Integumentary system ppt

INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
Cutaneous membrane
• Skin
• Largest organ
• Covers an area of about 2 square meters
• Weighs 4.5 to 5 kg
• Serves as a barrier
• 1 st line of defense for you body
SKIN
• Skin is our protective covering.
• It has 2 names
– Integument
– Integumentary system
Integumentary system
• Formed by the skin and its derivatives
– Sweat glands
– Oil glands
– Hair
– nails
Factoids
• You will shed about 40 pounds of skin in a lifetime
• There are over a million dust mites, microscopic organisms on you mattress and pillow eating the dead skin cells you shed during the night.
Factoids
• Skin must be cleaned regularly or it will become cracked or inflamed.
• Dead cells along with the dead skin cells are a food source for bacteria called a slurry. This slurry will emit a foul smell.
• As you age, skin becomes thinner and is easily damaged. It will sag due to loss of elasticity.
INTERESTING FACTS
• A human loses an average of 40 to 100 strand of hair a day.
• A fetus acquires fingerprints at the age of
3 months
• Every person has a unique tongue print.
• An average human scalp has 100,000 hairs.
• By the age of 60, most people have lost ½ of their taste buds.
• Every square inch of human skin consists of 20 feet of blood vessels.
• Every square inch of the human body has an average of 32 million bacteria on it.
• Fingernails grow faster than toenails
• Humans shed about 600,000 particles of skin every hour.
• That’s about 1.5 pounds a year.
• By the age of 70 years of age, an average person will have lost 105 pounds of skin.
SEVEN FUNCTION OF THE SKIN
• Protection
• Body temperature regulation
• Waterproof
• Excretion and absorption
• Helps to manufacture vitamin D
• Cutaneous sensations
– Site of many nerve endings
• Temporary storage of fat glucose, water, and salts such as sodium and chloride
• Screens out harmful ultraviolet radiation
(UV) contained in sunlight.
• It can absorb certain drugs and other chemicals
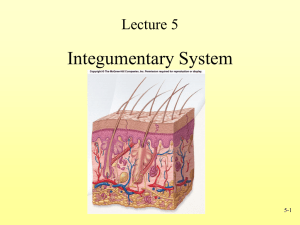
Layers of skin
• DERMIS
– 2 nd layer
– Has wider variety of sensory receptors
– Contains dense connective tissue
• EPIDERMIS
– Outer most
– Has sensory receptors
– Contains stratified squamous epithelial cells
Layers of epidermis
• 5 layers
• In order from deep to superficial
– Stratum basale
– S. spinosum
– S. granulosum
– S. lucidum
– S. corneum
S. Corneum
• Dead cells
• Outermost layer
• waterfproof
• Cells rub off
• Replaced every 35-45 days
LUCIDUM, GRANULOSUM,
SPINOSUM
• Cells become flattened
• become full of keratin
• die
S. Basale
•
• Composed of single rstem cells that undergo cell division to continually produce new kertinocytes.ow of cuboidal or columnar keratinocytes.
EPIDERMIS
• Avascular
• Contains melanocytes
– Cells that make melanin
• Keratinocytes
– Most epidermal cells
– Produce keratin which is a protein that helps to give epidermis its protective layer
• As these cells are pushed upward, keratin will become the dominant structure in the cells.
Melanin
• Responsible for the color of skin, eyes, hair
• Melanocyte
– Cell with projections that weave between other cells
– Produce melanin
• Melanocytes are in greatest concentration in nipples, anal region, and armpits
• Protects from UV radiation
• Pigment ranges from yellow to black
• Pigment protects from UV
• Freckles/moles
– Melanin concentration in one spot
• Over exposure to UV can cause cancer.
Langerhans cells
• Langerhans – easily damaged by UV
• works with immune system against microbes that invade the skin
Merkel cells
• Merkel cells contact the flattened process of a sensory neuron called a tactile
(Merkel
PARTS OF THE SKIN
Label the diagram and give the function of the following parts
PARTS OF THE SKIN
• Epidermis
• Dermis
• Hair shaft
• Papillae
• Arrector pili muscle
• Sebaceous gland
• Sweat gland
• Pore
• Subcutaneous layer
• Nerve
• Blood vessels
• Adipose
DERMIS
• Composed of areolar connective tissue containing collage and elastic fibers
• Dermal papillae section with small fingerlike projections that indent the epidermis.
