Nutrition and Energy Flow
advertisement

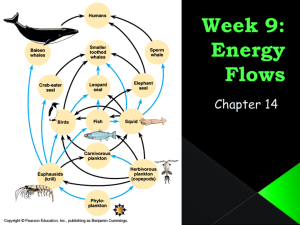
Unit 2: The Biosphere and Energy Flow Biosphere & Ecosystem Biosphere: Organisms and their environments (Includes living and dead organic matter) Ecosystem: A community of organisms (biotic/ living things) and their nonliving (abiotic) environment (what we learned about in Unit 1) An ecosystem is a smaller part of the overall biosphere I. Energy A. All organisms need energy to carry out bodily functions like growing, moving around, breathing, keeping our blood circulating, etc. -The ultimate source of energy for life on earth is the sun. -Energy is the ability to cause change. II. How Organisms Obtain Energy 1. Autotrophs: The producers. Producers turn light energy from the sun into food through a process called photosynthesis. Ex: Trees, plants, algae. Quick Questions (CFU) What provides energy for life on earth? -the sun What is energy? -the ability to cause change Is a producer and an autotroph the same thing? -yes What is an example of a producer? -a plant III. Heterotrophs Heterotrophs: The consumers. A consumer can’t make it’s own food so it has to eat other organisms. Ex: Lions, Humans, Rabbits. IV. Examples of heterotrophs: 1. Herbivore-eats only plants (autotrophs). Ex: Rabbits 2. Carnivore-eats only animals (heterotrophs). Ex: Lions 3. Omnivore-eats plants and animals. Ex: Humans 4. Scavenger-eats dead animals and garbage. Ex: Vultures 5. Decomposer-breaks down dead or dying material. Ex: Bacteria, fungi Questions (CFU) What is a consumer? -an organism that cannot make its own food. What is an example of a consumer? -humans Is a consumer the same thing as a heterotroph? -yes What kind of heterotroph is this? -carnivore What kind of heterotroph is this? -decomposer What kind of heterotroph is this? -herbivore What kind of heterotroph is this? -scavenger Most Humans: Omnivores V. Flow of Matter and Energy Energy in a Food Chain The arrows in a food chain or food web show the transfer of energy from one organism to another. B. Food chain - a model that shows how matter and energy moves through an ecosystem. berries → mice → black bear VI. Flow of Matter and Energy in Ecosystems Food Web-a model which shows all possible feeding relationships at each trophic level in a community. ***A food web is more realistic than a food chain because organisms depend on more than one other species for food. VII Trophic Levels In this class, we will think of these food webs in _levels_________. Level 1: Producers (plants) Level 2: Primary Consumers (who eat producers) Ex: Caterpillar, Giraffe Level 3: Secondary Consumers (who eat Primary Consumers) Ex: Large cats Level 4: Tertiary Consumers (who eat Secondary Consumers) Ex: Hawk Autotrophs Third-order heterotrophs First-order heterotrophs Second-order heterotrophs Decomposers In your notes write examples for the following: 1. A producer: A Tree, Algae, Grass, Plants 2. A primary consumer: Caterpillar, deer, antelope, cow 3. A secondary consumer: Lions (feed on antelope, which feed on plants) Seeds (producer) → Mice → Snakes 4. A tertiary consumer: Seeds (producer) → mice → snakes → Eagles II. Flow of Matter and Energy -Each organism in a food chain is a feeding step, or trophic level in the movement of matter and energy. -Only 10% of energy is passed up each trophic level!!! (Rule of 10) -Because so much energy is lost at each trophic level, there can only be 3-4 steps in a food chain. You will now practice with these terms with the worksheet provided 1. Heterotroph 2. Autotroph 3. Heterotroph 4. Heterotroph 5. Autotroph 6. Heterotroph 7. Heterotroph 8. Autotroph 9. Autotroph 10. Heterotroph More Answers: 1. Decomposer 2. Herbivore 3. Omnivore 4. Carnivore 5. Decomposer 6. Scavenger or Omnivore 7. Decomposer 8. Carnivore 9. Herbivore 10. Scavenger 11 and 12: Producers → Primary Consumer → secondary consumer → tertiary consumer 4.2.A.a Illustrate and describe the flow of energy within a food web Example Food Chain: Chihuahuan raven Honey mesquite (pods eaten by beetles) Pronghorn antelope Example Gambel quail Food Web Jackrabbit Long-tail weasel Desert tortoise Prickly pear cactus Coyote (top carnivore) Kangaroo rat (seed eater)Roadrunner ants Texas horned lizard Red spotted toad Mexican whiptail lizard Mojave rattlesnake Questions (fill the answers on WS #2) What does flow mean? -to move Energy flows from _______ to _______ in an ecosystem. -Energy flows from producer to consumer in an ecosystem. What is a food chain? -a model that shows how energy flows in an ecosystem. What is a food web? -a model which shows all the feeding relationships in an ecosystem. Which is more realistic, a food web or a food chain? -a food web is more realistic than a food chain b/c is shows all possible