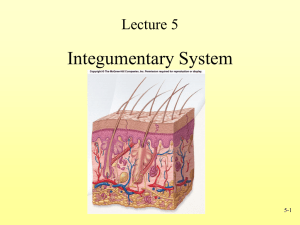
M ALE R EPRODUCTIVE S YSTEM
Robert Scranton ©2009
T HE PARTS
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
T ESTES
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Name the layers covering the testes from
outer to inner
Scrotum
____________
Tunica
Vaginalis
________________
Tunica
albuginea
_________________
Mediastinum
______________
T ESTES
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
The tunica vaginalis is made of a ________
parietal
visceral ______
serous __________
membrane .
and _______
The tunica albuginea is a ________
dense
__________
__________
connective ______.
tissue
irregular
Mediastinum
Where is it found?
__________________________
Posterior expansion of tunica albuginea
What does it contain? ________
Rete testes
Identify
•Mediastinum
•Seminiferous tubules
•Testicular Septae
•Testicular Lobule
•Tunica albuginea
T ESTES
The testicular parenchyma is composed of the:
Seminiferous tubules
___________________
_______________
Leydig Cells
Spermatozoa
Androgens (testosterone)
tubular
The main functions of the testes, a compund _________
hormone production
reproduction
gland, are ___________&
_________________.
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
S EMINIFEROUS T UBULES
Germ Cells
Spermatogonia
germ cells & ___________
sertoli cells
Composed of __________
Divide mitotically Spermatogonia (spermatocytogenesis)
Divide meiotically primary spermatocytes
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
S EMINIFEROUS T UBULES
Germ Cells
Spermatogonia
germ cells & ___________
sertoli cells
Composed of __________
1° Spermatocyte
2° Spermatocyte
Spermatids:
• Post-meiotic
• Haploid cells
•In process of spermiogenesis
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Spermatids
S EMINIFEROUS T UBULES
Germ Cells
Spermatogonia
germ cells & ___________
sertoli cells
Composed of __________
1° Spermatocyte
2° Spermatocyte
Process of Spermiogenesis:
1. Condensation of the nucleus
2. Reduction of cytoplasm volume
3. Formation of an acrosome
4. Formation of the flagellum
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Spermatids
S EMINIFEROUS T UBULES
Germ Cells
germ cells & ___________
sertoli cells
Composed of __________
Spermatogonia
1° Spermatocyte
Spermatozoa (male gamete)
2° Spermatocyte
Q:What is the significance of the syncytium
between the germ cells from a single
spermatogonium?
A: These small intercellular bridges allow for the
synchronization of meiotic division of these cells.
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Spermatids
Germ Cells
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Describe the morphology:
Leydig Cells
(interstitial)
Tubular cristi and lots of smooth ER
• Eosinophilic cytoplasm
• lots of mitochondria
• Reinke crystals
• Cytoplasmic location
• increase with age
• found in 50% of leydig cell
tumors
Stimulated by:
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
LH
Sertoli Cells
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
The Facts- Short & Sweet
Sertoli Cells
Describe the morphology:
• On the outside of the seminiferous tubule
• Basal end lines the basement membrane
• Apical surfaces form the luminal margin
• Nucleus located basally, triangular shape, prominent nucleolus
Describe the hormone interactions:
• Produce mullerian inhibiting factor (MIF)
• Stimulated by follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Describe the functions:
• Blood-testis barrier
• Phagocytosis
• Synthesis and secretion of inhibin
• Synthesis of androgen-binding protein
• Aromatization of androgen to estrogen
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Starting with the seminiferous tubules,
trace the ducts to the external environment
Tubili recti
Rete testes
Efferent ductules
Epididymus
Vas deferens
Ejaculatory ducts
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Urethra
Describe each segment
Tubili recti
sertoli cells only
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Describe each segment
Tubili recti
Rete testes
• Simple Cuboidal cells
• within the mediastinum
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Describe each segment
Tubili recti
Rete testes
Efferent ductules
• 10-12 short ducts
• Simple cuboidal cells Secretory action
• Columnar cells Ciliated
• thin band of circular smooth muscle on outside
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Describe each segment
Tubili recti
Rete testes
Epididymus
Efferent ductules
• Proximally Tall pseudostratified columnar w/ stereocilia
• Distally Short pseudostratified columnar w/ stereocilia
• Circular smooth muscle becomes thicker
• Sympathetic innervation
• Spermatozoa become functionally mature
• Decapacitation of spermatozoa
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Describe each segment
Tubili recti
Rete testes
Efferent ductules
Epididymus
Vas deferens
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
• Short pseudostratified columnar epithelium w/
stereocilia
• inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer longitudinal
smooth muscle layers
• mucosal folds
• distal dilation ampulla of vas deferens
• sympathetic innervation
Describe each segment
Tubili recti
Rete testes
Efferent ductules
Epididymus
Vas deferens
Ejaculatory ducts
• found within the prostate gland
• simple cuboidal epithelium
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Describe each segment
Tubili recti
Rete testes
Efferent ductules
Epididymus
Vas deferens
Ejaculatory ducts
Urethra
• Part of reproductive and urinary system
• Three sections:
1. Prostatic Transitional epithelium
2. Membraneous Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
3. Penile Pseudostratified columnar epithelium changes
to stratified squamous epithelium in the glans
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
1. Seminiferous Tubules
2. Straight Tubules
3. Rete Testes
6. Vas Deferens (20x below)
4. Efferent Ductules
5. Epididymus
7. Ejaculatory Duct (no image)
8. Urethra (no image)
Name the accessory glands
1.
2.
3.
4.
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Glands of Littre
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Glands of Littre
of the vas deferens
Drain into the ampulla
_________________.
Lined by Pseudostratified
__________ columnar
______
epithelium Epithelium secretion is
_______.
fructose _______,
fibrinogen and
composed of ______,
________.
of
ascorbic acid The secretion is ____%
70
the volume of ejaculate. The
vesicles have a smooth muscle wall
and sympathetic innervation.
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Glands of Littre
Central and peripheral zones
AKA “periurethral”- Benign
prostatic hypertrophy
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Prostatic adenocarcinoma
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Glands of Littre
branched tubuloalveolar glands draining
Parenchyma _______________,
into the Prostatic
______ ______.
urethra Secretion
choline citric
acid and
contains _____,
______,
___________.
acid phosphatase
liquifaction of semen.
PSA- responsible for _______
Production is stimulated by sex steroids
DHT
(____)
Stroma- __________
Fibroelastic CT + __________
smooth muscle
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Glands of Littre
For those that got a little lost on the last
slide……
BPH or ____________
Prostatic Cancer
PSA implies _____
Prostatic (serum) acid phosphatase
Cancer
implies Prostatic
___________
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Glands of Littre
• Paired glands secreting _____
mucus
UG diaphragm
• Found in the ___________
• Drain into _________________
Proximal penile urethra
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Seminal Vesicles
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Glands of Littre
• Branched tubuloalveolar glands
• Secrete lubricating mucus into penile urethra
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis
Penis
3 masses of erectile tissue covered by ____________
__
Fibroelastic CT
2 Corpora cavernosa
__
__
1 Corpus spongiosum + Glans Penis
Erectile tissue = Fibrous network of trabeculae
Venous sinusoids AKA lacuna
Helicine arterioles
• Testes
• Excretory Ducts
• Accessory Glands
• Penis