Teachingw
advertisement

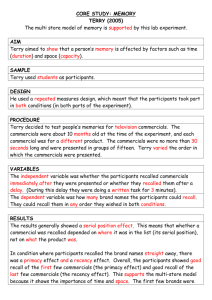
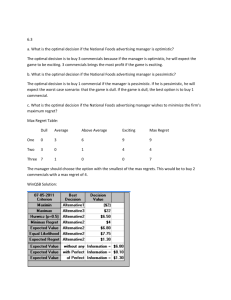
Wazzuppp!: Using Television Commercials to Teach Writing William Martínez, Jr. California Polytechnic State University Theoretical background in writing The Domains of Writing – 4 categories: • A. Sensory/ Descriptive • B. Imaginative/ Narrative • C. Practical/Informative • D. Analytic/ Expository A. Sensory/ Descriptive Based on on concrete details Gathering information through 5 senses Provide vivid descriptions Have the reader be an observer “Show not tell” Focus on the details Create appeal for the reader to read on B. Imaginative/ Narrative The purpose is to tell a story Organization of ideas into beginning, middle and end (plot, suspense and climax) Add details to actions Point of view Bringing the writing process to life by selecting unique details to tell C. Practical/Informative Focus on facts not speculation Writing that provides little interpretation Observations that add details to facts Sequence that helps readers “see” the action Ordering of importance in details Editing skills D. Analytic/ Expository Writing that explains in detail Writing that persuades with facts Writing that influences with development of ideas Anaysis, organization and development Building and explaining relationships that were not obvious D. Analytic/ Expository (continued) The use of logic Differentiation of fallacies A combination of skills learned in other domains to produce a logical, persuasive, argument. Theoretical background in the methodology Based on the Neurological Bimodal Learning Model (Multisensorial teaching model) – Neurological Bimodality Definition:“The notion that both hemispheres of the brain are involved in a complementary fashion in global language processing.” » Marcel Danesi “Neurological Bimodality,” 18 What is Multi-Sensorial Teaching? It attempts to stimulate both sides of the brain at the same time Left hemisphere: – – – – Phonological, Morphological, etc. (grammar) Link syntactic and semantic elements (style, tone, etc.) Implication of sentence (What does it mean?) Controls motor functions of speech What is Multi-Sensorial Teaching? (continued) Right Hemisphere: – Determines the sense of the sentence (question, statement, command, etc.) – Handles figurative meaning (metaphor, simile, etc) – Understands humor and double meaning – Processes most of the everyday occurrences How does it work? It presents students with more than one stimuli at any one time It uses technology (in all its forms) as a way to lower the affective filters It provides both text and context at the same time It increases the motivation of the students It helps giving students more context Danesi and Writing According to Danesi: – It is mostly a first year-type methodology – It emphasizes oral communication – By using metaphor it could be used for writing, but Danesi does not indicate how. My adaptations Stimulate students by using things that they know and understand-- TV Commercials Stimulate students by using props--Objects/ products used in TV Commercials Give them specific target writing assignments--Writing about or with TV Commercials My adaptations (continued) Motivate through technology – High and low technology items Incorporate cultural components in writing-- How do TV Commercials affect specific target groups? Integrate several technologies in a particular assignment. Using TV commercials--The writing process Some Examples Descriptive: Ask them to describe what is going on. Focus on different senses Describe colors and/or music Describe the nature of the product Produce a paragraph and have thesis statement at end. Discuss in class Narrative: Tell the story of the commercial What came first and what came next. Why this order? Have them explain what feelings these characters are demonstrating and why (Use of narrator) Have them create their own storyboards Informative: Have them explain the process of making a commercial. What would they change and why? How does meaning change with sound? Etc. (who, what, where, when, and how?) Report on the use of commercials in a particular event, a particular timeslot, etc. Analytic: Focus on the meaning--Reading “between the lines” Look at the cultural aspects Focus on specific characters in a commercial Produce their own commercial, explaining how it attempts to influence viewers. Advantages Students are more involved in writing Students feel that writing makes sense Students see marked improvement in all critical thinking skills Students use L2 in real life situations Students realize that L2 is a living, evolving language Students use techniques for all writing, not just L2 language situations Disadvantages It takes a great deal of energy Must give very detailed instructions on assignments Must be willing to drop everything at a moment’s notice--Not for the faint of heart! Need a lot of imagination It is difficult to get use to Evaluation of materials produced must be rigorous Bibliography Battenburg, John and William Martinez. Communicative Activities for the Second Language Classroom. Debuque, Iowa: Kendall-Hunt Publications, 1999. Britton, James. The Development of Writing Abilities. London: MacMillan Education, LTD. Schools Council Publications, 1975. Danesi, Marcel. “Neurological Bimodality and Theorys of Language Teaching.” in Studies in Second Language Acquisition. Vol. 10. 1988. Pp 13-31. --------. “Practical Application of Current Brain Research to Teaching of Italian.” in Italica, Vol. 64. 1987. Pp. 377-392. Lewis, Michael. The Lexical Approach: The State of ELT and a Way Forward. Hove, England: Langauge Teaching Publications, 1993. McHugh, Nancy. Practical Ideas for Teaching Writing as Process. Sacramento, CA: CA department of Education, 1987. Smith, William F. Modern Media in Foreign language Education: Theory and Implementation. Lincolnwood, IL: National Textbook Company, 1987.