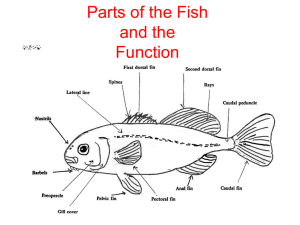
Describing nutritional requirements of fish
advertisement

Environmental Resources Unit C Animal Wildlife Management Problem Area 3 Fish Management Describing nutritional requirements of fish Lesson 3 Describing nutritional requirements of fish • From the nutritional labels provided: – Write amount of fat, carbohydrates, proteins, and vitamins. • What types of foods provide us with the different nutrients? • How does fish receive these nutrients? Terms • • • • • • • • Amino acid Blood meal Carbohydrates Carnivore Fat-soluble vitamins Fats Fish meal Herbivore • • • • • • • Minerals Omnivore Protein Soybean meal Trace elements Vitamins Water-soluble vitamins Objectives • Describe the role of protein in fish nutrition. • Describe the role of fats in fish nutrition. • Describe the role of carbohydrates in fish nutrition. • Describe the role of minerals in fish nutrition. • Describe the role of vitamins in fish nutrition. What is the role of protein in fish nutrition? • First major component required for proper nutrition of fish is protein. • Protein – Formed from compounds known as amino acids. ag.arizona.edu/aes/mac/catfish.htm What is the role of protein in fish nutrition? • Amino acids – Building blocks of protein. – Needed by animals for proper nutrition. – 10 amino acids are essential. – Broken down during digestion. – Used to produce new tissue or reproduce damaged tissue. Protein • Most critical component of fish feed. • Prepared fish feed will contain between 25 and 40 percent protein. agrino.org/fishing/htmldocs/ frswtrfish.html Sources of protein – Fish meal • High protein feed derived from fish. – Animal waste products • Blood meal –High protein feed derived from blood collected during the slaughter process. • Meat scraps – Soybean meal • High protein feed produced from soybeans. Protein requirements • Carnivore fish – Animals that eat meat. – Require 50% of its protein from animal sources. • Herbivore fish – Animals that eat plants. – Need only about 30% of the protein in their feed from animal sources. • Omnivores – Animals that eat both plants and animals. – Need only about 30% of the protein in their feed from animal sources. What is the role of fats in fish nutrition? • Fats – A required component of fish feeds. – Composed of fatty acids. – Used for proper health and growth. – Amount of fat in a feed usually between 4 and 15 percent. Fat requirements • Type of fat needed in fish feed depends on temperature of water. • To be digested, fat must be able to melt. • To melt, must have melting point below water temperature. • Cold water fish (trout) – Unsaturated fat derived from plants (vegetable oil). • Warm water fish (tilapia) – Saturated fat derived from animal products. What is the role of carbohydrates in fish nutrition? • Carbohydrates – A required component of fish feed. – Source of energy for fish. – Organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen. – Plants including sugars, starches, and cellulose are sources. Carbohydrate requirements • Fish herbivores (carp) – Better capable of digesting carbohydrates. – An enzyme (amylase) in their digestive system. • Fish carnivores (catfish) – Can’t digest carbohydrates as well. – Only need 10% carbohydrates in ration. What is the role of minerals in fish feed? • Minerals – Inorganic materials needed for health and growth. – Most only needed in small amounts. – Large amounts of minerals may be fatal to fish. – Often called trace elements • Needed in very small quantities. Required Minerals • • • • • • Calcium Iron Silicon Manganese Magnesium Boron • • • • • • Cobalt Copper Iodine Molybdenum Selenium Sodium www.teezz.co.uk/fishing/ catfish-2795/index.shtml Minerals • Testing the water can show mineral deficiencies. • Can give fish two ways – Add directly to the water. • If water is flowing or moving may be a waste – Added to a commercially prepared feed. What is the role of vitamins in fish nutrition? • Vitamins – Organic compounds needed in small amounts for proper growth and maintenance of body functions. – Specific vitamins are needed for different body functions. – Deficiencies can cause poor growth, anemia, skin lesions, clubbed gills and other problems. Types of Vitamins • Water-soluble – Taken in, used, and then excreted. – Include Thiamin, Riboflavin, and Folic Acid. • Fat-soluble – Taken in to the body and stored. – If excess amounts consumed can be unhealthy. – Include vitamin E, A, and D. Review / Summary • What is the role of protein in fish nutrition? • What is the role of fats in fish nutrition? • What is the role of carbohydrates in fish nutrition? • What is the role of minerals in fish nutrition? • What is the role of vitamins in fish nutrition?