends” • Methods – Cross Classification (tables) – Rates based on activity units (ITE) – Regression Trip Distribution • Determine origin and destination of trips • Methods – Gravity model (Need a good shortest path algorithm) – Growth factor models Find the shortest path from node 1 to all other nodes (from Garber and Hoel) 1 1 2 4 3 10 4 14 6 7 3 11 2 15 Yellow numbers 3 represent link travel times in minutes 8 1 3 1 4 4 1 1 3 2 13 6 3 2 3 2 9 3 4 2 5 2 12 1 4 16 FINAL 1 1 2 4 3 4 9 2 5 6 6 4 9 13 10 6 4 7 7 11 8 7 9 12 8 14 1 0 15 8 16 1 0 http://mitchlanaillustration.blogspot.com ©1995 - 2008, AMERICAN PHYSICAL SOCIETY APS encourages the redistribution of the materials included in this newspaper provided that attribution to the source is noted and the materials are not truncated or changed. From: Davison E. Soper Univ of Oregon Mode Choice (Split) • Which mode (transit, walk, carpool,drive alone, …) will be used? • Methods – Direct generation – Trip end models – Trip interchange models Traffic Assignment • Which route will the trips take? • Methods – Minimum path (distance or time) – Capacity restrained • Need a good shortest path algorithm