– Meissner corpuscles
– Free nerve endings
Reticular layer
• Deeper layer of dermis
• Contains blood vessels
• Sweat / oil glands
• Deep pressure receptors
• Hair follicles
• Collage and elastic fibers in the region provides the skin with strength and extensibility and elasticity
Accessory structures of skin
HAIR
• Protects the body
• Not present on palms, palmar surfaces of fingers, soles and plantar surfaces of toes
• Head region – guards the scalp from injury and the sun’s rays
• Eyebrows / eyelashes – protect the eyes
• Nostrils – protects against inhaling insects and foreign particles
Hair structures
• Cuticle – single layer of cells (shingles)
– Cntains keratin
– As it wear away hair gets fizzy and gets split ends
• Cortex – inner layer
• Medulla – central core
• Shaft – central portion and is above the suface
• Root – portion below the surface and penetrates into the dermis and subcutaneous layer
• Hair follicle – surrounds root
– Contains growth region
• Arrector pili - when contracted it causes hair to stand up – goose bumps
Glands
• Sebaceous galnds
• Sudoriferous glands
– Eccrine
– Appocrine
• Ceruminous glands
Sebaceous glands
• Oil glands
• Found all over the skin, except palms and soles
• Ducts empty into the hair follicle
• Some open directly onto the dkin
• Sebum
Sebum
• Product of sebaceous glands
• Oily
• Contains chemicals that kill bacteria
• Lubricant
– Keeps skin soft, moist
– Keeps hair from becoming brittle
• More active during adolescence
Sudoriferous glands
• Sweat glands
• Widely distributed in skin
• Two tyes
– Eccrine
– apocrine
Eccrine glands
• Most common
• Start to function soon after birth
• Found all over body, except margins of lips, nail beds of fingers, toes, glans penis, glans clitoris, labia minor, and eardrums
• produce sweat – contains water, salts, urea, uric acid, vit. C
• pH 4 to 6
• Regulates body heat
Apocrine Sweat Glands
• Found in the skin of the armpit, groin, areolae of the breasts, bearded regions of the face in males.
• Duct empties into hair follicle
• Secretion - fatty acids and proteins along with normal substances found in sweat
• Bacteria live on skin and when they break down these secretion, body odor results
• Stimulated during emotional stress, sexual excitement
• Do not begin to function until puberty
Ceruminous glands
• Se-ROO-mu-nus glands
• Present in external auditory canal
• \combination of secretions of ther ceruminous and sebaceous glands
• Called earwax
• Forms a sticky barrier against foreigh bodies.
Additional sensory receptors
• Free nerve endings
– Simplest
– No structural specializations
– Receptors for pain, thermal, tickle, itch, and some touch sensations
• Encapsulated
– Dendrites are enclosed in a connective tissue capsule
Touch
• Meissner corpuscles
• Hair root plexuses
• Merkel disks
• Ruffini corpuscles
Pressure / vibration
•
• Pacinian (pa-SIN – e – an )
Skin color
• 3 pigments
– Melanin
– Carotene – yellow orange pigment.
– Hemoglobin – oxygen carrying pigment in
RBS
• Freckles
• Age spots
Disease / disorders
• Skin graft
• Psoriasis
• Jaundice
• Cyanotic
• Hirsutism
• transdermal drug administration
• Albinism
• Decubitus ulcers
• wart
Burns
• Burns are traumatic injury as the result of radiation from the sun, heat lam or contact with boiling water, steam, fire, chemicals, or electricity.
• When the sin is burned, dehydration, and infection may occur.
• Either condition is life-threatening
• First
• Second
• Third
Degree of burns
Skin cancer
• Associated with exposure to UV light
Common types of skin cancer
• Basal cell carcinoma
• Squamous cell carcinoma
• Malignant melanoma
What to look for
• Brown or black irregular parch which occurs early
• Color or size change in preexisting wart or more
The skin and its relationship to microorganisms
• An intact skin is the best way the body can protect itself against pathogens and water loss.
• Cracking of dry skin can be prevented by lotions and creams
• The skin’s surface is not a favorable place for bacteria to grow because it is too dry.
• Skin bacteria grows where there is nutrients and moisture present.
• Most bacteria are found where the hair follicles and sweat glands are located.
• Underarm perspiration odor is caused by the interaction of bacteria on perspiration.
• This can be prevented by washing and using deoderants.
HANDWASHING
• #1 way to prevent the spread of disease.
• 10 – 30 seconds normal
• 2 – 4 minutes if you are in contact with infectious material.
• Exposure to blood or body secretions – wash hands, apply gloves, remove gloves and rewash hands.
AGING
• Most visible sings of aging are visible on the skin.
• Secrete less oil therefore skin becomes dry and more fragile.
• Skin loses elastin fibers causing the skin to lose elasticity.
• Loss of subcutaneous fat causes wrinkles, lines, and sagging.
• The dermal vascular network decreases in its ability to respond to heat and cold.