The Revenue Cycle and the Electronic Health Record
advertisement
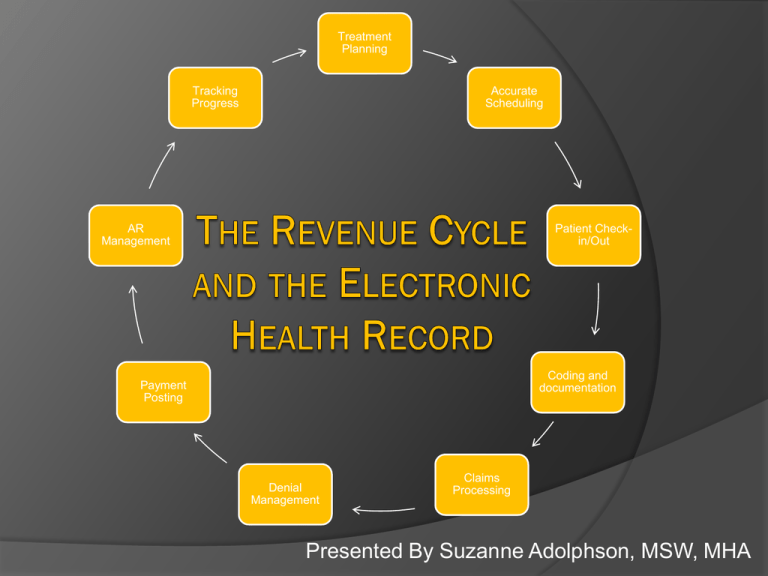
Treatment Planning Tracking Progress Accurate Scheduling AR Management Patient Checkin/Out Coding and documentation Payment Posting Denial Management Claims Processing Presented By Suzanne Adolphson, MSW, MHA • Located in Pomona, California • 1st class graduates in 2013 • Use a paperless system • Define the revenue cycle • Use the EHR to improve your revenue cycle • Use the EHR to track improvements Improve your revenue cycle rather than relying on cutting expenses. ‘…find the holes in your revenue cycle and then plug them...’ • More than just billing and collecting • Includes all processes and procedures that have potential to impact the revenue • Ex: treatment planning, scheduling, accounts, patient check-in/out, all things AR, etc. ORGANIZING YOUR THOUGHTS: SYSTEMS THEORY: Treatment Planning Tracking Progress Accurate Scheduling EHR AR Management Patient Checkin/Out EHR REVENUE CYCLE Payment Posting EHR Coding and documentation EHR Denial Management Claims Processing USING THE EHR WHAT IS THE EHR? • EHR = Electronic Health Record • Fully integrated EHR = all functions are interconnected and do not stand alone. TREATMENT PLAN • Lack of treatment plan=lack of communication • Communicates cost of treatment to patient • A sequenced treatment plan facilitates scheduling • Tracks potential revenue SCHEDULING • Need to know clinic activity. • Using the Treatment Plan = staff knows what to collect • Track patients who habitual fail or cancel = stable patient base • Tracks chair utilization • Digital format allows for use of outside vendor for confirmation of appointments PATIENT CHECK-IN • Treatment plan and accurate scheduling = patient check-in process • Ensures collection or verification of patient demographics • Allows for collection of payment before treatment • Do you want to manage credit or debt? CODING AND DOCUMENTATION • Treatment Plan = accurate coding • Inaccurate coding = slower reimbursement from 3rd party payers • No codes = missing charges and/or reduced productivity/revenue • Use EHR to track missing charges (codes) daily CLAIMS PROCESSING • Treatment Plan = accurate coding = accurate claims • Accurate claims = faster reimbursement • Electronic Claims and electronic attachments = faster reimbursement • Real time processing information DENIAL MANAGEMENT • EHR flags incomplete claims. • Electronic claims allows for real time management. • Real time management = faster claim correction = faster reimbursement • Reduces the amount of time staff spends on the phone with 3rd party payers A/R MANAGEMENT • Accurate demographics = fewer returned statements • Digital format provides for sending file to 3rd party vendors for statement processing. • Allows staff to use time in more productive manner • Reports that assist staff in claims and outstanding balance follow-up PAYMENT POSTING • Tracks the amount of time from check posting in the system to allocation to individual claim • Future: 3rd party payers will send electronic files that download payments automatically • Staff will only have to look at the payments with exceptions PATIENT COLLECTIONS • Report generation for outstanding claims/patient balances • Ease of working with collection agencies • Collection agency can access files and download information into their system. • Streamlines process and reduce staff involvement TRACKING IMPROVEMENTS • Determine which benchmarks to use to gauge improvement • Apply a simple pre-test/post-test method to determine improvement • Use the data your EHR collects to determine improvements • Determine which intervals to check for improvements CERTAIN BENCHMARKS CAN BE USED TO TRACK PROGRESS: • Average days in A/R <50 days • <20% % of A/R over 90 day • % of A/R over 120 days • Billing turn-around <10% within 5 days of treatment • Payer turn-around Electronic claims Paper claims 10-15 days <45 days • <2% Bad debt expense (% of net revenue) QUESTIONS? REFERENCES Quist, Jim & Robertson, Brian. (2004). Key Revenue Cycle Metrics. Healthcare Financial Management, 58 (9), 71-72. Palmer, Diane. (2004). Key Tools For Turning Receivables Into Cash. Healthcare Financial Management, 58 (2), 62-67. Hammer, David. (2007). The Next Generation Of Revenue Cycle Management. Healthcare Financial Management, 61 (7), 49-57. Amatayakul, Margaret. (2005). Are You Using The EHR-Really?. Healthcare Financial Management, 59 (11), 126-128.











