CH 06
advertisement

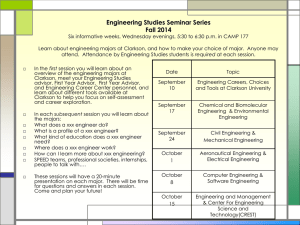
I 6 網際網路和全球資訊網技術 INTERNET AND WORLD WIDE WEB TECHNOLOGIES 資訊管理導論 Ross Malaga 6-1 學習目標 LEARNING GOALS • • • • • • 說明Internet目前的架構 確認和說明主要的Internet應用 定義全球資訊網和它的結構 瞭解Internet和全球資訊網的搜尋如何運作 說明Internet是如何管理的 定義企業內部網路和企業外部網路,並解釋 公司如何使用它們 6-2 LEARNING GOALS • Describe the Internet’s current architecture. • Identify and describe the major Internet applications. • Define the World Wide Web and its structure. • Understand how Internet and World Wide Web searches work. • Describe how the Internet is governed. • Define intranets and extranets and explain how companies use them 6-3 在Bead Bar的Internet和WWW • 由 Bead Bar 總公司連線到每個工作坊的專線費用, 每個月超過 1000 美金 • Meredith 相信 Bead Bar 應該要用一個網站。網站的 可能用途有: – – – – 賣珠寶 Sell jewelry 工作坊的促銷 Promotion of studios 與經銷商的溝通 Communicate with franchises 幫助建立商標知名度 Help establish brand name • Suzanne 想要跟工作坊之間有高速的連線(high-speed connections) • Mitch 想要能夠在網路上搜尋有關遊輪產業的資訊 (information) • Julia 關心的是成本的控制(controlling the costs) • Rachel 想要利用企業內部網路來處理經銷商的採購需 求,以改善(improve)反應的時間 6-4 Internet 架構 • Internet 的簡單歷史 (A Brief History of the Internet) – 由 Internet 開始興起時就參興的某些人所寫 • Hobbes 的 Internet 時程表 v7.0(Hobbes' Internet Timeline v7.0) • 今日的 Internet – 數以千計的網路(Thousands of networks) – 透過一些法津協議和商業合約所連結起來(Connected by legal agreements and commercial contracts) – 使用 TCP/IP 通訊協定(Uses TCP/IP protocol) – Internet服務供應商(Internet service providers,ISPs) • 提供個人存取 Internet • 撥接連線 • 數據機和常見的電話線路 • xDSL 和纜線數據機提供寬頻存取 6-5 存取 Internet 骨幹 Accessing the Internet Backbone • 絕大多數的 Internet 流量都是跨越好幾個 ISPs • 網路接取點(Network Access Points,NAPs) – 高速路由器處理 ISPs 和 Internet 骨幹之間的流量 – 骨幹 – 一堆的光纖纜線,是由大型的電信公司所擁有和維 護 • UUNet 的 North America Internet network 6-6 TCP/IP • 一組通訊協定Communications protocol suite – 封包交換協定(Packet switched protocol) • 不需端對端的連線 • 每個訊息都被拆解成很多小段,叫做封包 • 封包可能經由不同的路徑到達目的地 – 傳輸控制協定(Transmission Control Protocol,TCP) • 將訊息拆解成封包 • 將封包依順序編號 • 封包在目的端重組 – 網際網路協定(Internet Protocol,IP) • 將封包轉送到目的地 6-7 圖6.3 TCPIP 6-8 網域名稱Domain Names • 每一台連接到 Internet 的電腦都要有一個獨一無二 的 IP 位址 – IP 位址的格式是 xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx,xxx 是介於 0 到 255 之間的數字 • 我們怎麼知道 207.46.245.222 是 Microsoft? • 網域名稱系統(Domain Name System,DNS) – 一個 Internet 名稱的資料庫 – DNS 伺服器將 Internet 名稱轉換成 IP 位址 – 頂層網域 6-9 圖6.4 網域名稱系統 6-10 Internet 應用Internet Applications • • • • E-Mail 檔案傳輸 File transfers 即時傳訊 Instant messaging (IM) 新聞群組Newsgroups • 串流影音Streaming audio and video • 網路電話 Internet telephony • 全球資訊網 (WWW) World Wide Web (WWW) 6-11 E-Mail • 最廣為使用的 Internet 應用 • 每天發送 300 億封電子郵件 (e-mail) – Spam – 垃圾郵件訊息(junk e-mail messages) – Spam 每年造成美國 90 億美元的損失 • 每一封電子郵件訊息都含有標頭(head),說明 (describes)訊息的來源和目的地 • 電子郵件訊息是文字,不過可以附加許多類型的數 位資料 – 病毒通常經由 e-mail 來傳遞 6-12 檔案傳輸File Transfers • 檔案傳輸協定(File transfer protocol,FTP) – 伺服器與使用者電腦之間傳輸檔案的通訊協定 • 點對點 (P2P) 檔案共享(Peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing) – 電腦之間共享資料 – 每個使用者都可以成為伺服器 – Napster • Kazaa • Gnutella – 有了 P2P, 每個網路上的使用者都可以和其它網路上的使 用者分享資料 6-13 即時傳訊Instant Messaging • 讓使用者可以和其它人建立私人的聊天室() • • • • 即時傳訊是從 AOL 開始 即時傳訊侵入了公司網路 IM sneaking into corporate networks 許多以網路為基礎的公司使用即時傳訊技術來提供 客戶服務 – 維吉尼亞州 – eBay 6-14 Usenet新聞群組Newsgroups • • • • • • • • • • • 線上的電子佈告欄、討論場所 使用者發佈和閱讀訊息 有超過10萬個新聞群組 有數百萬的新聞群組閱讀者 重要的資訊來源,特別是技術相關的議題和產品 新聞群組的訊息散佈使用公開的標準 – 有許多是未經審查的 Online, bulletin board discussion forums Users