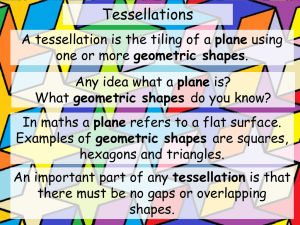
22 KDI 34: Shapes
advertisement

KDI Mathematics KDI Objectives Participants will be able to: • Identify the Mathematics Key Developmental Indicators • State the components of each individual Math KDI • Identify strategies and classroom materials that support children’s math learning 2 KDI What is Math? • Have you seen adults get excited when children can rote count to high numbers? • What does the ability to rote count really say about young children’s math development? • What components are included in math development? 3 KDI KDI KDI 31: Number Words and Symbols 31: Number Words and Children recognize and use number words Symbols and symbols Children: • Recognize and name numerals in their environment • Begin to write numbers • Understand that cardinal numbers (e.g., one, two , three) refer to quantity • Understand that ordinal numbers (e.g., first, second, last) refer to the order of things 4 KDI KDI 32: Counting KDI 32: Counting Children count things Children: • Count using one-to-one correspondence • Understand that the last number counted means how many there are • Use comparison words (more, fewer, same) to compare quantities • Understand adding to and taking away 5 KDI KDI 33: Part-Whole Relationships KDI 33:combine Part-Whole Relationships Children and separate quantities of objects Children: • Understand that a set of objects can be divided into parts • Understand that the parts can be combined into the whole 6 KDI Numbers: Station to Station Station1 Station 7 Station 2 Station 6 Station 3 Station 5 7 Station 4 KDI • Were you able to identify the Number KDIs? • Which of these activities might be appropriate for children? 8 KDI I See a Pattern Here… • What is patterning? • From your seat look for an example of a pattern in the room. Share with your table group 9 KDI KDI 38: Patterns KDI 38: Patterns Children identify, describe, copy, complete, and create patterns Children: • Work with simple alternating patterns • Progress to more complex patterns 10 KDI Developmental Sequence • Color • Shape • Size 11 KDI Ah Ha! • Sometimes we can sabotage children’s patterning efforts by adding too many variables at one time! • Remember the developmental sequence of doing a patterning activity for small-group time: First color, then shape, then size! 12 KDI When Children Pattern, They: • First, identify a pattern • Next, create their own pattern • Finally, extend or grow a pattern 13 KDI 14 So this is what patterning look like!?! KDI 15 • In table groups, collect data about something having to do with your breakfast today. • Once you’ve collected your data, share it in some way on the chart paper (e.g., a graph, a chart, or a table. KDI KDI 39: Data Analysis 39: Dataabout Analysis ChildrenKDI use information quantity to draw conclusions, make decisions, and solve problems Children: • Collect, organize and compare information based on measureable attributes • Represent data in simple ways • Interpret and apply information in work and play 16 KDI Sign In Sheet 17 KDI 18 Message Board KDI 19 Planning or Recall Time KDI 20 Recall Time KDI 21 Small-Group Time Explorations KDI KDI 34: Shapes KDI 34: Shapes Children identify, name and describe shapes Children: • Recognize, compare and sort two- and three-dimensional shapes • Understand what makes a shape a shape – i.e., all triangles have 3 sides and 3 points • Transform shapes by putting things together and taking them apart 22 KDI Shape Hunt Revisited • Circle • Rectangle • Triangle 23 Did you know that this is the developmental sequence that children learn shapes? KDI More 2-D Shapes • Right Triangle • Isosceles Triangle 24 3-D Shapes KDI • Sphere • Rectangular Prism • Cube • Cylinder • Cone 25 KDI What Makes a Shape a Shape? • What are the specific attributes or properties that make up each shape? 26 KDI Thinking About Shapes • After making your own shapes, discuss your assigned question in your table group. • Be ready to share your thoughts with the whole group. 27 KDI Shape Pictures • Use the shapes to create your own “shape picture.” • Leave your shape picture in front of you to use for another activity. 28 KDI KDI 35: Spatial Awareness KDI 35: Spatial Awareness Children recognize spatial relationships among people and objects Children: • Use position, direction and distance words to describe actions and the location of objects in the environment • Solve simple spatial problems in play – e.g., building with blocks, wrapping objects, doing puzzles 29 KDI Heavy and Light • Bring something “heavy” and something “light” to your table. • In table groups, answer the following questions: 1. Who has the lightest object? 2. Who has the heaviest object? 3. Can an object be both heavy and light? • Put all of the objects from your table in order from heaviest to lightest. 30 KDI KDI 36: Measurement KDImeasure 36: Measurement Children to describe, compare and order things Children: • Use measurement terms to describe attributes – e.g., length, volume, weight, temperature, time • Compare quantities and order them – Same/different, bigger/smaller, more/less, heavier/lighter • Estimate relative quantities – e.g., whether something has more or less 31 KDI Use the masking tape to make a tape line that is the same length as either you or your partner, then do the following: Measurement 1 • Use your pack of sticky notes to measure your tape line. Record your results. Measurement 2 • Use a dollar bill or a pencil to measure the same tape line. Record your results. 32 or KDI • • • • 33 Which measuring method was easier? Why was it easier? What did you find out about measuring? What steps (specifically) must you take in order to measure accurately? KDI KDI 37: Unit KDI 37:andUnit Children understand use the concept of unit Children: • Understand that a unit is a standard (unvarying) quantity • Measure using unconventional and conventional measuring tools – e.g., a block or a ruler • Use correct measuring procedures – Begin at the baseline and measure without gaps or overlaps 34 KDI Measurement Unit 35 • Measurement terms • Smaller/bigger, heavier/lighter • Estimate approximate quantities (has more or less) • Standard unit • Unconventional and conventional tools • No gaps or overlaps KDI Can You Find the Math? • In pairs, read the anecdotal notes in your training booklet. • Identify the math KDI that each anecdote represents. 36 KDI Strategies that Support Math Learning • Recognize and support children’s mathrelated play – Join in children’s math play as a partner • Describe or comment on children’s mathrelated play – Layer on math language 37 KDI Strategies that Support Math Learning (cont.) • Investigate children’s math thinking by asking what and why questions – What do you think about…? – Why do you think that…? • Encourage children to make predictions – I wonder what would happen if...? – What would be different if…? 38 KDI What would you say? What would you do? • With a partner, select 2 or 3 anecdotes. • Apply these strategies to your selected anecdotes. – Specifically, write down what you would say or do if you were the adult in the situation. 39 KDI Wish List • Complete the Implementation Plan in the Training Booklet, indicating materials you would like to add to your classroom to support mathematics. 40