PAD190 PRINCIPLES OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION
advertisement

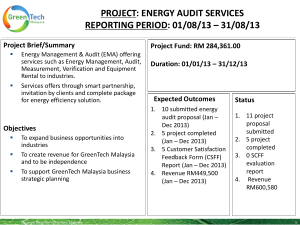
PAD190 PRINCIPLES OF PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION LESSON 9 PUBLIC FINANCE ADMINISTRATION INTRODUCTION Government collects taxes and other source of revenues to finance the expenditure. The revenues collected must be properly managed and considered as public money. Every year the government has to prepare the budget for parliamentary approval. Budget approved by the parliament then should become the financial prospectus of the government in utilizing the fund. How the government manage the fund? Public Finance administration. THE OBJECTIVES OF THIS LESSON After attended this lecture student should be able to:1. Define financial administration. 2. Describe the importance of public finance administration. 3. Describe the cycle and activities of public finance administration. 4. Explain the public finance administration process and practices in Malaysia 5. Describe the challenges of public finance administration in Malaysia WHAT IS PUBLIC FINANCE ADMINISTRATION • Public finance administration concerns with the techniques of managing public monies. • Deals with how the government utilizing the public fund in delivering the services to public. • As an activity of public administration that concerns with how the government should manage the collection of potential revenues and spend the revenues. THE IMPORTANCE OF PUBLIC FINANCE ADMINISTRATION • To ensure the government has enough money for financing the program and activities and to achieve the state’s desired goal. • To ensure the public fund is managed in a proper manner by following the law, rules and procedures; • To avoid any misused of the fund and achieve efficiency in spending the public money. THE ROLES OF PUBLIC FINANCIAL ADMINISTRATION • As a tool of management It is an effort to enable a particular agency to spend money for execution of the policy. • “As a public manager, you will find that the budget process is critical to your success and that of your agency, quite simply because the budget process establishes the level of funding for your programs and those of others”. (Denhardt & Grubbs, 2003) • As an Instrument of Public Policy The budget represented the public policies and measure of support for specific program. It also appears for enforcing government policies. • As an Instrument of Fiscal Policy The budget is a fiscal tool for influencing the operation and directions of an economy of a government such as level of taxation, public expenditure and public debt (Kumar & Mittal, 2002). The fiscal policy can be clearly decided through budget. • To estimate the income and expenditure By using budget a proper income and expenditure can be planned. It can be done through the formulation stage where every detail of allocation and distribution can be discussed or debated. • To measure performance Controlling and monitoring of the budget. Budgeting can ensure the accountability of the financial administration. It makes sure the execution of the public funds comply with the government plan. • Source of information Budget is the source of information for the past activities, present activities and future activities for the government. It provides records of utilization of the public funds. PUBLIC FINANCE ADMINISTRATION CYCLE PLANNING REVIEW AUDITING BUDGETING ACCOUNTING STAGE 1 - PLANNING • The task of determining the financial plan of achieving the strategic goals and objectives. • The financial plan describes in detail the program, activities and resources that are needed to achieve these goals, as well as the timeframes involved. • The final output of financial plan is a budget statement. STAGE 2 - BUDGETING • Budgeting is a process of the government allocating financial resources to various agencies. • Budgeting is a political process which involves two major branches of government, the executive and legislative body. • Several techniques might be used in budgeting; such as Line item Budgeting, PPBS, MBS and Zero Based Budgeting System. BUDGET • Budget is a financial plan of intended revenues and expenditure of the government • Provide a forecast of revenues and expenditures i.e. construct a model of how the government might perform financially and carried out the programs and activities. • Enable the actual financial operation of the government stated in a monetary terms. • is a legal document that is often passed by the legislature, and approved by the chief executive -or president. Budgetary Process/Cycle • Revenue Estimation performed in the executive branch by the finance director, clerk's office, budget director, manager, or a team. • Budget Call issued to outline the presentation form, recommend certain goals. • Budget Formulation reflecting on the past, set goals for the future and reconcile the difference. • Budget Hearings can include departments, sections, the executive, and the public to discuss changes in the budget. • Budget Adoption final approval by the legislative body. • Budget Execution amending the budget as the fiscal year progresses. STAGE 3 - ACCOUNTING • The art of recording, classifying, and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money, transactions and events which are, in part at least, of financial character, and interpreting the results thereof; • Accounting provides financial information or report about the government business to people inside and outside the government entity. • The process of accounting is carried out by professional accountant and by following the standard financial procedures established by the Accountant General Office. ACCOUNTANT GENERAL OF MALAYSIA • The Malaysian Federal Government Financial Statement is prepared annually by the Accountant General of Malaysia in accordance with Section 16[1] of the Financial Procedure Act 1957 [Act 61]. • The objective of Accountant General is to enhance accountability and transparency in Federal Government’s accounting and financial management. STAGE 4 - AUDITING • Audits are performed to ascertain the validity and reliability of information; also to provide an assessment of a system's internal control. • audit is an independent assessment of the fairness by which a company's financial statements are presented by its management. • Auditors of financial statement can be carried out by internal auditors (established by the organization) and external auditor (An independent audit firm) Government auditing • Government audits were mainly associated with gaining information about financial systems and the financial records of a government department or agency • Carried out by Auditor General. • The appointment as well as the responsibilities of the Auditor General are spelt out under Article 105 of the Federal Constitution and the Audit Act 1957. • Auditor General Report will highlight any issues on public finance administration. National Audit Department • To prepare quality and timely Audit Reports to Parliament and State Legislatures • To carry out audit activities and prepare reports in an independent and balanced manner • To fulfill the needs and expectations of stakeholders and auditees • To manage audit activities efficiently and effectively • To be a model employer SATGE 5 – FINANCIAL REVIEW • An assessment on the achievement of an organization/agency in terms of the financial performance that has been achieved through out the year. • The report highlight the achievement, shortcoming and weaknesses of the current financial plan. • The financial review report can be used as a basis for preparing the future budget plan PUBLIC FINANCE ADMINISTRATION IN MALAYSIA • Treasury Malaysia, Ministry of Finance is the Central Agency that responsible in preparing and managing the Federal Government Budget and other financial matters. • Financial administration in Malaysia is subject to Financial Procedure Act 1957 (Act 61) Treasury Instructions, Treasury Circulars • The act to provide for the control and management of public finance in Malaysia. Internet Links • http://www.treasury.gov.my/ • http://www.agc.gov.my/agc/Akta/Vol.%202/A ct%2061.pdf • http://www.anm.gov.my/public_html/eng/def ault/org.php • http://www.audit.gov.my/ TUTORIAL • Define financial administration. • Describe public finance administration practices in Malaysia. THAT ALL FOR TODAY SEE YOU AGAIN NEXT LECTURE LESSON 10 “CONTEMPORARY ISSUES IN PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION” THANK YOU