post and read messages More than 100,000 newsgroups Millions of newsgroup readers Important information resource, especially for technical issues and products • Newsgroup messages distributed using open standard 6-15 串流影音Streaming Audio and Video • 建立和傳送影音檔案(Creating and sending audio and video files) – 運動(Sports)_ • sports.yahoo.com • Major league baseball – 新聞(News) • Fox News • CNN radio – 商業(Business) • ZDNet – 教育(Education) • Warriors of the Net 6-16 網路電話Internet Telephony • Voice-over Internet Protocol (VoIP) • 電腦當作電話來用 • 透過軟體與Internet上的其它電腦連線,並傳送語音 資料 • 節省電話費 • Voice-over Internet Protocol (VoIP) • Use your computer like a telephone • Software connects computers via the Internet and transmits voice data • Savings comes from eliminating toll charges between locations 6-17 全球資訊網The World Wide Web • Internet 上的超連結電腦檔案的集合(Collection of hyperlinked computer files on the Internet) • 主從式應用Client-server application – Web 伺服器 – Web 瀏覽器是用戶端 • WWW 標準(WWW standards) – 超文件標示語言(Hypertext markup language,HTML) • 目前網站的寫作標準 • 是 SGML 一部分,特別用在網頁上 • HTML 中的標籤告訴用戶端瀏覽器如何呈現網頁的內容 – 超文件傳輸協定(Hypertext transfer protocol,HTTP) • 在 Web 伺服器和用戶端之間建立連線的通訊協定 – 延伸標示語言(Extensible markup language,XML) • 是一種說明-標示語言 • 利用 XML 標籤賦予資料義意 6-18 靜態和動態網頁Static versus Dynamic Web Pages • HTML 和 XML 只能顯示和交換資料(HTML and XML only display and exchange data) • 沒有互動; 沒有資料的處理(No interactivity; no processing of data) • 腳本語言(Scripting languages) – 提供基本的互動 • 下拉選單 • 跑馬燈 – JavaScript – VBScript • 全功能的網頁程式設計(Full-featured Web programming) – – – – Java 用戶端腳本語言 Applets J2EE • 通用閘道介面(Common Gateway Interface,CGI) – 讓 HTML 網頁和電腦程式之間可以傳遞資料 6-19 圖6.8 伺服器端 的腳本語言 6-20 搜尋WWW Searching the WWW • Internet 上大部分的資料都是WWW的一部分 • 搜尋引擎 (Search engines )– WWW 內容索引的大型 資料庫 • 建立搜尋引擎資料庫engine database – 將新網站提交給搜尋引擎的管理者 – 蜘蛛 • 說明標籤 – Google – Yahoo 6-21 Internet管理Internet Governance • Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) – 開發Internet的標準(Works in groups to develop standards) • Internet Engineering Steering Group (IESG) – 認可或否決 IETF 提出的標準(Approves or disapproves standards developed by the IETF) • Internet Architecture Board (IAB) – 監督Internet標準的制訂流程(The oversight authority for the standards development process) • World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) – 推廣WWW和開發新的Web技術和標準 (Promotes the WWW and develops new web technologies and standards) 6-22 企業內部網路和企業外部網路 Intranets and Extranets • 企業內部網路(Intranet) – – – – 一個內部的公司網路,使用 Internet 和 Web 的技術 有彈性 省錢 使用 • 尋找和共享文件 • 共同工作 • 溝通 – 只有經過授權的使用者 • 受防火牆保護 • 企業外部網路(Extranet) – 讓客戶和商業夥伴能夠有限制地存取組織的內部網路 – 使用虛擬私人網路(VPN)來增加安全性 6-23 Internet和WWW的影響 • Meredith – Internet 讓 Bead Bar 成為全球化的公司 並擴展市場 • Leda and Miriam– 使用網站來改善品牌(brand)形象 和建立經銷商的網站 • Mitch – 搜尋遊輪產業的資訊並尋找 Bead Bar 的商 機 • Julia – 對於網站的低成本(low cost)和減少經銷商 (headquarters)連接到總公司的成本感到滿意 • Rachel – Intranet 可以提供採購流程改造的機會 • Jim – 制訂訓練員工使用網路和網路只能用於商業 用途的政策 6-24 學習目標摘要 Internet目前的架構 確認和說明主要的Internet應用 定義全球資訊網和它的結構 Internet和全球資訊網的搜尋如何運作 Internet如何管理 定義企業內部網路和企業外部網路,並解釋 公司如何使用它們 6-25 Learning Goals Summary In this chapter you have learned: The Internet’s current architecture To identify and describe the major Internet applications The structure and definition of the World Wide Web How Internet and World Wide Web searches work How the Internet is governed What are intranets and extranets and how companies use them 6-26