English Language Arts Part 2
advertisement

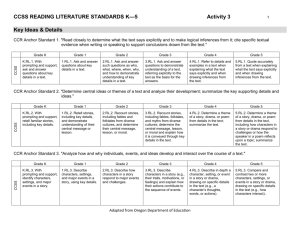
Denise Wright, BCPS Elementary Instructional Coach OVERVIEW OF THE ELA COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS Participants will gain an understanding of the design and organization of the CCSS document. Design There are four strands: • Reading + Reading Foundational Skills K-5 • Writing • Speaking and Listening • Language The ELA Common Core supports an integrated model of literacy. There are media requirements blended throughout. 4/13/2015 • page 4 Reading Foundational Skills Grades K-5 • Print concepts (K−1) • Phonological awareness (K−1) • Phonics and word recognition (K−5) • Fluency (K−5) College and Career Readiness (CCR) Anchor Standards The CCR Anchor Standards: • Have broad expectations consistent across grades and content areas. • Are based on evidence about college and workforce training expectations. • Expect instruction to cover a broad range of increasingly challenging text. CCR Anchor Standards The CCR Anchor Standards “anchor” the document and define general, cross-disciplinary literacy expectations that must be met for students to be prepared to enter college and workforce training programs ready to succeed. Each CCR Anchor Standard has an accompanying grade-specific standard that translates the broader CCR statement into grade-appropriate end-of-year expectations. Grade Specific Standards K−12 Standards: • Are grade-specific end-ofyear expectations. • Are developmentally appropriate. There is a cumulative progression of skills and understandings. • Have a one-to-one correspondence with CCR Anchor Standards. 4/13/2015 • page 8 GRADE 3 CCR ANCHOR STANDARD CCSS GRADE SPECIFIC STANDARD College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Reading Reading Literature Key Ideas and Details 1. Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. 2. Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and ideas. 3. Analyze how and why individuals, events, and ideas develop and interact over the course of a text. 1. Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. 2. Recount stories, including fables, folktales, and myths from diverse cultures; determine the central message, lesson, or moral and explain how it is conveyed through key details in the text. 3. Describe characters in a story (e.g., their traits, motivations, or feelings) and explain how their actions contribute to the sequence of events. 4/13/2015 • page 9 Annotating the Anchors 1. Circle every strand in the CCR Anchor Standards. 2. Underline the clusters. 3. Place a star next to the most challenging Anchor Standard in each strand. Intentional Design Limitations The Standards do NOT define: • • • • • • How teachers should teach. All that can or should be taught. The nature of advanced work beyond the core. The interventions needed for students well below grade level. The full range of support for English Language Learners and students with special needs. Everything needed to be college and career ready. Balanced Literacy CCSS Reading CCSS Language Balanced Literacy CCSS Writing CCSS Speaking and Listening 4/13/2015 • page 12 CROSSWALKING WITH THE STANDARDS Participants will recognize the rigor and specificity in the new CCSS. Crosswalk Document Activity • Using the rubric provided and the Crosswalk handout, identify the level of alignment between the NC ELA Standard Course of Study and the ELA Common Core State Standards. • Place the alignment score in the “Comments” section of the Crosswalk - selected pages are provided for K-5, 6-12 grade spans. 4/13/2015 • page 14 Crosswalk Activity Rubric 3 The concepts and skills of the NC ELA Standard Course of Study are strongly aligned to the concepts and skills in the English Language Arts Common Core State Standards. 2 The concepts and skills of the NC ELA SCOS are reasonably aligned to the concepts and skills in the ELA CCSS. 1 The concepts and skills of the NC ELA SCOS are minimally aligned to the concepts and skills in the ELA CCSS. NE The standard is a new expectation found in the CCSS. 4/13/2015 • page 15 VERTICAL ALIGNMENT Participants will recognize the K-12 progression of grade level expectations for the Standards and their connection to the Anchor Standards. They will determine and compare the skill requirements between two grade levels. 4/13/2015 • page 16 Grow a Standard 4/13/2015 • page 17 Grow a Standard • Begin with the CCR Anchor Standard (in bold). • Put the puzzle pieces in order from basic to more sophisticated expectations. 4/13/2015 • page 18 Answers: Speaking and Listening (SL.3) K-5 Kindergarten Ask and answer questions in order to seek help, get information, or clarify something that is not understood. Grade 1 Ask and answer questions about what a speaker says in order to gather additional information or clarify something that is not understood. Grade 2 Ask and answer questions about what a speaker says in order to clarify comprehension , gather additional information, or deepen understanding of a topic or issue. 4/13/2015 • page 19 Answers: Speaking and Listening (SL.3) K-5 Third Grade Ask and answer questions about information from a speaker, offering appropriate elaboration and detail. Fourth Grade Identify the reasons and evidence a speaker provides to support particular points. Fifth Grade Summarize the points a speaker makes and explain how each claim is supported by reasons and evidence. 4/13/2015 • page 20 Looking Deeper at Vertical Alignment How do the anchor standards translate through the grades? Directions: •For each standard, mark the changes at each grade level. (What’s different?) •Revisit two grade-level standards that are side-by-side and focus on the differences between the two. What are the different expectations for students? 4/13/2015 • page 21 1. How does vertical alignment speak to classroom instruction? 2. What other ways can you use vertical alignment? 3. How does vertical alignment help teachers understand where scaffolding might be needed as they assist all students in accessing the content? Reflection 4/13/2015 • page 22