9-Clicker-Questions-Induction

MCDB 4650
Induction and Mesoderm
Patterning
If you isolate animal cap cells from a Xenopus embryo at the 8-cell stage and assay them 1 day later, they will not have made mesoderm. If you combine vegetal cells with animal cells at the same stage and assay them 1 day later, the animal cells will now have made mesoderm. This tells you that: a. the animal cells are committed at the 8-cell stage.
b.
the vegetal cells are not committed at the 8-cell stage.
c.
the vegetal cells induce the animal cells to make mesoderm.
d.
the animal cells induce the vegetal cells to make mesoderm.
e.
the two sets of cells interact by lateral inhibition.
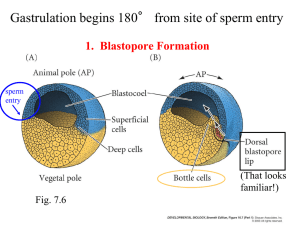
Which of the following is NOT true of the organizer?
a. Induces gastrulation b. Inhibits ventral ectoderm c. Converts ventral mesoderm to intermediate mesoderm d. Involutes through the dorsal lip of the blastopore e. Becomes intermediate mesoderm
The initial induction of mesoderm is accomplished by a. activation of the Wnt pathway b. activation of the TGFb pathway c. activation of the Shh pathway d. activation of the Ras pathway e. activation of the FGF pathway
The patterning of dorsal mesoderm as different from ventral mesoderm involves a. higher concentrations of signaling molecules on the dorsal side than on the ventral b. transcription of molecules that can inhibit molecules present on the ventral side c. transcription of molecules that direct synthesis of dorsal-specific proteins
How could you best assay whether the Xnr’s were in a
concentration gradient across the embryo?
a. Grind up different parts of Xenopus embryos and assay protein level b. Make embryos mutant for Xnrs and assay the outcome c. Transplant the Niewkoop center into a UV irradiated embryo and assay the outcome d. Put purified Xnr protein into a bead (from which the
Xnr can diffuse) and put the bead into culture with animal cap cells. Assay types of cells made e. Two of the above would work equally well
The organizer induces neural ectoderm by: a. inhibiting an inhibitor that normally prevents neural fate b. directly inhibiting epidermal fate c. activating a neural transcription factor d. activating b-catenin signaling e. segregation of neural-specific transcription factors
Mesoderm arises near the equator (in the marginal zone) of the
Xenopus blastula because a) animal hemisphere cells in this region are autonomously determined to become mesodermal precursors.
b) vegetal hemisphere cells in this region are autonomously determined to become mesodermal precursors.
c) animal hemisphere cells in this region receive signals from underlying vegetal hemisphere cells and become mesodermal precursors.
d) vegetal hemisphere cells in this region receive signals from overlying animal hemisphere cells and become mesodermal precursors.
Activin was postulated as a mesoderm-inducing morphogen because it a) was found in the medium after incubation of animal cap cell cultures.
b) was found in the medium after incubation of vegetal cell cultures.
c) induced different mesodermal cell types when incubated at different concentrations with animal cap cells in culture.
d) induced different mesodermal cell types when incubated at different concentrations with vegetal cells in culture.
Which of these statements is true in the Xenopus embryo?
a) The organizer induces formation of neural ectoderm by locally inhibiting an inhibitor of neural cell fates in the animal cap.
b) The organizer induces formation of neural ectoderm by locally inducing animal cap cells that would otherwise adopt epidermal fates.
c) The organizer moves during gastrulation toward the future anterior of the body axis and then retracts again toward the ventral side, leaving notochord tissue behind it.
d) The organizer cells contain activated
-catenin as a master transcriptional regulator.
e) The organizer secretes factors that activate formation of the Nieuwkoop center.