feeding relationships. What is a trophic level? -a feeding step. How much energy can be passed up each trophic level? -10% Why can there only be 3-4 trophic levels? -There can only be 3-4 trophic levels b/c only 10% of the energy is passed up each level, which means that after 3 or 4 levels, energy will run out. Food Web Example #2 What are the producers? Algae and Plants How can you tell? Are at the bottom of food webs; are green What three organisms does the fish eat? Annelids, Mollusks, and Arthropods What gives the birds of prey its energy? Mammals and Birds What are Bacteria and fungi known as? Decomposers What do the Bacteria and fungi do? Breakdown dead organisms Where are the plants getting inorganic nutrients from? Bacteria and fungi What are the two top carnivores? Birds of prey and Humans Answers to WS #3 1. Produce own food through photosynthesis. 2. Eat other organisms for food. 3. Eat other organisms for food. 4. Break down dead material for energy. 5. 10% is passed up each level. 6. They are using it for life processes such as moving and breathing and some energy is lost as heat as it is transferred to different trophic levels. Food Webs: 1. Phytoplankton 2. Smaller toothed whales 3. Leopard Seals 4. Krill 5. Phytoplankton and zooplankton 6. other birds, fish, penguins 7. penguins, leopard seals, zooplankton, baleen whales, elephant seals 1. Which organisms are the top carnivores? Foxes, hawks and owls, snakes. 2. snakes 3. rabbits, squirrels, mice, seed-eating birds 4. Plants 5. rabbits, squirrels, mice, seed-eating birds WWBAT explain why there are generally more producers than consumers in an energy pyramid. WWBAT explain how energy distribution will change due to changes in the food web. The last couple of days we have learned about the terminology of unit 2 and all about food webs. Today we are learning about energy pyramids. A. Types of Food Pyramids: 1. Ecological Pyramids-a model which shows how energy flows through an ecosystem. Pyramid of Energy -Pyramid of Energy-shows how energy decreases at each trophic level. Only 10% of the energy is passed up each level! Heat Heat 0.1% Consumers 1% Consumers 10% Consumer Heat Heat 100% Producers -Pyramid of Biomassshows the weight at each Biomass trophic level. (________ means how many living plants and animals) Pyramid of Biomass Pyramid of Numbers Fox (1) Birds (25) Grasshoppers (250) Grasses (3000) 1 kg of human tissue 10 kg of beef 100 kg of grain That means for every 1000 kg of grass only enough biomass is transferred to make 1 kg of human tissue. -Pyramid of Numbers shows the number of organisms eaten by the animal above it on the pyramid. You will now finish the backs of WS #3! You will work on the worksheet for 20 minutes and then we will discuss it as a group. Stay on Task! Dixie Cup Food Pyramid (10 cups) Use the cups provided to build and label your own food pyramid with the following: 1. Autotroph OR Heterotroph? 2. Producers/Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Consumers? 3. Carnivore/Herbivore/Omnivore? 4. Percentage of Energy from the Sun? 5. Example Organism? (A picture would be nice) STOP: You are going for an interview! You are going for an interview and must become an expert on the following questions in the next 3 minutes. Row 1 answer questions 1-5 Row 2 answers questions 6-10 Row 3 answers questions 11-14 We will share out our answers in 3 minutes. Ready, Set, Go! Questions: In your notes answer the following questions: 1. What is the Pyramid of Energy? -shows how much energy is in each trophic level. 2. Does the amount of energy increase or decrease as you go up each trophic level? -decrease 3. Why does the amount of energy decrease? -energy is lost to the environment as heat. 4. How much energy is transferred up each level? 10% 5. What is the Pyramid of Numbers? -shows how many organisms exist at each trophic level. 6. What is the Pyramid of Biomass? -shows how much weight exists at each trophic level. 7. What is biomass? -amount of living material 8. Which trophic level has the most biomass? The producers or the bottom of the pyramid 9. Which trophic level has the least amount of biomass? The tertiary consumers 10. Give 2 examples for the organisms living at the lowest tropic level. Plants, Trees, Algae, Grass 11. Give two examples of organisms at the trophic level that has the most biomass? The top, the tertiary consumers 12. If all of the producers were removed from a food Consumers web, all the ______________ would eventually starve to death. 13. If organism A was organism B’s food, and organism A was removed, the population of organism B would… Decrease 12. If tarantulas eat crickets and crickets eat plants, what will happen to the number of plants if all the tarantulas are removed? Decrease