AntebellumSouth
advertisement

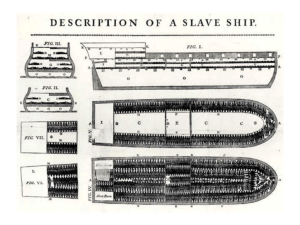
• Agenda EQ: What political, social, and economic factors caused the division between the North and South? Warm-Up: What are two main characteristics of the North in the 1800’s and what do you think are two characteristics of Southern society? MLQ: How can we learn about Antebellum Southern Society by determining important facts and details from an expository reading passage? Vocabulary Socialite: a socially important person that can influence others Diverse: having a variety or different elements or characteristics Michelle Obama is a leading socialite in American society. I.S.61 has a diverse group of students, which makes the school such a wonderful place. Work period: Students will: 1) In your group read tiered passage 2) Answer tiered questions Share: Share answers Closing: Summary of lesson H.W. Read Growing Differences Worksheet and Answers Questions Characteristics of the Antebellum South 1. Primarily agrarian. 2. Economic power shifted from the “upper South” to the “lower South.” 3. “Cotton Is King!” * 1860 5 mil. bales a yr. (57% of total US exports). 4. Very slow development of industrialization. 5. Undeveloped financial system. 6. Inadequate transportation system. Southern Society and Culture • Southern society was made up of many different kinds of people, including white plantation owners, yeoman farmers, poor whites, slaves and free African Americans. • Most of the economy was on based farming and most farms were small, however large plantation did exist and dominated southern society. The planter aristocracy - a small percent of southern society - controlled the social, political, and economic power of the south • In 1860, 25% of all Southerners owned slaves. • Of that 25% – 52% owned 1-5 slaves – 35% owned 6-9 slaves – 11% owned 20-99 slaves – 1 % owned 100 or more slaves • Those who owned 20 or more slaves was 3% of the entire white population controlled the social, political, and economic power of the South. Southern Society (1850) 6,000,000 “Slavocracy” [plantation owners] The “Plain Folk” [white yeoman farmers] Black Freemen 250,000 Black Slaves 3,200,000 Total US Population 23,000,000 [9,250,000 in the South = 40%] Southern A griculture Plantation Life • Few families had plantations with many slaves, these owners were very powerful especially in politics. • Male planters were main job was to raise crops and supervise the slaves working on the plantation. • These powerful plantation owners showed off their wealth by living in beautiful mansions and having grand parties. • The wives of plantation owners oversaw the raising of their children, supervised the slaves working in the household, and planned social events. Tara – Plantation Reality or Myth? Hollywood’s Version? T he Southern “Belle” A Real Georgia Plantation Slaves Picking Cotton on a Mississippi Plantation A Slave Family Slaves posing in front of their cabin on a Southern plantation. A Real Mammie & Her Charge Yeoman Class and Poor White Families • Most white southerners were yeoman, owners of small farmers. • Most Yeoman owned few slaves if they did they worked along side them or none at all. • Most farms were about 100 acres. • All family members worked whether it was in the field or in the home. • The poorest white southerners lived on the land that could not grow crops, so they hunted, fished, raised small gardens. Free African Americans • Although, most African Americans in the south during the early 1800’s were slaves, approximately 250,000 free African Americans lived in the region. • Free African Americans lived in both rural and urban settings, most work as paid laborers on farms or plantations. • Free African Americans faced much discrimination, they could not vote, travel freely, or hold most jobs. Southern Population Work Period • • • • • • • Red Group 1) What were the largest and smallest groups of southern society? 2) Which group held the most power and why? 3) What was life like for slaves working on plantations and how did they try to ease their hardships? Green Group 1) What were some of the duties of domestic slaves? 2) What were some of the negative aspects of being a domestic slave? 3) What were some of the positive aspects of being a domestic slave? Blue Group 1) How did enslaved Africans gain their freedom? 2) What jobs were available to free African Americans in the south? 3) What type of discrimination did free African Americans face living in the south during the 1800’s? Skills Task Vocabulary- select two unknown vocabulary words and look them up in the dictionary and write two sentences that describe the topic in your reading passage Main Idea- Summarize the three most important facts of your reading passage Cause and Effect- List two causes and their effects from your reading passage • Agenda EQ: What political, social, and economic factors caused the division between the North and South? Warm-Up: Answer questions on quiz worksheet MLQ: How can we learn about the cruelties of slavery by analyzing poetry? Vocabulary Atrocity: behavior or an action that is wicked or ruthless Season: to make or become mature or experienced The Holocaust was an atrocity. To become a seasoned athlete, you must practice. Work period: Students will: 1) In groups analyze the poem “Strange Fruit” 2) Answer tiered