3. Female Reproductive System WEB

Reproductive System Cont.
Female Anatomy & Physiology
Chapter 28
FEMALE ANATOMY
•
Ovaries = produce eggs
• Ovarian follicles = contain eggs in various stages of development and the cells that surround them; surrounding cells nourish the eggs & produce estrogen
•
Corpus luteum = remnants of a mature follicle after ovulation
(after egg is released); produces estrogen, progesterone, and relaxin
• Uterine tubes
(oviducts/fallopian tubes) = transport eggs from the ovary to the uterus; fertilization occurs in the oviducts
• Uterus = organ in which the fetus develops
• Endometrium = uterine lining
•
Cervix = lower end of uterus
• Vagina = passageway between the uterus and the outside
•
Vulva = external genitals of the female
Female
Reproductive
Cycles:
1. Ovarian Cycle
&
2. Menstrual
(Uterine) Cycle
Female Reproductive Cycles
Female reproductive cycles prepare the female body for pregnancy
1. Ovarian cycle = cyclic events that occur in the ovaries
2. Menstrual (uterine) cycle = cyclic events that occur in the uterus
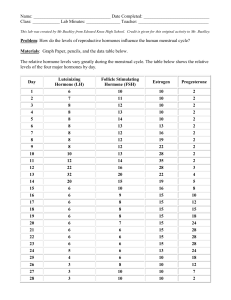
• Last 28 days on average
• Influenced by
1. hormones secreted by pituitary gland: FSH and LH
2. hormones secreted by ovary: estrogen and progesterone
OVARIAN CYCLE
1. Follicular phase – prior to ovulation:
• One ovarian follicle becomes the dominant follicle and begins to mature when the pituitary gland releases FSH
•
Maturing follicle releases estrogen and causes the pituitary gland to release LH (this is an example of positive feedback : an increase in one hormone results in increase of another hormone)
2. Ovulation (day 14):
• levels of LH reach its peak and initiate ovulation
• Ovulation = egg is released from the dominant follicle
3. Luteal phase – after ovulation:
• Ruptured follicle becomes corpus luteum and secretes estrogen and progesterone
• High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit FSH and LH (this is an example of negative feedback : increase in one hormone results in decrease of another hormone)
MENSTRUAL CYCLE
• If the egg does not become fertilized, levels of estrogen and progesterone fall and cause endometrium to be shed = menstrual flow or menstruation (days 1-5)
• Starting with day 6, increasing levels of estrogen cause endometrium to thicken and prepare uterus for possible implantation of fertilized egg
FERTILIZATION
• Fertilization = union of sperm and egg; the resulting cell is called zygote
• Takes place in the uterine tube
• Implentation
= the zygote passes into the uterus where it attaches into the uterine lining (by the sixth day after fertilization)