questions Share: Share answers Closing: Summary of lesson and MLQ H.W. Answer Questions on Slavery Worksheet Capture and the Middle Passage • After capture, Africans were packed tightly into slave ships. • The death rate of the “passengers” was 50%. Destination, Auction, and Seasoning • Slaves were auctioned off to the highest bidder. • Slaves were put through a process “seasoning” to get them ready for work. • They learned an European language, were named an European name, and were shown labor requirements. The Beginnings of Slavery in the United States • The Portuguese and Spanish had already brought Africans to South and Latin America. • In 1619, the first Africans were brought to the colony Jamestown, Virginia by the Dutch. Slave Auction Notice, 1823 Slave Auction: Charleston, SC-1856 T he Ledger of John W hite Matilda Selby, 9, $400.00 sold to Mr. Covington, St. Louis, $425.00 Brooks Selby, 19, $750.00 Left at Home – Crazy Fred McAfee, 22, $800.00 Sold to Pepidal, Donaldsonville, $1200.00 Howard Barnett, 25, $750.00 Ranaway. Sold out of jail, $540.00 Harriett Barnett, 17, $550.00 Sold to Davenport and Jones, Lafourche, $900.00 Slave Accoutrements Slave Master Brands Slave muzzle Slave Accoutrements Slave leg irons Slave shoes Slave tag, SC Anti-Slave Pamphlet Reasons for Using Enslaved African Labor • Proximity-It only took 2-6 weeks to get to the colonies from the Caribbean at first. • Experience-They had previous experience and knowledge working in sugar and rice production. • Immunity from diseases-Less likely to get sick due to prolonged contact over centuries. • Low escape possibilities-They did not know the land, had no allies, and were highly visible because of skin color. Slaves and Work • Most enslaved Africans Americans lived and worked on plantations in the fields, planting, plowing, and picking crops, such as cotton and tobacco. • Most plantation owners used the gang-labor system, meaning that all slaves worked on the same task at the same time. • Usually, slaves work long hard hours, from sunrise to sunset and usually didn’t get any breaks and lived in poor conditions. • Slaves were often punished if they could not keep up with the work or disobey their owners in anyway. • Some slaves worked in the planter’s homes and these slaves had better food, clothing, and shelter. • Some slaves worked skilled jobs such as blacksmithing or carpentry. Sometimes slaves were allowed to keep some of the money they earned, this allowed save up money to buy their freedom. Punishment • Slaves were often brutally punished for misbehaving. • Punishments included: whipping, branding, being sold, gagged (silence), and other torturous methods were used. Slave Culture • Many African Americans found comfort in their community and culture. • Family was the most important aspect of the slave community. • African parents keep their heritage alive by telling folktales (stories with a moral) to the children, which helped them cope with the harsh conditions of slavery. • Religion also played an important part of the slave culture. Most slaves were Christian by the 1800’s. They sang religious song called spirituals. The Slave Auction The Slave Auction By Frances Ellen Watkins Harper 1825–1911 The sale began—young girls were there, Defenseless in their wretchedness, Whose stifled sobs of deep despair Revealed their anguish and distress. And mothers stood, with streaming eyes, And saw their dearest children sold; Unheeded rose their bitter cries, While tyrants bartered them for gold. And woman, with her love and truth— For these in sable forms may dwell— Gazed on the husband of her youth, With anguish none may paint or tell. And men, whose sole crime was their hue, The impress of their Maker’s hand, And frail and shrinking children too, Were gathered in that mournful band. Ye who have laid your loved to rest, And wept above their lifeless clay, Know not the anguish of that breast, Whose loved are rudely torn away. Ye may not know how desolate Are bosoms rudely forced to part, And how a dull and heavy weight Will press the life-drops from the heart. Southern trees bear a strange fruit, Blood on the leaves and blood at the root, Black body swinging in the Southern breeze, Strange fruit hanging from the poplar trees. Pastoral scene of the gallant South, The bulging eyes and the twisted mouth, Scent of magnolia sweet and fresh, And the sudden smell of burning flesh! Here is a fruit for the crows to pluck, For the rain to gather, for the wind to suck, For the sun to rot, for a tree to drop, Here is a strange and bitter crop. Work Period Tasks • • • • • • • • • • Red Group 1) What is this poem describing? 2) What are three examples of imagery in the poem? Green Group 1) What is the strange fruit Southern trees bear? What verse(s), in what stanza gave you a clue? 2) How does this poem illustrate the cruelties that African Slaves faced? Blue 1) What is the recurrent word in the poem? 2) What happens to the fruit in the third stanza? 3) The fruit is a metaphor… but what does it stand for? Task Questions Vocabulary: In the verse “Pastoral scene of the gallant South” Define pastoral and gallant Main Idea: What was the topic of the poem “Strange Fruit”? Usenevidence from the poem to support your answer Cause and Effect: using the poem, what were some of the causes of slavery and their effects?